Korean J Ophthalmol.
2013 Apr;27(2):120-125. 10.3341/kjo.2013.27.2.120.
Lower Energy to Make a Corneal Flap with a 60 kHz Femtosecond Laser Reduces Flap Inflammation and Corneal Stromal Cell Death But Weakens Flap Adhesion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hwtchah@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Bio-medical Institute of Technology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1503804
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2013.27.2.120
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare corneal flaps created in rabbits with a 60 kHz femtosecond (FS) laser using different levels of raster energy and to measure early inflammation, corneal stromal cell death, and late postoperative adhesion strength.
METHODS
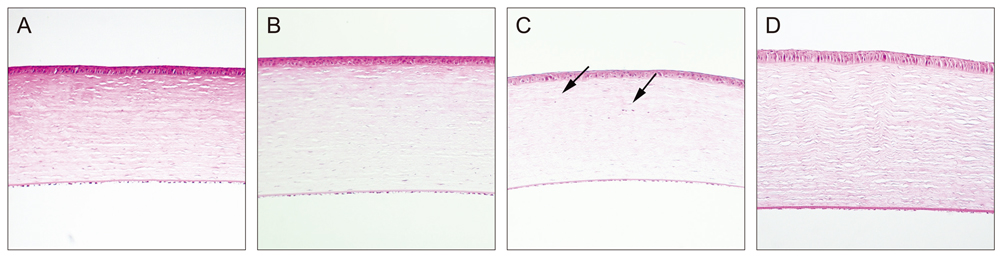
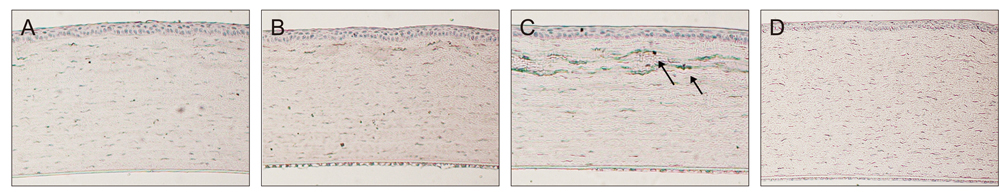
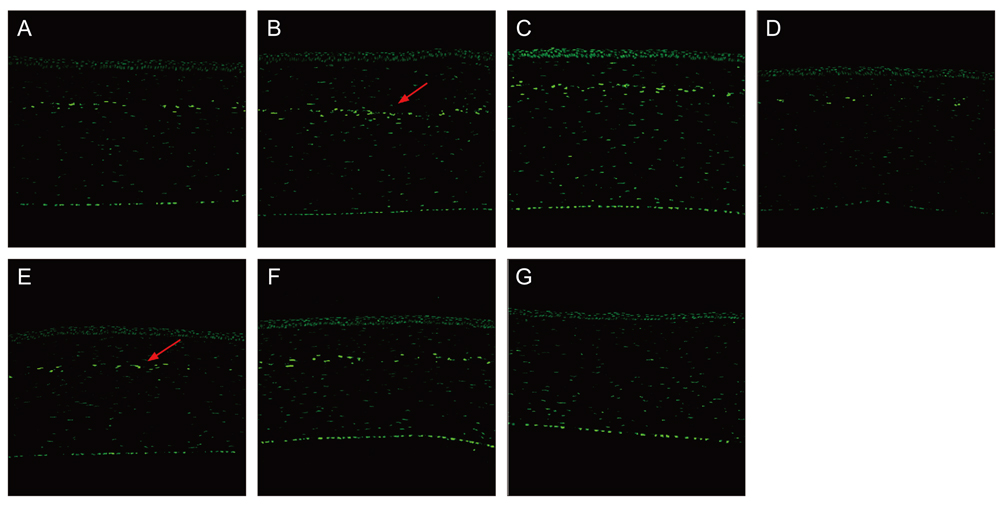
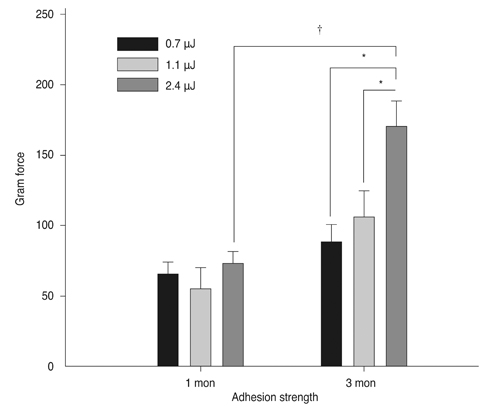
Sixty rabbits were divided into three groups of 20 each. A flap 110 micrometer thick and 9.0 mm in diameter was made in one eye of each rabbit at raster energies of 0.7 microJ, 1.1 microJ, and 2.4 microJ. Histopathological evaluation for inflammation and apoptosis using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining was performed at 4 and 24 hours after flap creation. The adhesion strength of the flaps was measured with a tension meter at 1 and 3 months.
RESULTS
Twenty four hours after flap creation, the 2.4 microJ group had more inflammatory and CD11b-positive cells than the 0.7 and 1.1 microJ groups. The number of TUNEL-positive cells increased with raster energy at 4 and 24 hours. The grams of force (gf) needed to detach the flaps at 3 months was significantly higher in 2.4 microJ group (170 gf) than in 0.7 microJ group (97.5 gf) and 1.1 microJ group (100 gf, p = 0.03).
CONCLUSIONS
Using raster energy lower than 1.1 microJ to make a flap with a 60 kHz FS laser decreases inflammatory cell infiltration and corneal stromal cell death in the central cornea but may result in a weaker flap than using higher raster energy (2.4 microJ).
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sugar A, Rapuano CJ, Culbertson WW, et al. Laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia and astigmatism: safety and efficacy: a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2002. 109:175–187.2. Gimbel HV, Penno EE, van Westenbrugge JA, et al. Incidence and management of intraoperative and early postoperative complications in 1000 consecutive laser in situ keratomileusis cases. Ophthalmology. 1998. 105:1839–1847.3. Stulting RD, Carr JD, Thompson KP, et al. Complications of laser in situ keratomileusis for the correction of myopia. Ophthalmology. 1999. 106:13–20.4. Wilson SE. LASIK: management of common complications: laser in situ keratomileusis. Cornea. 1998. 17:459–467.5. Binder PS. Flap dimensions created with the IntraLase FS laser. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004. 30:26–32.6. Holzer MP, Rabsilber TM, Auffarth GU. Femtosecond laser-assisted corneal flap cuts: morphology, accuracy, and histopathology. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006. 47:2828–2831.7. Kim JY, Kim MJ, Kim TI, et al. A femtosecond laser creates a stronger flap than a mechanical microkeratome. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006. 47:599–604.8. Nordan LT, Slade SG, Baker RN, et al. Femtosecond laser flap creation for laser in situ keratomileusis: six-month follow-up of initial U.S. clinical series. J Refract Surg. 2003. 19:8–14.9. Meltendorf C, Burbach GJ, Buhren J, et al. Corneal femtosecond laser keratotomy results in isolated stromal injury and favorable wound-healing response. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007. 48:2068–2075.10. Kezirian GM, Stonecipher KG. Comparison of the IntraLase femtosecond laser and mechanical keratomes for laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004. 30:804–811.11. Lim T, Yang S, Kim M, Tchah H. Comparison of the IntraLase femtosecond laser and mechanical microkeratome for laser in situ keratomileusis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006. 141:833–839.12. Netto MV, Mohan RR, Medeiros FW, et al. Femtosecond laser and microkeratome corneal flaps: comparison of stromal wound healing and inflammation. J Refract Surg. 2007. 23:667–676.13. De Medeiros FW, Kaur H, Agrawal V, et al. Effect of femtosecond laser energy level on corneal stromal cell death and inflammation. J Refract Surg. 2009. 25:869–874.14. Binder PS, Sarayba M, Ignacio T, et al. Characterization of submicrojoule femtosecond laser corneal tissue dissection. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008. 34:146–152.15. Chang JS. Complications of sub-Bowman's keratomileusis with a femtosecond laser in 3009 eyes. J Refract Surg. 2008. 24:S97–S101.16. Spadea L, Fasciani R, Necozione S, Balestrazzi E. Role of the corneal epithelium in refractive changes following laser in situ keratomileusis for high myopia. J Refract Surg. 2000. 16:133–139.17. Wilson SE, Ambrosio R Jr. Sporadic diffuse lamellar keratitis (DLK) after LASIK. Cornea. 2002. 21:560–563.18. Helena MC, Baerveldt F, Kim WJ, Wilson SE. Keratocyte apoptosis after corneal surgery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998. 39:276–283.19. Knorz MC, Vossmerbaeumer U. Comparison of flap adhesion strength using the Amadeus microkeratome and the IntraLase iFS femtosecond laser in rabbits. J Refract Surg. 2008. 24:875–878.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reproducibility of IntraLASIK Flap Thickness Measured with Optical Coherence Tomography
- A Case of Acute Central Stromal Melting after LASIK
- The Consistency of Corneal Flap Thickness and Size in LASIK using the Innovatome Automatic Micro keratome
- Factors Influencing Corneal Flap Thickness in Laser In Situ Keratomileusis with a Femtosecond Laser
- Corneal Flap Thickness according to Suction Time of Microkeratome in Porcine Eye