J Korean Endocr Soc.
2009 Jun;24(2):144-147. 10.3803/jkes.2009.24.2.144.
Central Diabetes Insipidus Surmised as from Post-obstructive Diuresis after Decompression Treatment for Neurogenic Bladder
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Konyang University, College of Medicine, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, the Catholic University, College of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 1468511
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.2.144
Abstract
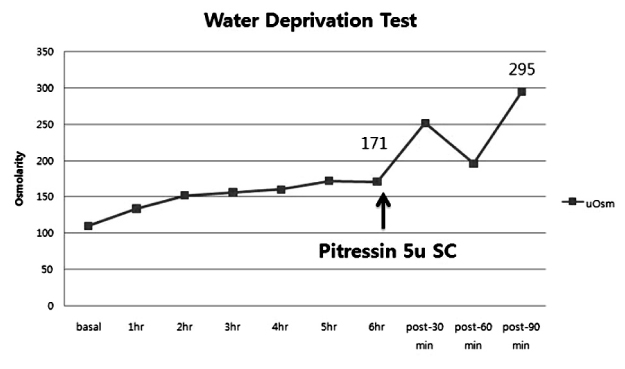
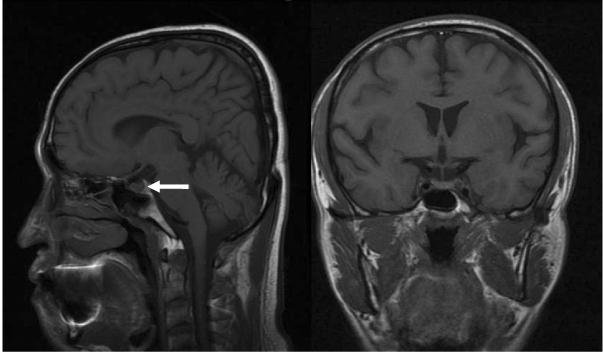
- Post-obstructive diuresis after treatment for neurogenic bladder-induced obstructive kidney disease is a common symptom. As polyuria may develop in many other conditions as well, the present case is about a patient with a chief complaint of polyuria accompanied by nocturia, that was initially diagnosed as hydronephrosis due to the presence of neurogenic bladder and bladder dysfunction. The result of the water deprivation test, which was conducted for persistent diluted polyuria, yielded a final diagnosis of central diabetes insipidus, notwithstanding the strong impression of post-obstructive diuresis initially made because of a sudden increase in urine output after an indwelling catheter was inserted for bladder decompression.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nyman MA, Schwenk NM, Silverstein MD. Management of urinary retention: rapid versus gradual decompression and risk of complications. Mayo Clin Proc. 1997. 72:951–956.2. Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Kasper DK, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo JL. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 2008. 17th ed. New York: the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.;2218–2221.3. Lee JW, Choi H, Oh SJ. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus associated with nonobstructive dilatation of the urinary tract and voiding difficulty. Korean J Urol. 2008. 49:562–565.4. Chang YY, Kim HU, Kim HD, Shin YS, Lee JM, Kim HS, Kim SK, Bang BK. A case of congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus with bilateral hydronephrosis and hydroureter. Korean J Nephrol. 2002. 21:1026–1031.5. Park CY, Kim HS. Treatment of renal injury in a patient presenting pituitary diabetes insipidus associated with bilateral hydronephrosis: a case report. Korean J Urol. 1994. 35:74–81.6. Korzets A, Sachs D, Gremitsky A, Gershkovitz R, Farrage G, Chlibowsky A, Erlich N. Unexplained polyuria and non-obstructive hydronephrosis in a urological department. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004. 19:2410–2412.7. Kim HJ, Kang MY, Kim KW, Jeong HS, Kim HS, Kim SW, Kim SY. Retrospective observation of long-term clinical courses of idiopathic central diabetes insipidus in adults. J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006. 21:482–489.8. Kim BW. Idiopathic central diabetes insipidus in adult. J Korean Endocr Soc. 2001. 16:185–189.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Congenital Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus with Bilateal Hydronephrosis: Indomethacin in Treatment of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
- A Case of Central Diabetes Insipidus Associated with Brachycephaly
- Morphea and Verruca Plana Complicated in Central Diabetes Insipidus
- A Case of Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome in a Patient with Central Diabetes Insipidus and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Central Diabetes Insipidus Occurring during Therapy for Tsutsugamushi Disease