Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 Apr;74(4):151-162. 10.4046/trd.2013.74.4.151.
Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Severance Hospital, Institute of Chest Diseases, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. pms70@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1495855
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2013.74.4.151
Abstract
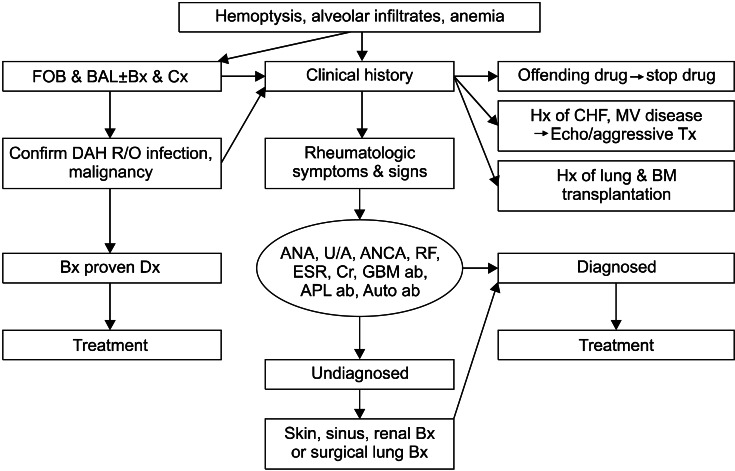
- Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH) is a life-threatening and medical emergency that can be caused by numerous disorders and presents with hemoptysis, anemia, and diffuse alveolar infiltrates. Early bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage is usually required to confirm the diagnosis and rule out infection. Most cases of DAH are caused by capillaritis associated with systemic autoimmune diseases such as anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis, anti-glomerular basement membrane disease, and systemic lupus erythematosus, but DAH may also result from coagulation disorders, drugs, inhaled toxins, or transplantation. The diagnosis of DAH relies on clinical suspicion combined with laboratory, radiologic, and pathologic findings. Early recognition is crucial, because prompt diagnosis and treatment is necessary for survival. Corticosteroids and immunosuppressive agents remain the gold standard. In patients with DAH, biopsy of involved sites can help to identify the cause and to direct therapy. This article aims to provide a general review of the causes and clinical presentation of DAH and to recommend a diagnostic approach and a management plan for the most common causes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adrenal Cortex Hormones
Anemia
Anti-Glomerular Basement Membrane Disease
Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis
Antibodies, Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic
Autoimmune Diseases
Biopsy
Bronchoalveolar Lavage
Bronchoscopy
Capillaries
Emergencies
Hemoptysis
Hemorrhage
Humans
Immunosuppressive Agents
Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic
Pulmonary Alveoli
Transplants
Vasculitis
Adrenal Cortex Hormones
Antibodies, Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic
Immunosuppressive Agents
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Negative Pressure Pulmonary Hemorrhage after Laryngospasm during the Postoperative Period
In Soo Han, Bo Mi Han, Soo Yeon Jung, Jun Rho Yoon, Eun Yong Chung
Acute Crit Care. 2018;33(3):191-195. doi: 10.4266/acc.2016.00689.Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Regulate Macrophage Polarization to Attenuate Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-Associated Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage in Mice
Xun Chen, Qing Wei, Hongmei Sun, Xiaobo Zhang, Changrong Yang, Ying Tao, Guangmin Nong
Int J Stem Cells. 2021;14(3):331-340. doi: 10.15283/ijsc20156.
Reference
-
1. Collard HR, Schwarz MI. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Clin Chest Med. 2004; 25:583–592. PMID: 15331194.
Article2. Colby TV, Fukuoka J, Ewaskow SP, Helmers R, Leslie KO. Pathologic approach to pulmonary hemorrhage. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2001; 5:309–319. PMID: 11598860.
Article3. Lara AR, Schwarz MI. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Chest. 2010; 137:1164–1171. PMID: 20442117.
Article4. Ioachimescu OC, Stoller JK. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage: diagnosing it and finding the cause. Cleve Clin J Med. 2008; 75:258–280. PMID: 18491433.
Article5. Cordier JF, Cottin V. Alveolar hemorrhage in vasculitis: primary and secondary. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2011; 32:310–321. PMID: 21674416.
Article6. Brown KK. Pulmonary vasculitis. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2006; 3:48–57. PMID: 16493151.7. Newsome BR, Morales JE. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. South Med J. 2011; 104:269–274. PMID: 21606695.
Article8. Ewan PW, Jones HA, Rhodes CG, Hughes JM. Detection of intrapulmonary hemorrhage with carbon monoxide uptake: application in goodpasture's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1976; 295:1391–1396. PMID: 980094.9. Specks U. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage syndromes. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001; 13:12–17. PMID: 11148710.
Article10. Schnabel A, Holl-Ulrich K, Dalhoff K, Reuter M, Gross WL. Efficacy of transbronchial biopsy in pulmonary vaculitides. Eur Respir J. 1997; 10:2738–2743. PMID: 9493653.
Article11. Travis WD, Colby TV, Lombard C, Carpenter HA. A clinicopathologic study of 34 cases of diffuse pulmonary hemorrhage with lung biopsy confirmation. Am J Surg Pathol. 1990; 14:1112–1125. PMID: 2252102.
Article12. Fauci AS, Haynes BF, Katz P, Wolff SM. Wegener's granulomatosis: prospective clinical and therapeutic experience with 85 patients for 21 years. Ann Intern Med. 1983; 98:76–85. PMID: 6336643.
Article13. Jayne D. Evidence-based treatment of systemic vasculitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000; 39:585–595. PMID: 10888702.
Article14. Frankel SK, Schwarz MI. The pulmonary vasculitides. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012; 186:216–224. PMID: 22679011.
Article15. Klemmer PJ, Chalermskulrat W, Reif MS, Hogan SL, Henke DC, Falk RJ. Plasmapheresis therapy for diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in patients with small-vessel vasculitis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003; 42:1149–1153. PMID: 14655185.
Article16. Henke D, Falk RJ, Gabriel DA. Successful treatment of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage with activated factor VII. Ann Intern Med. 2004; 140:493–494. PMID: 15023729.
Article17. Ahmed SH, Aziz T, Cochran J, Highland K. Use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in a patient with diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Chest. 2004; 126:305–309. PMID: 15249477.
Article18. Keogh KA, Wylam ME, Stone JH, Specks U. Induction of remission by B lymphocyte depletion in eleven patients with refractory antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:262–268. PMID: 15641078.
Article19. Jayne D, Rasmussen N, Andrassy K, Bacon P, Tervaert JW, Dadoniene J, et al. A randomized trial of maintenance therapy for vasculitis associated with antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:36–44. PMID: 12840090.
Article20. Stone JH, Tun W, Hellman DB. Treatment of non-life threatening Wegener's granulomatosis with methotrexate and daily prednisone as the initial therapy of choice. J Rheumatol. 1999; 26:1134–1139. PMID: 10332980.21. Wegener's Granulomatosis Etanercept Trial (WGET) Research Group. Etanercept plus standard therapy for Wegener's granulomatosis. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:351–361. PMID: 15673801.22. Specks U. Schwarz MI, King TE, editors. Chapter 22. Pulmonary vasculitis. Interstitial lung disease. 2003. 4th ed. Hamilton: BC Decker Inc.;p. 599–631.23. Lynch JP, Leatherman . Fisherman AP, Elias JA, Fishman JA, Grippi MA, Senior RM, Pack AI, editors. Chapter 77. Alveolar hemorrhage syndrome. Fishman's pulmonary diseases and disorders. 2008. 4th ed. New York: McGraw Hill Inc.;p. 1281–1297.24. Ahn JH. Pulmonary vasculitis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2000; 48:825–836.
Article25. Chang TW. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. Chapter 10-3. Pulmonary vasculitis and diffuse alveolar hemorrhage syndrome. Respiratory diseases. 2004. Seoul: Koonja Publishing Inc.;p. 549–561.26. Betensley AD, Yankaskas JR. Factor viia for alveolar hemorrhage in microscopic polyangiitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 166:1291–1292. PMID: 12403702.
Article27. Channick RN, Rubin LJ. Mason RJ, Broaddus VC, Murray JF, Nadel JA, editors. Chapter 49. Pulmonary vasculitis and primary pulmonary hypertension. Murray and Nadel's textbook of respiratory medicine. 2005. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders Inc.;p. 1459–1465.28. Travis WD, Koss MN. Dail DH, Hammar SP, editors. Pulmonary vasculitis. Pulmonary pathology. 1994. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, Inc.;p. 1027–1095.29. Kang KH. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage syndrome. 1999. In : Tuberc Respir Dis Workshop; 1999 Nov 13; Seoul, Korea. Seoul: The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Disease;p. 43–52.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Microscopic Polyangiitis Presenting As Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage
- An Unusual Radiologic Manifestation of Pulmonary Tuberculosis with Bilateral Multiple Lung Nodules and Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage: A Case Report
- A case of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage with thoracocervicofacial purpura after a generalized tonic-clonic seizure
- Acute respiratory failure due to diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in mycoplasma pneumonia
- A case of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage following administration of artecoll