Lab Anim Res.
2010 Mar;26(1):1-6. 10.5625/lar.2010.26.1.1.
Anti-hepatofibrogenic Effect of Turnip Water Extract on Thioacetamide-induced Liver Fibrosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Animal Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea. mjlee@kangwon.ac.kr
- 2College of Pharmacy, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Veterinary Infectious Diseases and Avian Disease, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chonbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea.
- 6Traditional Food Research Group, Korea Food Research Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1458933
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2010.26.1.1
Abstract
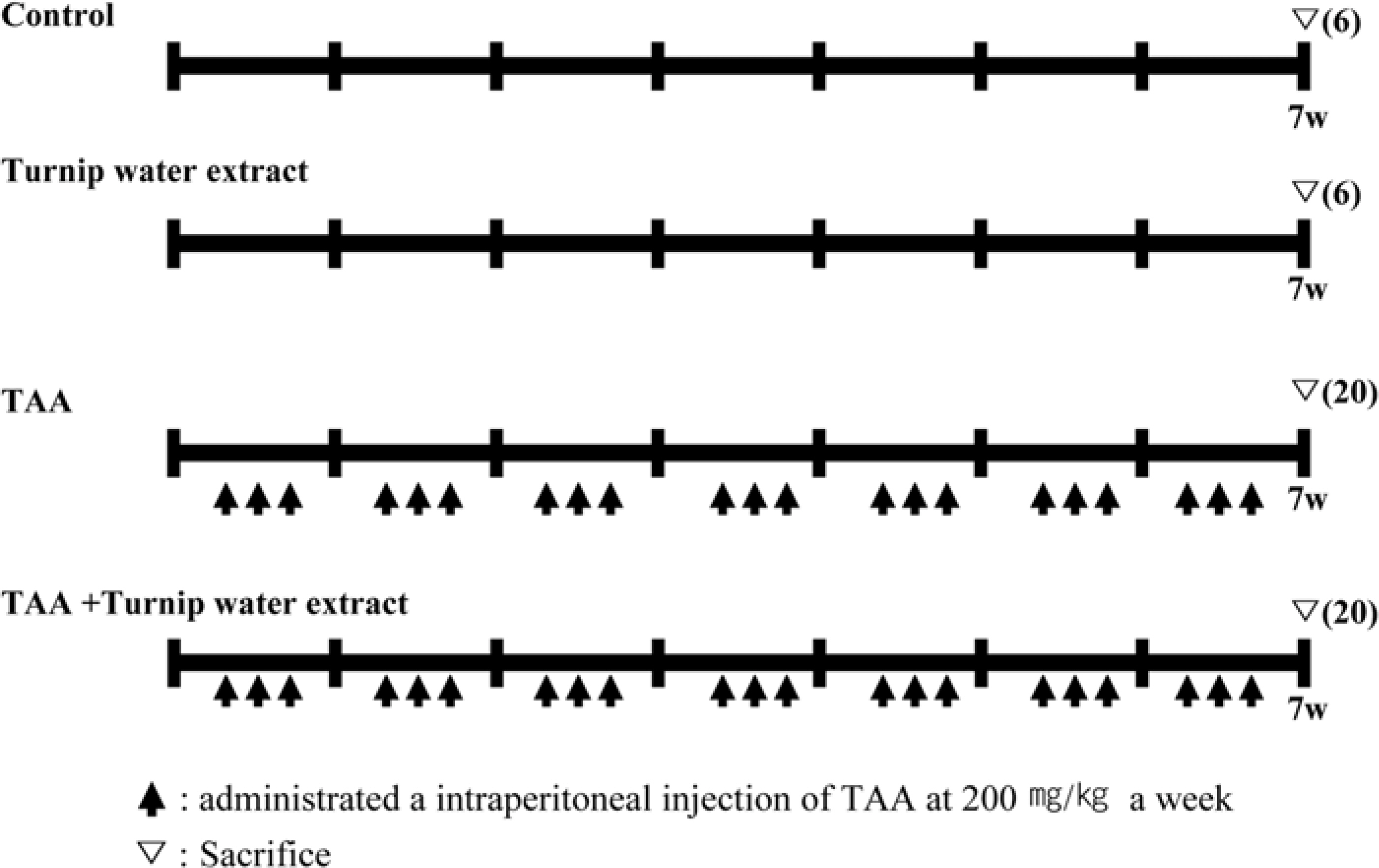
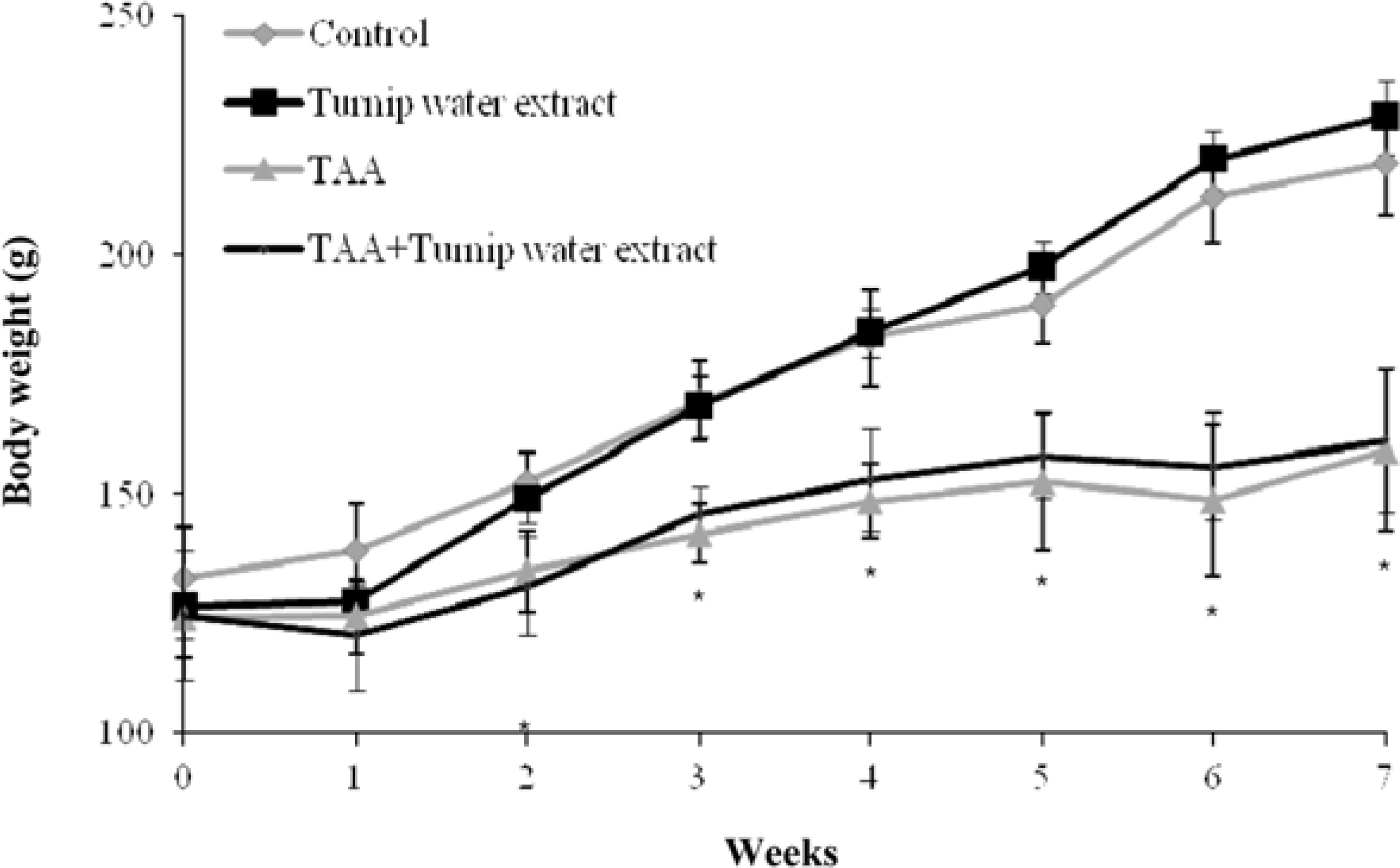
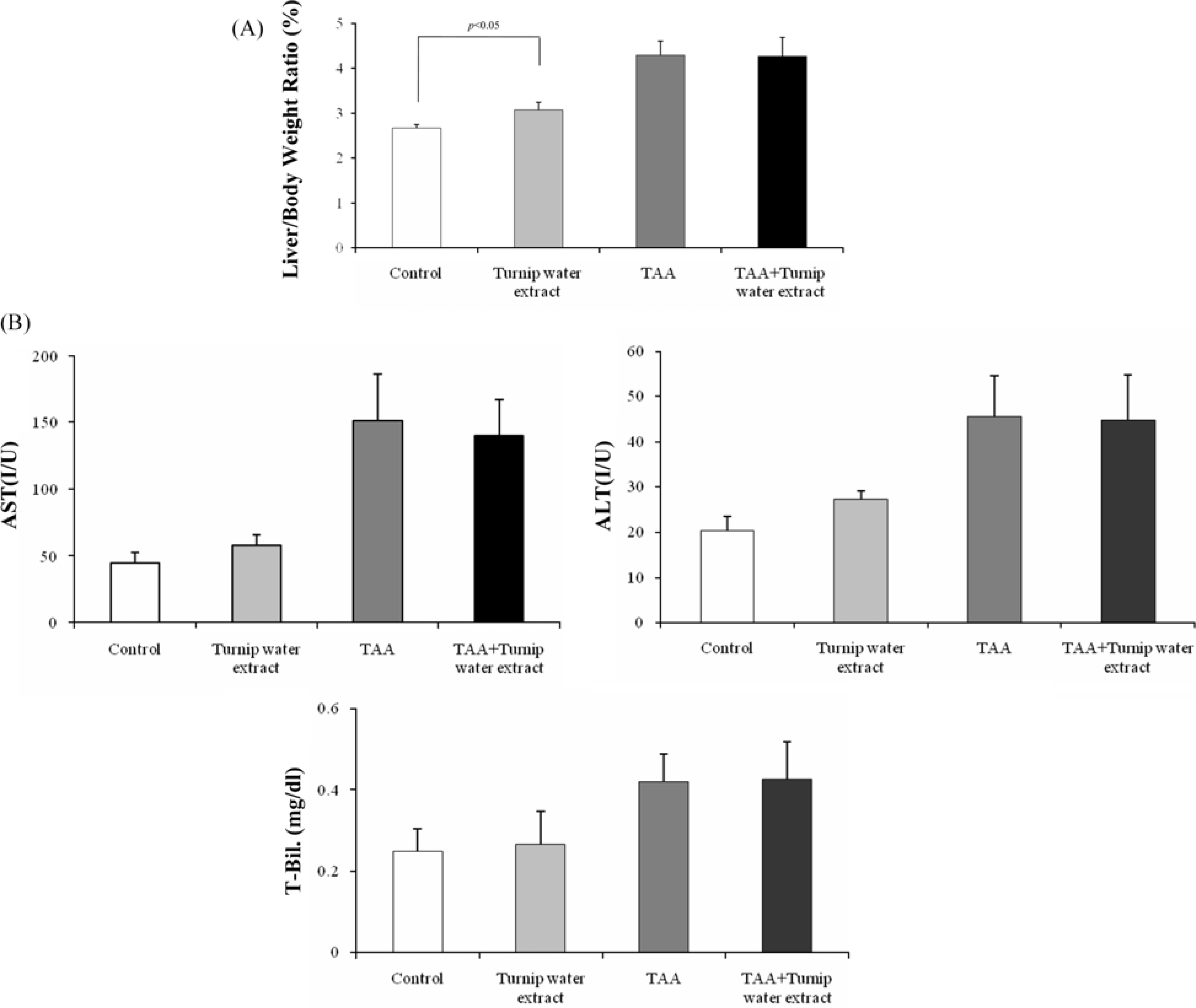
- Liver fibrosis is a chronic liver disease and lots of people in Korea are suffered. There are many efforts to find candidates to suppress liver fibrogenesis and several chemical-induced model or bile duct ligation model have been used to research and develop hepatic fibrogenic suppressor. From the previous study about functional effects of turnip which cultivated in Kangha Island, we got the feasibility which turnip might be able to inhibit heptatic fibrogenesis. TAA is a representative hepatic fibrosis inducer, repeated 7-weeks i.p. injection of it results in hepatic fibrosis. We compared the level of hepatic fibrosis in TAA-turnip group, TAA group, and vehicle control group. Nodules-formed by TAA were observed; they were rarely shown in vehicle control group, observed in most area in TAA group, but only shown in periportal regions in TAA-turnip group. These results were confirmed through Masson's trichrom stain; fibrous structures increased in TAA group (fibrosis score: 4) but significantly decreased in TAA-turnip group (fibrosis score: 2-3). In conclusion, we got the result that turnip water extract has a potency to protect TAA-induced hepatic fibrogenesis but it is necessary further study to find its mechanism.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
An J.H.., Seong J.., Oh H.., Kim W.., Han K.H.., Paik Y.H.2006. Protein expression profiles in a rat cirrhotic model induced by thioacetamide. Kor. J. Hepatol. 12(1):93–102.Cha J.Y.., Park J.C.., Ahn H.Y.., Eom K.E.., Park B.K.., Jun B.S.., Lee C.H.., Cho Y.S.2009. Effect of Monascus purpureus -fermented Korean red ginseng powder on the serum lipid levels and antioxidative activity in rats. J. Kor Soc Food Sic Nutr. 38(9):1153–1160.Chang J.J.., Jeon S.Y.., Song J.Y.., Kim J.H.., Li L.., Park D.H.., Lee Y.L.., Park J.J.., Woo D.W.., Kim G.J.., Lee M.J.2008. Alteration of X-linked inhibitors of apoptosis (XIAP) expression in rat model with DEN-induced hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 4(4):278–284.Choi H.J.., Han M.J.., Baek N.I.., Kim D.H.., Jung H.G.., Kim N.J.2006. Hepatoprotective Effects of Brassica rapa (Turnip) on d-Galactosamine Induced Liver Injured Rats. Kor. J. Phamacogn. 37(4):258–265.Friedman S.L.2008. Mechanisms of Hepatic Fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 314:1655–1669.
ArticleHillebrandt S.2005. Complement factor 5 is a quantitative trait gene that modifies liver fibrogenesis in mice and humans. Nature Genetics. 37:835–843.
ArticleHu S.L.., Yin S.., Jiang X.D.., Huang D.B.., Shen G.2009. Melatonin protects against alcoholic liver injury by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and apoptosis. Europ. J. Pharm. 616:287–292.
ArticleInao M.., Mochida S.., Matsui A.., Eguchi Y.., Yulutuz Y.., Wang Y.., Naiki K.., Kakinuma T.., Fujimori K.., Nagoshi S.., fujiwara K.2004. Japanese herbal medicine inchin-ko-to as a therapeutic drug for liver fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 41:584–591.
ArticleJung U.J.., Baek N.I.., Chung H.G.., Bang M.H.., Jeong T.S.., Lee K.T.., Kang Y.J.., Lee M.K.., Kim H.J.., Yeo J.., Choi M.S.2008. Effects of the ethanol extract of the roots of Brassica rapa on glucose and lipid metabolism in C57BL/KsJ - db/db mice. Clinical. Nutrition. 27:158–167.Kim D.H.., Kim J.H.., Kim C.H.., Kwon M.C.., Kim H.S.., Chung H.G.., Kang H.Y.., Lee H.J.., Lee H.Y.2008. Effects of alcohol oxidation of Brassicarapa L. extraction process in Kang-Hwa. Kor. J. Medicinal Crop Sci. 14(1):45–48.Krahenbuhl S.., Brass EP.., Hoppel C.L.2000. Decreased carnitine biosynthesis in rats with secondary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 3(1):1217–1223.
ArticleMa X.., Zhao J.., Lieber C.S.1996. Polyenylphospha-tidylcholine Attenuates non-alcoholic hepatic fibrosis and accelerates its regression. J. Hepatol. 24:604–613.
ArticleShapiro H.., Ashkenazi M.., Weizman N.., Shahmurov M.., Aeed H.., Bruck R.2006. Curcumin ameliorates acute thioacetamide-induced hepatotoxicity. J. Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 21(2):358–366.
ArticleShin H.W.., Park S.Y.., Lee K.B.., Shin E.., Lee M.J.., Kim Y.J.., Jang J.J.2006. Inhibitory effect of turnip extract on thioacetamide-induced rat hepatic fibrogenesis. Cancer Prevention Research. 11:265–272.Shin H.W.., Park S.Y.., Lee K.B.., Shin E.., Ryu H.S.., Kim M.S.., Ahn J.B.., Kim Y.J.., Jang J.J.2006-1. Inhibitory Effect of Turnip extract fractions on Hepatic Fibrogenesis. Lab. Anim. Res. 22(3):279–288.Yang S.., Leow C.K.2006. Expression patterns of cytokine, growth factor and cell cycle-related genes after partial hepatectomy in rats with thioacetamide-induced cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 12:1063–1070.
ArticleYoung S.C.., Wang C.J.., Lin J.J.., Peng P.L.., Hsu J.L.., Chou F.P.2007. Protection effect of piper betel leaf extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats. Arch Toxicol. 81:45–55.
ArticleZhou K.., Lu G.2009. Assessment of fibrosis in chronic liver diseases. J. Digestive Diseases. 10:7–14.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Pentoxifylline on Liver Fibrosis and Cell Cycle Related Proteins in Thioacetamide-Induced Rat Cirrhosis
- Therapeutic potentials occurring during the early differentiation process of mesenchymal stem cells in a rats model with thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis
- Protective effect of Artemisiae Capillaris Herba water extract on liver injury induced by thioacetamide
- The Factors Affecting Transplanted Hepatocytes Repopulation in Rats with Liver Fibrosis
- Role of cytoglobin, a novel radical scavenger, in stellate cell activation and hepatic fibrosis