J Bacteriol Virol.
2010 Jun;40(2):83-89. 10.4167/jbv.2010.40.2.83.
Antibody Production of Baculovirus-expressed VP6 from Porcine Group C Rotavirus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. paik@catholic.ac.kr
- 2AdipoGen Inc., Incheon, Korea.
- 3Division of Enteric and Hepatitis Viruses, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Seoul, Korea.
- 4National Institute of Animal Science, Rural Development Administration, Suwon, Korea.
- 5Apgujung St. Mary's Eye Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Senigen Co., Gwacheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1456271
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2010.40.2.83
Abstract
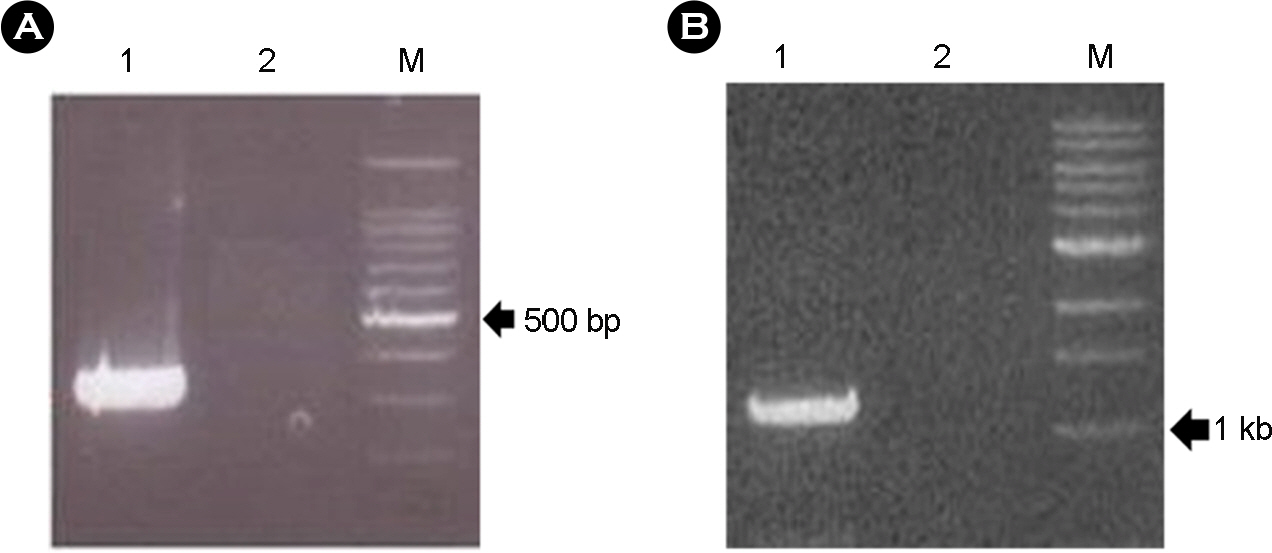
- The emerging pathogen, group C rotavirus (RVC) has been reported to cause acute diarrhea. But there was the limitation on the detection and monitoring for the absence of rapid sensitive diagnosis system. For the molecular biology study and diagnostic system development, we could detect porcine RVC by reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) analyses from 60 diarrheal disease porcine stool samples. VP6 full length RT-PCR product (CA-2 RVC, 1352 bp) was cloned and compared the nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences with those of previously reported other porcine, human, and bovine rotavirus group A, B and C strains. Analyses data showed >82% homology on the nucleotide sequences and >90% homology on the deduced amino acid sequences with other RVCs. Recombinant baculovirus was prepared with cloned PCR product corresponding to VP6 coding sequence (CDS) (position 22~1206) into BaculoDirect(TM) C-term linear DNA, and used for the transfection of insect cells. The polyclonal antibody was produced from mice with purified recombinant VP6 and confirmed with western blot. Both of VP6 antigen and antibody, are useful for the development of rapid diagnostic system against RVC.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Protein Expression of the Human Norovirus Capsid Gene using the Baculovirus Expression System
Ji-Young Jin, Chul Jong Park, Seung-Won Park, Soon-Young Paik
J Bacteriol Virol. 2011;41(3):183-187. doi: 10.4167/jbv.2011.41.3.183.
Reference
-
1). Estes KM., Kapikian AZ. Rotaviruses. pp 1917-74. In Fields Virology. 5th ed.Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. (Ed),. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;Philadelphia, PA.: 2007.2). Tian P., Hu Y., Schilling WP., Lindsay DA., Eiden J., Estes MK. The nonstructural glycoprotein of rotavirus affects intracellular calcium levels. J Virol. 1994. 68:251–7.
Article3). Mitui MT., Bozdayi G., Dalgic B., Bostanci I., Nishizono A., Ahmed K. Molecular characterization of a human group C rotavirus detected first in Turkey. Virus Genes. 2009. 39:157–64.
Article4). Parashar UD., Gibson CJ., Bresse JS., Glass RI. Rotavirus and severe childhood diarrhea. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006. 12:304–6.
Article5). Hung T., Chen GM., Wang CG., Chou ZY., Chao TX., Ye WW, et al. Rotavirus-like agent in adult non-bacterial diarrhoea in China. Lancet. 1983. 2:1078–9.6). Hung T., Chen GM., Wang CG., Yao HL., Fang ZY., Chao TX, et al. Waterborne outbreak of rotavirus diarrhoea in adults in China caused by a novel rotavirus. Lancet. 1984. 1:1139–42.7). Jiang B., Dennehy PH., Spangenberger S., Gentsch JR., Glass RI. First detection of group C rotavirus in fecal specimens of children with diarrhea in the United States. J Infect Dis. 1995. 172:45–50.
Article8). Saif LJ., Bohl EH., Theil KW., Cross RF., House JA. Rotavirus-like, calicivirus-like, and 23-nm virus-like particles associated with diarrhea in young pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1980. 12:105–11.
Article9). Rodger SM., Bishop RF., Holmes IH. Detection of a rotavirus-like agent associated with diarrhea in an infant. J Clin Microbiol. 1982. 16:724–6.
Article10). Torres-Median A. Isolation of an atypical rotavirus causing diarrhea in neonatal ferrets. Lab Anim Sci. 1987. 37:167–71.11). Tsunemitsu H., Saif LJ., Jiang BM., Shimizu M., Hiro M., Yamaguchi H, et al. Isolation, characterization, and serial propagation of a bovine group C rotavirus in a monkey kidney cell line (MA104). J Clin Microbiol. 1991. 29:2609–13.
Article12). Jeong YJ., Park SI., Hosmillo M., Shin DJ., Chun YH., Kim HJ, et al. Detection and molecular characterization of porcine group C rotaviruses in South Korea. Vet Microbiol. 2009. 138:217–24.
Article13). Castello AA., Argüelles MH., Villegas GA., Olthoff A., Glikmann G. Incidence and prevalence of human group C rotavirus infections in Argentina. J Med Virol. 2002. 67:106–12.
Article14). Iturriza-Gomara M., Clarke I., Desselberger U., Brown D., Thomas D., Gray J. Seroepidemiology of group C rotavirus infection in England and Wales. Eur J Epidemiol. 2004. 19:589–95.
Article15). Schnagl RD., Boniface K., Cardwell P., McCarthy D., Ondracek C., Coulson B, et al. Incidence of group C human rotavirus in central Australia and sequence variation of the VP7 and VP4 genes. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. 42:2127–33.
Article16). Rahman M., Banik S., Faruque AS., Taniguchi K., Sack DA., Van Ranst M, et al. Detection and characterization of human group C rotaviruses in Bangladesh. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:4460–5.
Article17). Bányai K., Jiang B., Bogdán A., Horváth B., Jakab F., Meleg E, et al. Prevalence and molecular characterization of human group C rotaviruses in Hungary. J Clin Virol. 2006. 37:317–22.
Article18). Abid I., Guix S., Aouni M., Pinto R., Bosch A. Detection and characterization of human group C rotavirus in the pediatric population of Barcelona, Spain. J Clin Virol. 2007. 38:78–82.
Article19). Clark KB., Lin SC., Humphrey C., Foytich K., Esona M., Wang Y, et al. Expression and characterization of human group C rotavirus virus-like particles in insect cells. Virology. 2009. 387:267–72.
Article20). Yee EL., Jiang B., Kendall RS., Humphrey C., Glass RI. Group C rotavirus in a pediatric kidney transplant patient with diarrhea. J Clin Virol. 2006. 36:306–8.
Article21). Esona MD., Humphrey CD., Dennehy PH., Jiang B. Prevalence of group C rotavirus among children in Rhode Island, United States. J Clin Virol. 2008. 42:221–4.
Article22). Choi AH., McNeal MM., Basu M., Bean JA., VanCott JL., Clements JD, et al. Functional mapping of protective epitopes within the rotavirus VP6 protein in mice belonging to different haplotypes. Vaccine. 2003. 21:761–7.
Article23). Sánchez-Fauquier A., Roman E., Colomina J., Wilhelmi I., Glass RI., Jiang B. First detection of group C rotavirus in children with acute diarrhea in Spain. Arch Virol. 2003. 148:399–404.24). Cooke SJ., Clarke IN., Freitas RB., Gabbay YB., Lambden PR. The correct sequence of the porcine group C/Cowden rotavirus major inner capsid protein shows close homology with human isolates from Brazil and the U.K. Virology. 1992. 190:531–7.
Article25). Matthijnssens J., Rahman M., Van Ranst M. Two out of the 11 genes of an unusual human G6P[6] rotavirus isolate are of bovine origin. J Gen Virol. 2008. 89:2630–5.
Article26). Matthijnssens J., Potgieter CA., Ciarlet M., Parreño V., Martella V., Bányai K, et al. Are human P[14] rotavirus strains the result of interspecies transmissions from sheep or other ungulates that belong to the mammalian order Artiodactyla? J Virol. 2009. 83:2917–29.27). Buragohain M., Cherian SS., Prabhakar G., Chitambar SD. VP6 capsid protein of chicken rotavirus strain CH2: sequence, phylogeny and in silico antigenic analyses. Virus Res. 2008. 137:173–8.
Article28). Ghosh S., Varghese V., Samajdar S., Bhattacharya SK., Kobayashi N., Naik TN. Molecular characterization of a porcine Group A rotavirus strain with G12 genotype specificity. Arch Virol. 2006. 151:1329–44.
Article29). Yang JH., Kobayashi N., Wang YH., Zhou X., Li Y., Zhou DJ, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of a human group B rotavirus WH-1 detected in China in 2002. J Med Virol. 2004. 74:662–7.
Article30). Ghosh S., Kobayashi N., Nagashima S., Chawla-Sarkar M., Krishnan T., Ganesh B, et al. Molecular characterization of the VP1, VP2, VP4, VP6, NSP1 and NSP2 genes of bovine group B rotaviruses: identification of a novel VP4 genotype. Arch Virol. 2010. 155:159–67.
Article31). Jiang B., Tsunemitsu H., Gentsch JR., Glass RI., Green KY., Qian Y, et al. Nucleotide sequence of gene 5 encoding the inner capsid protein (VP6) of bovine group C rotavirus: comparison with corresponding genes of group C, A, and B rotaviruses. Virology. 1992. 190:542–7.
Article32). Castello AA., Argüelles MH., Rota RP., Humphrey CD., Olthoff A., Gentsch JR, et al. Detection and characterization of group C rotavirus in Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1997-2003. J Med Virol. 2009. 81:1109–16.
Article33). Collins PJ., Martella V., O'Shea H. Detection and characterization of group C rotaviruses in asymptomatic piglets in Ireland. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. 46:2973–9.
Article34). Kuzuya M., Fujii R., Hamano M., Nishijima M., Ogura H. Detection and molecular characterization of human group C rotaviruses in Okayama Prefecture, Japan, between 1986 and 2005. J Med Virol. 2007. 79:1219–28.
Article35). Khamrin P., Peerakome S., Malasao R., Mizuguchi M., Okitsu S., Ushijima H, et al. Genetic characterization of group C rotavirus isolated from a child hospitalized with acute gastroenteritis in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Virus Genes. 2008. 37:314–21.
Article36). Gabbay YB., Borges AA., Oliveira DS., Linhares AC., Mascarenhas JD., Barardi CR, et al. Evidence for zoonotic transmission of group C rotaviruses among children in Belém, Brazil. J Med Virol. 2008. 80:1666–74.
Article37). Kuzuya M., Hamano M., Nishijima M., Fujii R., Ogura H., Tanaka M, et al. An outbreak of acute gastroenteritis caused by human group C rotavirus in a welfare institution in Okayama prefecture. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2005. 58:255–7.38). Xu L., Harbour D., McCrae MA. The application of polymerase chain reaction to the detection of rotaviruses in faeces. J Virol Methods. 1990. 27:29–37.
Article39). Yu J., Langridge W. Expression of rotavirus capsid protein VP6 in transgenic potato and its oral immunogenicity in mice. Transgenic Res. 2003. 12:163–9.40). Choi AH., Basu M., McNeal MM., Flint J., VanCott JL., Clements JD, et al. Functional mapping of protective domains and epitopes in the rotavirus VP6 protein. J Virol. 2000. 74:11574–80.
Article41). Hunt I. From gene to protein: a review of new and enabling technologies for multi-parallel protein expression. Protein Expr Purif. 2005. 40:1–22.
Article42). Chang KO., Nielsen PR., Ward LA., Saif LJ. Dual infection of gnotobiotic calves with bovine strains of group A and porcine-like group C rotaviruses influences pathogenesis of the group C rotavirus. J Virol. 1999. 73:9284–93.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Production and characterization of VP6-specific monoclonal antibodies against bovine group C rotavirus
- Usefulness of Escherichia coli-expressed Recombinant VP6 Proteins of Group A Rotavirus in Serodiagosis of Rotavirus Infection
- Characterization of the Recombinant Proteins of Porcine Circovirus Type2 Field Isolate Expressed in the Baculovirus System
- Sequence Analysis and Expression of the VP7 Gene of G1 Rotavirus Isolated from an Infant in Korean
- Improvement of titration methods for porcine rotavirus, its serum neutralizing antibody and of virus isolation from feces