Immune Netw.
2013 Oct;13(5):194-198. 10.4110/in.2013.13.5.194.
Treatment of Autoimmune Diabetes by Inhibiting the Initial Event
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 135-710, Korea. mslee0923@skku.edu
- KMID: 1493613
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2013.13.5.194
Abstract
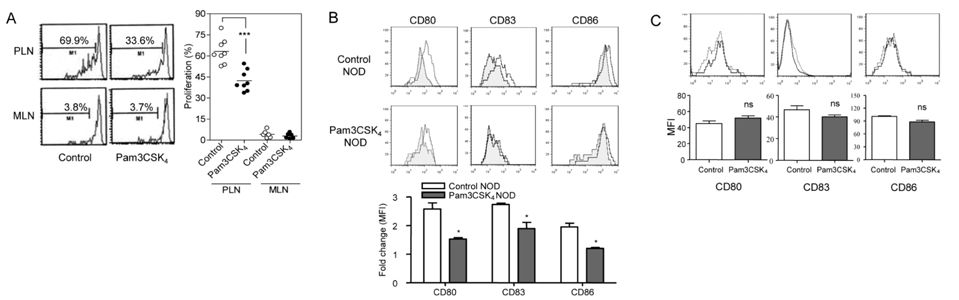
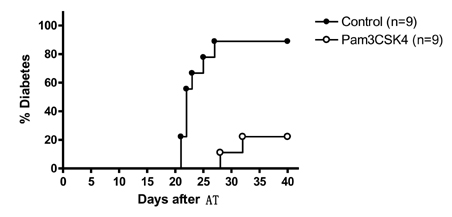
- Recent papers have shown that the initial event in the pathogenesis of autoimmune type 1 diabetes (T1D) comprises sensing of molecular patterns released from apoptotic beta-cells by innate immune receptors such as toll-like receptor (TLR). We have reported that apoptotic beta-cells undergoing secondary necrosis called 'late apoptotic' beta-cells stimulate dendritic cells (DCs) and induce diabetogenic T cell priming through TLR2. The role of other innate immune receptors such as TLR7 or TLR9 in the initiation of T1D has also been suggested. We hypothesized that TLR2 blockade could inhibit T1D at the initial step of T1D. Indeed, when a TLR2 agonist, Pam3CSK4 was administered chronically, the development of T1D in nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice was inhibited. Diabetogenic T cell priming by DCs was attenuated by chronic treatment with Pam3CSK4, indicating DC tolerance. For the treatment of established T1D, immune tolerance alone is not enough because beta-cell mass is critically reduced. We employed TLR2 tolerance in conjunction with islet transplantation, which led to reversal of newly established T1D. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitors are a new class of anti-diabetic agents that have beneficial effects on beta-cells. We investigated whether a combination of DPP4 inhibition and TLR2 tolerization could reverse newly established T1D without islet transplantation. We could achieve normoglycemia by TLR2 tolerization in combination with DPP4 inhibition but not by TLR2 tolerization or DPP4 inhibition alone. beta-cell mass was significantly increased by combined treatment with TLR2 tolerization and DPP4 inhibition. These results suggest the possibility that a novel strategy of TLR tolerization will be available for the inhibition or treatment of established T1D when combined with measures increasing critically reduced beta-cell mass of T1D patients such as DPP4 inhibition or stem cell technology.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim YH, Kim S, Kim KA, Yagita H, Kayagaki N, Kim KW, Lee MS. Apoptosis of pancreatic β-cells detected in accelerated diabetes of NOD mice:no role of Fas-Fas ligand interaction in autoimmune diabetes. Eur J Immunol. 1999; 29:455–465.
Article2. OBrien BA, Harmon BV, Cameron DP, Allan DJ. Apoptosis is the mode of β-cell death responsible for the development of IDDM in the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse. Diabetes. 1997; 46:750–757.
Article3. Finegood DT, MaArthur MD, Kojwang D, Thomas MJ, Topp BG, Leonard T, Buckingham RE. β-cell mass dynamics in Zucker Diabetic Fatty rats. Diabetes. 2001; 50:1021–1029.
Article4. Trudeau JD, Dutz JP, Arany E, Hill DJ, Fieldus WE, Finegood DT. Neonatal beta-cell apoptosis: a trigger for autoimmune diabetes? Diabetes. 2000; 49:1–7.
Article5. Kim HS, Han MS, Chung KW, Kim S, Kim E, Kim MJ, Jang E, Lee HA, Youn J, Akira S, Lee MS. Toll-like receptor 2 senses beta-cell death and contributes to the initiation of autoimmune diabetes. Immunity. 2007; 27:321–333.
Article6. Diana J, Simoni V, Furio L, Beaudoin L, Agerberth B, Barrat F, Lehuen A. Crosstalk between neutrophils, B-1a cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells initiates autoimmune diabetes. Nat Med. 2013; 19:65–73.
Article7. Cavaillon JM, Adrie C, Fitting C, Adib-Conquy M. Endotoxin tolerance: is there a clinical relevance? J Endotoxin Res. 2003; 9:101–107.
Article8. Kim DH, Lee JC, Kim S, Oh SH, Lee MK, Kim KW, Lee MS. Inhibition of autoimmune diabetes by TLR2 tolerance. J Immunol. 2011; 187:5211–5220.
Article9. Xiong Y, Pennini M, Vogel SN, Medvedev AE. IRAK4 kinase activity is not required for induction of endotoxin tolerance but contributes to TLR2-mediated tolerance. J Leukocyte Biol. 2013; 94:291–300.
Article10. Mu J, Woods J, Zhou YP, Roy RS, Li Z, Zycband E, Feng Y, Zhu L, C L, Howard AD, Moller DE, Thonberry NA, Zhang BB. Chronic inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 with a sitagliptin analog preserves pancreatic beta-cell mass and function in a rodent model of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2006; 55:1695–1704.
Article11. Xu G, Stoffers DA, Habener JF, Bonner-Weir S. Exendin-4 stimulates both beta-cell replication and neogenesis, resulting in increased beta-cell mass and improved glucose tolerance in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1999; 48:2270–2276.
Article12. Butler AE, Campbell-Thompson M, Gurlo T, Dawson DW, Atkinson M, Butler PC. Marked expansion of exocrine and endocrine pancreas with incretin therapy in humans with increased exocrine pancreas dysplasia and the potential for glucagon-producing neuroendocrine tumors. Diabetes. 2013; 62:2595–2604.
Article13. Cho JM, Jang HW, Cheon H, Jeong YT, Kim DH, Lim YM, Choi Sh, Yang EK, Shin CY, Son MH, Kim SH, Kim HJ, Lee MS. A novel dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor DA-1229 ameliorates streptozotocin-induced diabetes by increasing β-cell replication and neogenesis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011; 91:72–79.
Article14. Kim DH, Lee JC, Lee MK, Kim KW, Lee MS. Treatment of autoimmune diabetes by toll-like receptor 2 tolerance in conjunction with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibition. Diabetologia. 2012; 55:3308–3317.
Article15. Jeon K, Lim H, Kim JH, Thuan NV, Park SH, Lim YM, Choi HY, Lee ER, Kim JH, Lee MS, Cho SG. Differentiation and Transplantation of functional pancreatic beta cells generated from induced pluripotent stem cells derived from a type 1 diabetes mouse model. Stem Cells Dev. 2012; 21:2642–2655.
Article16. Turley S, Poirot L, Hattori M, Benoist C, Mathis D. Physiological beta cell death triggers priming of self-reactive T cells by dendritic cells in a type-1 diabetes model. J Exp Med. 2003; 198:1527–1537.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults: Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults with Slowly Progressive beta-cell Failure
- How Do We Prepare Educational Events for Patients with Diabetes?
- Autoantibodies and Polymorphism of the TNF gene in Autoimmune Diabetes Mellitus
- Cyclosporine Treatment in a Patient with Concurrent Autoimmune Urticaria and Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Gene Therapy for the Prevention of Autoimmune Diabetes