J Korean Soc Transplant.
2011 Dec;25(4):249-256. 10.4285/jkstn.2011.25.4.249.
The Characteristics and Treatment of Bone Loss after Liver Transplant
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul National University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kssuh2000@gmail.com
- KMID: 1450973
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/jkstn.2011.25.4.249
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Bone loss after liver transplant (LT) is a long-term problem associated with an increased morbidity due to pathologic fractures. We reviewed our management of post-LT bone loss.
METHODS
We collected retrospective data from 82 adult LT recipients between January 2006 and December 2009 who had preoperative and postoperative (12 to 24 months) bone mineral density (BMD) data measured by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). BMD was decreased in 52 out of 82 patients before LT. These patients were managed with calcium plus alendronate, calcium only, or no treatment. We compared the efficacy of these three modalities and the factors influencing BMD changes and investigated the incidence of pathologic fractures.
RESULTS
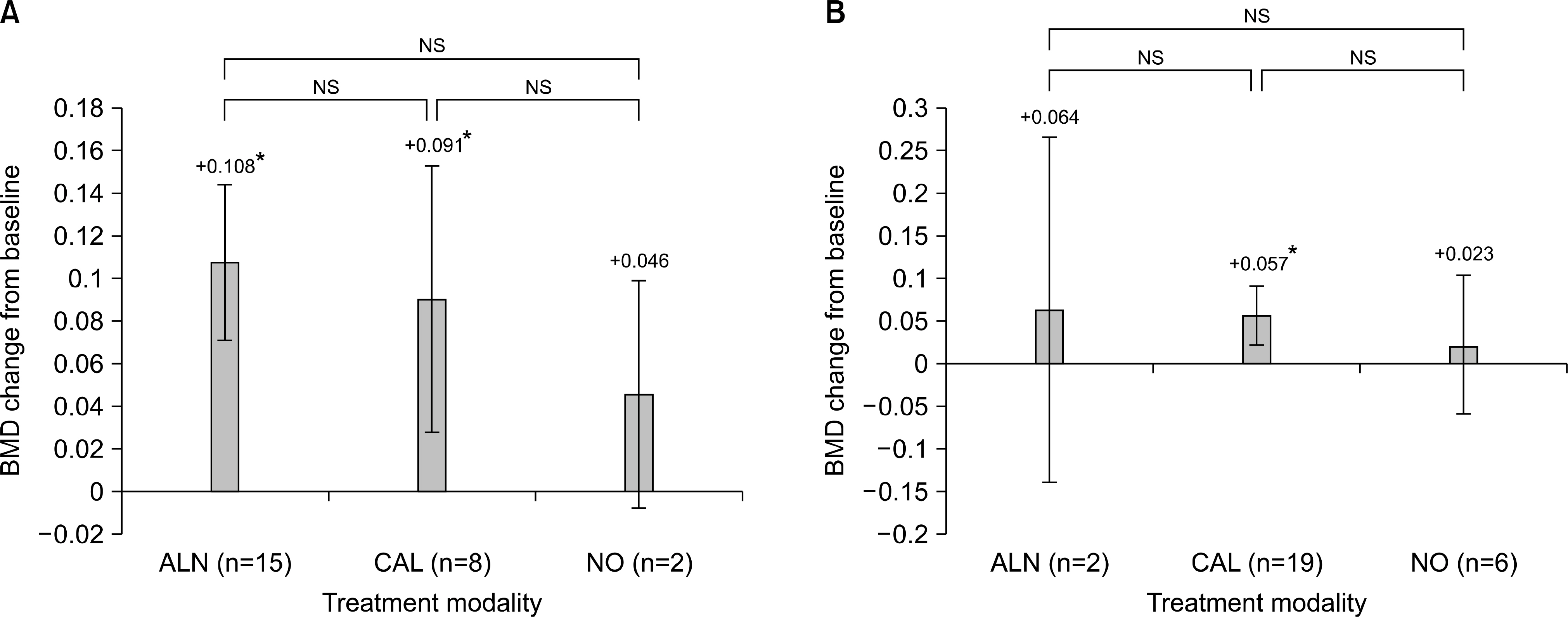
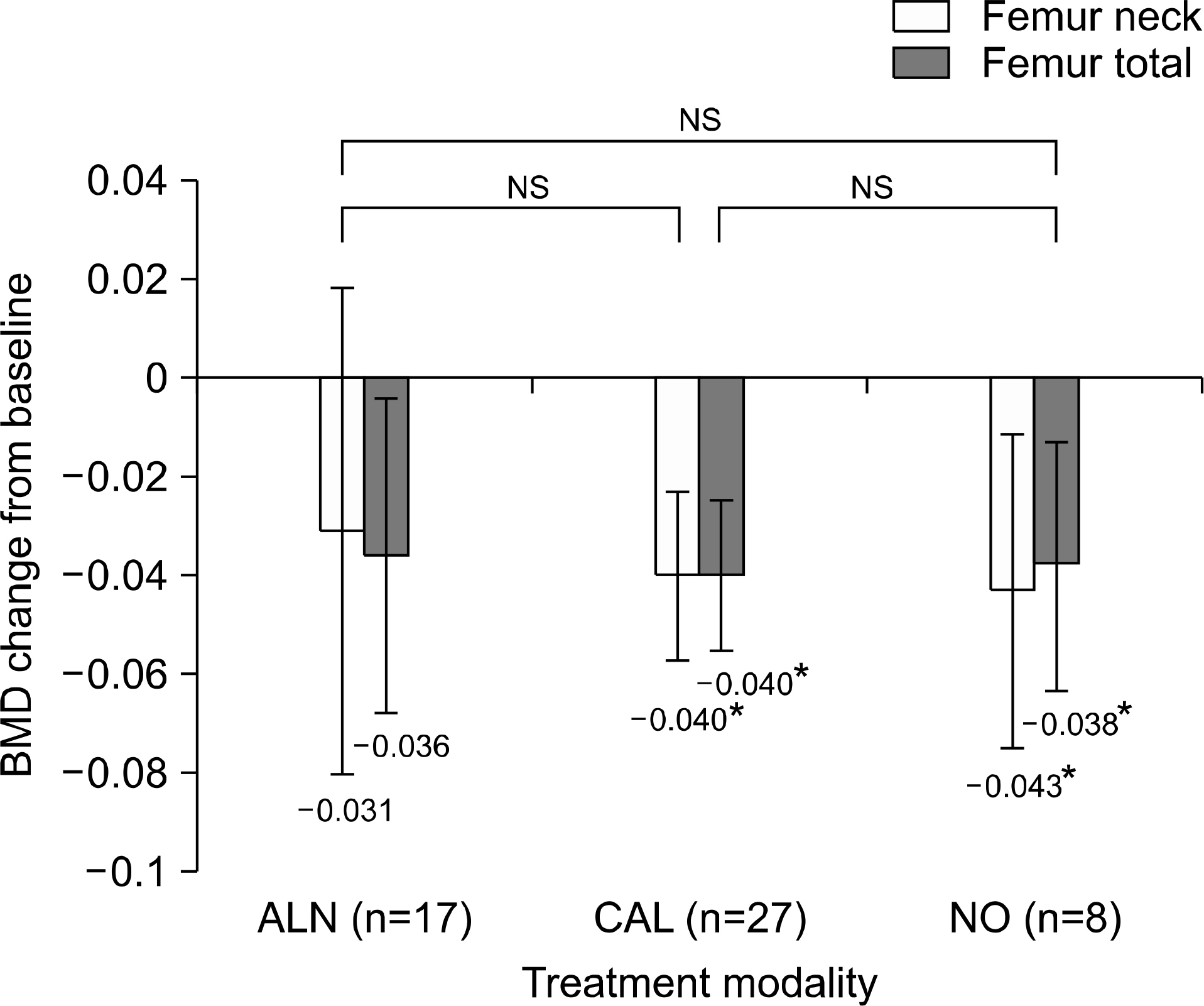
In decreased BMD patients (n=52), the postoperative spinal BMD was increased with all three treatment modalities. A more significant increase was found with ALN treatment (+0.103) compared to NO treatment (+0.029) (P-value: 0.016). However, femoral BMD decreased despite ALN treatment. Alendronate use was a significant factor for post-LT spinal BMD improvement in the univariate and multivariate analysis. There were significant newly-developed pathologic fractures after LT especially in osteoporotic patients (28%).
CONCLUSIONS
Weekly alendronate with daily calcium may be helpful for the spinal bone mineral protection in preoperative patients with decreased BMD.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). Collier J. Bone disorders in chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 2007; 46:1271–8.
Article2). Karges W, Trautwein C. Liver transplantation and osteoporosis: securing "bone-fied" success. Liver Transpl. 2006; 12:1322–3.
Article3). Ebeling PR. Approach to the patient with transplantation-related bone loss. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 94:1483–90.
Article4). Kasturi KS, Chennareddygari S, Mummadi RR. Effect of bisphosphonates on bone mineral density in liver transplant patients: a metaanalysis and systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Transpl Int. 2010; 23:200–7.
Article5). Leidig-Bruckner G, Hosch S, Dodidou P, Ritschel D, Conradt C, Klose C, et al. Frequency and predictors of osteoporotic fractures after cardiac or liver transplantation: a follow-up study. Lancet. 2001; 357:342–7.
Article6). Rodino MA, Shane E. Osteoporosis after organ transplantation. Am J Med. 1998; 104:459–69.
Article7). Sambrook P. Corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis. Aust Fam Physician. 1994; 23:1965–6.
Article8). Sambrook PN, Kelly PJ, Keogh AM, Macdonald P, Spratt P, Freund J, et al. Bone loss after heart transplantation: a prospective study. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1994; 13:116–20.9). Millonig G, Graziadei IW, Eichler D, Pfeiffer KP, Fink-enstedt G, Muehllechner P, et al. Alendronate in combination with calcium and vitamin D prevents bone loss after orthotopic liver transplantation: a prospective singlecenter study. Liver Transpl. 2005; 11:960–6.
Article10). Shane E, Rodino MA, McMahon DJ, Addesso V, Staron RB, Seibel MJ, et al. Prevention of bone loss after heart transplantation with antiresorptive therapy: a pilot study. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1998; 17:1089–96.11). Wissing KM, Broeders N, Moreno-Reyes R, Gervy C, Stallenberg B, Abramowicz D. A controlled study of vitamin D3 to prevent bone loss in renal-transplant patients receiving low doses of steroids. Transplantation. 2005; 79:108–15.
Article12). Weinstein RS. Clinical practice. Glucocorticoid-induced bone disease. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365:62–70.13). Favus MJ. Bisphosphonates for osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:2027–35.
Article14). Crawford BA, Kam C, Pavlovic J, Byth K, Handelsman DJ, Angus PW, et al. Zoledronic acid prevents bone loss after liver transplantation: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2006; 144:239–48.15). Bodingbauer M, Wekerle T, Pakrah B, Roschger P, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Silberhumer G, et al. Prophylactic bisphosphonate treatment prevents bone fractures after liver transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2007; 7:1763–9.
Article16). Atamaz F, Hepguler S, Karasu Z, Kilic M, Tokat Y. The prevention of bone fractures after liver transplantation: experience with alendronate treatment. Transplant Proc. 2006; 38:1448–52.
Article17). Kaemmerer D, Lehmann G, Wolf G, Settmacher U, Hommann M. Treatment of osteoporosis after liver transplantation with ibandronate. Transpl Int. 2010; 23:753–9.
Article18). Watts NB, Geusens P, Barton IP, Felsenberg D. Relationship between changes in BMD and nonvertebral fracture incidence associated with risedronate: reduction in risk of nonvertebral fracture is not related to change in BMD. J Bone Miner Res. 2005; 20:2097–104.
Article19). Hardinger KL, Ho B, Schnitzler MA, Desai N, Lowell J, Shenoy S, et al. Serial measurements of bone density at the lumbar spine do not predict fracture risk after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2003; 9:857–62.
Article20). Guichelaar MM, Kendall R, Malinchoc M, Hay JE. Bone mineral density before and after OLT: longterm follow-up and predictive factors. Liver Transpl. 2006; 12:1390–402.
Article21). Raisz LG. Clinical practice. Screening for osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:164–71.22). Cockerill W, Lunt M, Silman AJ, Cooper C, Lips P, Bhalla AK, et al. Health-related quality of life and radiographic vertebral fracture. Osteoporos Int. 2004; 15:113–9.
Article23). Melton LJ 3rd, Thamer M, Ray NF, Chan JK, Chesnut CH 3rd, Einhorn TA, et al. Fractures attributable to osteoporosis: report from the National Osteoporosis Foundation. J Bone Miner Res. 1997; 12:16–23.
Article24). Ninkovic M, Skingle SJ, Bearcroft PW, Bishop N, Alexander GJ, Compston JE. Incidence of vertebral fractures in the first three months after orthotopic liver transplantation. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000; 12:931–5.
Article25). Kang MI, Ko JM, et al. Physician's guide for diagnosis and treatment of osteoporosis. Seoul, Korea: The Korean Society of Bone Metabolism;2008.26). Monegal A, Guanabens N, Suarez MJ, Suarez F, Clemente G, Garcia-Gonzalez M, et al. Pamidronate in the pre-vention of bone loss after liver transplantation: a randomized controlled trial. Transpl Int. 2009; 22:198–206.
Article27). Ninkovic M, Love S, Tom BD, Bearcroft PW, Alexander GJ, Compston JE. Lack of effect of intravenous pamidronate on fracture incidence and bone mineral density after orthotopic liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 2002; 37:93–100.
Article28). Ninkovic M, Love SA, Tom B, Alexander GJ, Compston JE. High prevalence of osteoporosis in patients with chronic liver disease prior to liver transplantation. Calcif Tissue Int. 2001; 69:321–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Super-fast-track discharge of liver transplant recipients
- Delayed recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation: case series
- Expanding Indications for Liver Transplant: Tumor and Patient Factors
- Change of Bone Mineral Density after Kidney Transplantation and Factors Influencing Post-transplant Bone Mineral Density Loss
- Pediatric Liver Transplantation