Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2012 Oct;16(5):355-360. 10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.5.355.
Simultaneous Determination of Glutamate, Glycine, and Alanine in Human Plasma Using Precolumn Derivatization with 6-Aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl Carbamate and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Pharmacy and Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Binzhou Medical University, Yantai 264003, China. lqingzhong@yahoo.com.cn
- 2Department of General Surgery, Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital, Yantai 264003, China.
- 3Department of Quality Inspection, Hubei Provincial Bafeng Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals Share Co., Ltd, Hefeng 445800, China.
- KMID: 1493970
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.5.355
Abstract
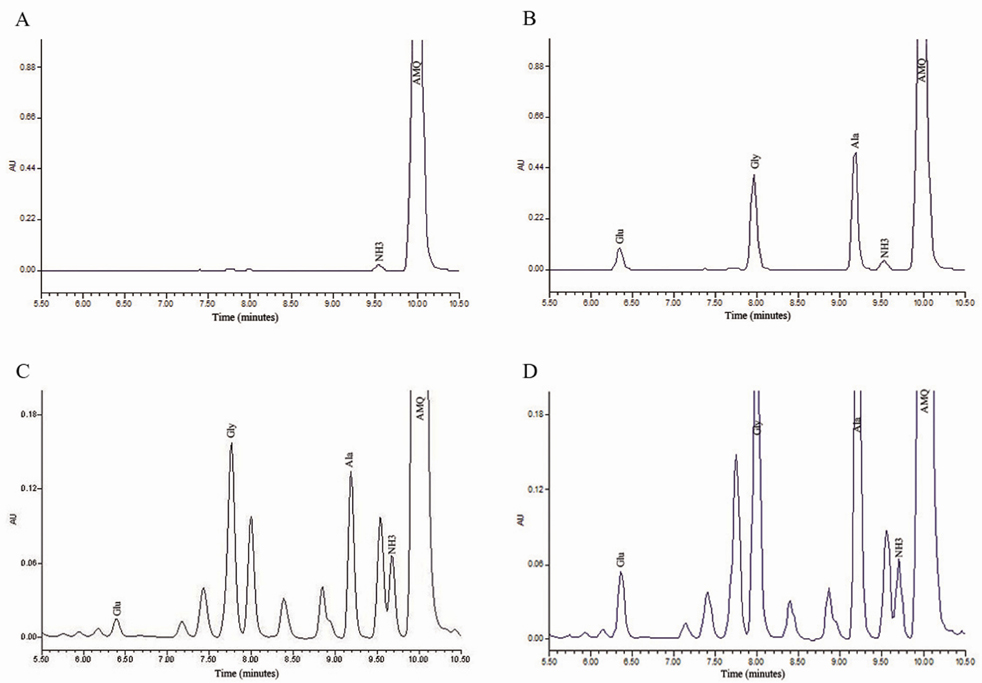
- A simple, sensitive and reproducible high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method has been validated for determining concentrations of glutamate, glycine, and alanine in human plasma. Proteins in plasma were precipitated with perchloric acid, followed by derivatization with 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate (AQC). Simultaneous analysis of glutamate, glycine, and alanine is achieved using reversed-phase HPLC conditions and ultraviolet detection. Excellent linearity was observed for these three amino acids over their concentration ranges with correlation coefficients (r)>0.999. The intra- and inter-day precision were below 10%. This method utilizes quality control samples and demonstrates excellent plasma recovery and accuracy. The developed method has been successfully applied to measure plasma glutamate, glycine, and alanine in twenty volunteers.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee GJ, Choi SK, Eo YH, Kang SW, Choi S, Park JH, Lim JE, Hong KW, Jin HS, Oh BS, Park HK. The effect of extracellular glutamate release on repetitive transient ischemic injury in global ischemia model. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009. 13:23–26.2. Castellanos M, Sobrino T, Pedraza S, Moldes O, Pumar JM, Silva Y, Serena J, García-Gil M, Castillo J, Dávalos A. High plasma glutamate concentrations are associated with infarct growth in acute ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2008. 71:1862–1868.3. Mitani H, Shirayama Y, Yamada T, Maeda K, Ashby CR Jr, Kawahara R. Correlation between plasma levels of glutamate, alanine and serine with severity of depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2006. 30:1155–1158.4. Andreadou E, Kapaki E, Kokotis P, Paraskevas GP, Katsaros N, Libitaki G, Petropoulou O, Zis V, Sfagos C, Vassilopoulos D. Plasma glutamate and glycine levels in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. In Vivo. 2008. 22:137–141.5. Wesseldijk F, Fekkes D, Huygen FJ, van de Heide-Mulder M, Zijlstra FJ. Increased plasma glutamate, glycine, and arginine levels in complex regional pain syndrome type 1. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2008. 52:688–694.6. Ohnuma T, Arai H. Significance of NMDA receptor-related glutamatergic amino acid levels in peripheral blood of patients with schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011. 35:29–39.7. Zhao JL. Clinical therapeutic effects of sparfloxacin and glutamic acid, alanine acid and glycine acid capsules in the treatment of chronic prostatis. Chin Clin Prac Med. 2007. 1:33–35.8. Fekkes D. State-of-the-art of high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of amino acids in physiological samples. J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl. 1996. 682:3–22.9. Le Boucher J, Charret C, Coudray-Lucas C, Giboudeau J, Cynober L. Amino acid determination in biological fluids by automated ion-exchange chromatography: performance of Hitachi L-8500A. Clin Chem. 1997. 43:1421–1428.10. Fekkes D, Voskuilen-Kooyman A, Jankie R, Huijmans J. Precise analysis of primary amino acids in urine by an automated high-performance liquid chromatography method: comparison with ion-exchange chromatography. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 2000. 744:183–188.11. Turnell DC, Cooper JD. Rapid assay for amino acids in serum or urine by pre-column derivatization and reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Clin Chem. 1982. 28:527–531.12. Heinrikson RL, Meredith SC. Amino acid analysis by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography: precolumn derivatization with phenylisothiocyanate. Anal Biochem. 1984. 136:65–74.13. Anumula KR, Taylor PB. Quantitative determination of phenyl isothiocyanate-derivatized amino sugars and amino sugar alcohols by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1991. 197:113–120.14. Kutlán D, Presits P, Molnár-Perl I. Behavior and characteristics of amine derivatives obtained with o-phthaldialdehyde/3-mercaptopropionic acid and with o-phthaldialdehyde/N-acetyl-L-cysteine reagents. J Chromatogr A. 2002. 949:235–248.15. Bosch L, Alegría A, Farré R. Application of the 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysccinimidyl carbamate (AQC) reagent to the RP-HPLC determination of amino acids in infant foods. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2006. 831:176–183.16. Cohen SA. Amino acid analysis using precolumn derivatization with 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate. Methods Mol Biol. 2000. 159:39–47.17. Cohen SA, Michaud DP. Synthesis of a fluorescent derivatizing reagent, 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate, and its application for the analysis of hydrolysate amino acids via high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1993. 211:279–287.18. Terrlink T, van Leeuwen PA, Houdijk A. Plasma amino acids determined by liquid chromatography within 17 minutes. Clin Chem. 1994. 40:245–249.19. Chih-Kuang C, Shuan-Pei L, Shyue-Jye L, Tuan-Jen W. Plasma free amino acids in Taiwan Chinese: the effect of age. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2002. 40:378–382.20. Frank MP, Powers RW. Simple and rapid quantitative high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of plasma amino acids. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007. 852:646–649.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Glutamate Levels in the Vitreous Body of an In Vivo Model of Optic Nerve Ischemia
- Circadian variation of plasma histamine in healthy volunteers measured by high-performance liquid chromatography
- HPLC-UV method for the simultaneous determinations of ascorbic acid and dehydroascorbic acid in human plasma
- A Simple and Sensitive Assay for Cefepime in Human Plasma Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography
- Comparison of High Performance Liquid Chromatography and Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassay for Determination of Total Homocysteine in Human Plasma