Caffeine and 2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl Borate (2-APB) Have Different Ability to Inhibit Intracellular Calcium Mobilization in Pancreatic Acinar Cell
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, Konyang University, Daejeon 302-718, Korea. hspark@konyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 1457676
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.2.105
Abstract
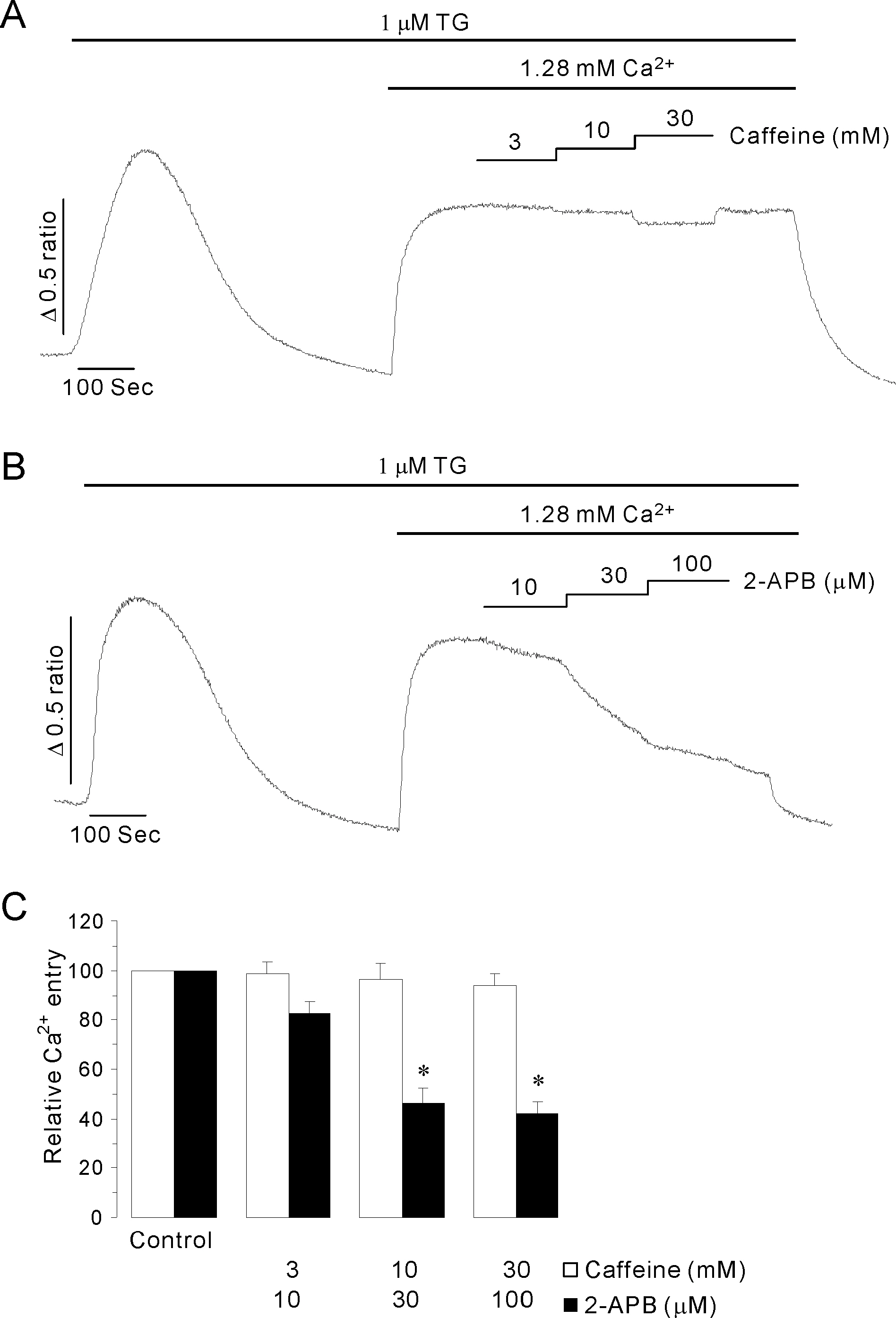
- Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors (InsP3Rs) modulate Ca2+ release from intracellular Ca2+ store and are extensively expressed in the membrane of endoplasmic/sarcoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. Although caffeine and 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) have been widely used to block InsP3Rs, the use of these is limited due to their multiple actions. In the present study, we examined and compared the ability of caffeine and 2-APB as a blocker of Ca2+ release from intracellular Ca2+ stores and Ca2+ entry through store-operated Ca2+ (SOC) channel in the mouse pancreatic acinar cell. Caffeine did not block the Ca2+ entry, but significantly inhibited carbamylcholine (CCh)-induced Ca2+ release. In contrast, 2-APB did not block CCh-induced Ca2+ release, but remarkably blocked SOC-mediated Ca2+ entry at lower concentrations. In permeabilized acinar cell, caffeine had an inhibitory effect on InsP3-induced Ca2+ release, but 2-APB at lower concentration, which effectively blocked Ca2+ entry, had no inhibitory action. At higher concentrations, 2-APB has multiple paradoxical effects including inhibition of InsP3-induced Ca2+ release and direct stimulation of Ca2+ release. Based on the results, we concluded that caffeine is useful as an inhibitor of InsP3R, and 2-APB at lower concentration is considered a blocker of Ca2+ entry through SOC channels in the pancreatic acinar cell.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Hydrogen peroxide inhibits Ca2+ efflux through plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase in mouse parotid acinar cells
Min Jae Kim, Kyung Jin Choi, Mi Na Yoon, Sang Hwan Oh, Dong Kwan Kim, Se Hoon Kim, Hyung Seo Park
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018;22(2):215-223. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.2.215.Alteration of Ryanodine-receptors in Cultured Rat Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells
Eun Ji Kim, Dong Kwan Kim, Shin Hye Kim, Kyung Moo Lee, Hyung Seo Park, Se Hoon Kim
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011;15(6):431-436. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2011.15.6.431.Ca2+-induced Ca2+ Release from Internal Stores in INS-1 Rat Insulinoma Cells
Kyung Jin Choi, Dong Su Cho, Ju Young Kim, Byung Joon Kim, Kyung Moo Lee, Shin Hye Kim, Dong Kwan Kim, Se Hoon Kim, Hyung Seo Park
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011;15(1):53-59. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2011.15.1.53.
Reference
-
References
1. Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003; 4:517–529.
Article2. Petersen OH, Michalak M, Verkhratsky A. Calcium signalling: past, present and future. Cell Calcium. 2005; 38:161–169.
Article3. Williams JA, Yule DI. Stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic acinar cell. Johnson LR, editor. ed.Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract. 4th ed.New York: Elsevier Academic Press;2006. p. 1337–1369.4. Berridge MJ. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009; 1793:933–940.
Article5. Putney JW, Bird GS. Cytoplasmic calcium oscillations and store-operated calcium influx. J Physiol. 2008; 586:3055–2059.
Article6. Taylor CW, Prole DL, Rahman T. Ca2+ channels on the move. Biochemistry. 2009; 48:12062–12080.7. Li W, Llopis J, Whitney M, Zlokarnik G, Tsien RY. Cell-permeant caged InsP3 ester shows that Ca2+ spike frequency can optimize gene expression. Nature. 1998; 392:936–941.8. Ehrlich BE, Kaftan E, Bezprozvannaya S, Bezprozvanny I. The pharmacology of intracellular Ca2+-release channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994; 15:145–149.9. Solovyova N, Fernyhough P, Glazner G, Verkhratsky A. Xestospongin C empties the ER calcium store but does not inhibit InsP3-induced Ca2+ release in cultured dorsal root ganglia neurons. Cell Calcium. 2002; 32:49–52.10. Maruyama T, Kanaji T, Nakade S, Kanno T, Mikoshiba K. 2APB, 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate, a membrane-penetrable modulator of Ins(1,4,5)P3-induced Ca2+ release. J Biochem. 1997; 122:498–505.11. Missiaen L, Callewaert G, De Smedt H, Parys JB. 2-Amino-ethoxydiphenyl borate affects the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor, the intracellular Ca2+ pump and the non-specific Ca2+ leak from the non-mitochondrial Ca2+ stores in permeabilized A7r5 cells. Cell Calcium. 2001; 29:111–116.12. Bilmen JG, Michelangeli F. Inhibition of the type 1 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor by 2-aminoethoxydiphenylborate. Cell Signal. 2002; 14:955–960.
Article13. Soulsby MD, Wojcikiewicz RJ. 2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl borate inhibits inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor function, ubiquitination and downregulation, but acts with variable characteristics in different cell types. Cell Calcium. 2002; 32:175–181.
Article14. Prakriya M, Lewis RS. Potentiation and inhibition of Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ channels by 2-aminoethyldiphenyl borate (2-APB) occurs independently of IP3 receptors. J Physiol. 2001; 536:3–19.15. Gregory RB, Rychkov G, Barritt GJ. Evidence that 2-aminoethyl diphenylborate is a novel inhibitor of store-operated Ca2+ channels in liver cells, and acts through a mechanism which does not involve inositol trisphosphate receptors. Biochem J. 2001; 354:285–290.16. Park MK, Lee KK, Uhm DY. Slow depletion of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ stores and block of store-operated Ca2+ channels by 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2002; 365:399–405.17. Bootman MD, Collins TJ, Mackenzie L, Roderick HL, Berridge MJ, Peppiatt CM. 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) is a reliable blocker of store-operated Ca2+ entry but an inconsistent inhibitor of InsP3-induced Ca2+ release. FASEB J. 2002; 16:1145–1150.18. DeHaven WI, Smyth JT, Boyles RR, Bird GS, Putney JW Jr. Complex actions of 2-aminoethyldiphenyl borate on store-operated calcium entry. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283:19265–19273.
Article19. Park HS, Betzenhauser MJ, Won JH, Chen J, Yule DI. The type 2 inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate (InsP3) receptor determines the sensitivity of InsP3-induced Ca2+ release to ATP in pancreatic acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283:26081–26088.20. Betzenhauser MJ, Wagner LE 2nd, Park HS, Yule DI. ATP regulation of type-1 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor activity does not require walker A-type ATP-binding motifs. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284:16156–16163.
Article21. Yule DI, Gallacher DV. Oscillations of cytosolic calcium in single pancreatic acinar cells stimulated by acetylcholine. FEBS Lett. 1988; 239:358–362.
Article22. Sei Y, Gallagher KL, Daly JW. Multiple effects of caffeine on Ca2+ release and influx in human B lymphocytes. Cell Calcium. 2001; 29:149–160.23. Han MH, Kawasaki A, Wei JY, Barnstable CJ. Miniature postsynaptic currents depend on Ca2+ released from internal stores via PLC/IP3 pathway. Neuroreport. 2001; 12:2203–2207.24. Nakamura T, Nakamura K, Lasser-Ross N, Barbara JG, Sandler VM, Ross WN. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3)-mediated Ca2+ release evoked by metabotropic agonists and backpropagating action potentials in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci. 2000; 20:8365–8376.25. Sjödin L, Gylfe E. Caffeine inhibits a low affinity but not a high affinity mechanism for cholecystokinin-evoked Ca2+ signalling and amylase release from guinea pig pancreatic acini. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2000; 361:113–119.26. Parekh AB, Putney JW Jr. Store-operated calcium channels. Physiol Rev. 2005; 85:757–810.
Article27. Putney JW. Physiological mechanisms of TRPC activation. Pflugers Arch. 2005; 451:29–34.
Article28. Smyth JT, Dehaven WI, Jones BF, Mercer JC, Trebak M, Vazquez G, Putney JW Jr. Emerging perspectives in store-operated Ca2+ entry: roles of Orai, Stim and TRP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006; 1763:1147–1160.29. McCarron JG, Bradley KN, MacMillan D, Muir TC. Sarco-lemma agonist-induced interactions between InsP3 and ryanodine receptors in Ca2+ oscillations and waves in smooth muscle. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003; 31:920–924.30. Rousseau E, Ladine J, Liu QY, Meissner G. Activation of the Ca2+ release channel of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum by caffeine and related compounds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988; 267:75–86.31. Toescu EC, O'Neill SC, Petersen OH, Eisner DA. Caffeine inhibits the agonist-evoked cytosolic Ca2+ signal in mouse pancreatic acinar cells by blocking inositol trisphosphate production. J Biol Chem. 1992; 267:23467–23470.32. Ashby MC, Petersen OH, Tepikin AV. Spatial characterisation of ryanodine-induced calcium release in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem J. 2003; 369:441–445.
Article33. Straub SV, Giovannucci DR, Yule DI. Calcium wave propagation in pancreatic acinar cells: functional interaction of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors, ryanodine receptors, and mitochondria. J Gen Physiol. 2000; 116:547–560.34. Ascher-Landsberg J, Saunders T, Elovitz M, Phillippe M. The effects of 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate, a novel inositol 1,4, 5-trisphosphate receptor modulator on myometrial contractions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999; 264:979–982.35. Peppiatt CM, Collins TJ, Mackenzie L, Conway SJ, Holmes AB, Bootman MD, Berridge MJ, Seo JT, Roderick HL. 2-Aminoeth-oxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) antagonises inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release, inhibits calcium pumps and has a use-dependent and slowly reversible action on store-operated calcium entry channels. Cell Calcium. 2003; 34:97–108.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of IP3 Receptor Inhibition Using 2-APB on Gentamicin Ototoxicity in Cochlear Sensory Cell
- Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ Release from Internal Stores in INS-1 Rat Insulinoma Cells
- Effect of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate on Intracellular Free Ca2+ in Cat Esophageal Smooth Muscle Cells
- Hydrogen peroxide attenuates refilling of intracellular calcium store in mouse pancreatic acinar cells
- Polyarthritis and Pancreatic Panniculitis in a Patient with Pancreatic Acinar Cell Carcinoma