J Bacteriol Virol.
2011 Sep;41(3):205-207. 10.4167/jbv.2011.41.3.205.
Regulation of Innate Immunity via MHC Class II-mediated Signaling; Non-classical Role of MHC Class II in Innate Immunity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biotechnology, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, 43-1 Yeokgok 2-dong, Wonmi-gu, Bucheon, Gyeonggi-do, Korea. jhnam@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1449896
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2011.41.3.205
Abstract
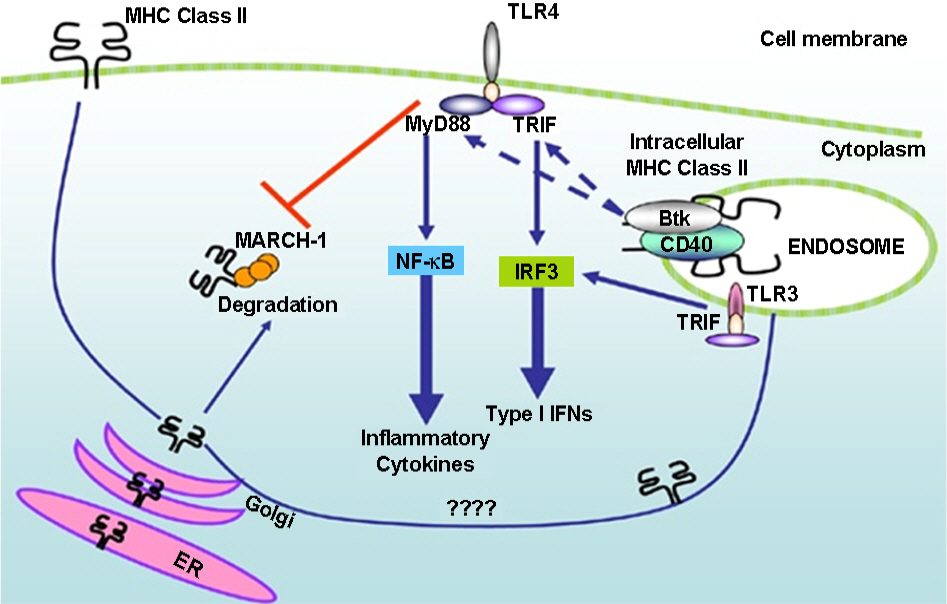
- MHC class II has long been known to play a classical role in antigen presentation and to act as a signal transducer capable of inducing the adaptive immunity needed to produce pathogen specific antibodies. However, it has recently been revealed that MHC class II can also promote the activation of Toll-like receptor mediated signaling by functioning as an adapter. This means that in addition to its classical function of adaptive immunity, MHC class II also plays an intriguing role in the mechanisms that regulate innate immunity. That being the case, queries inevitably arise regarding the fact that many pathogens have tried to control the induction of MHC class II so as to escape the host immune response. Liu et al (Nat Immunol 2011;12:416-424) demonstrated that intracellular MHC class II interacted with Btk, and that this activated Btk promoted TLR signaling via Myd88 and TRIF. The results of this study provide insight regarding the possibility of a novel role for MHC class II, which was heretofore regarded solely as a classical molecule involved in adaptive immune responses, as a regulator of innate immune responses.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Liu X., Zhan Z., Li D., Li X., Ma F., Zhang P, et al. Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining activation of the kinase Btk. Nat Immunol. 2011. 12:416–24.
Article2). Kissner TL., Ruthel G., Alam S., Ulrich RG., Fernandez S., Saikh KU. Activation of MyD88 signaling upon Staphylococcal enterotoxin binding to MHC class II molecules. PLoS One. 2011. ;6. e15985.
Article3). Frei R., Steinle J., Birchler T., Loeliger S., Roduit C., Steinhoff D, et al. MHC class II molecules enhances Toll-like receptor mediated innate immune responses. PLoS One. 2011. ;5. e8808.4). Hegde NR., Chevalier MS., Johnson DC. Viral inhibition of MHC class II antigen presentation. Trends Immunol. 2003. 24:278–85.
Article5). Piani A., Hossle JP., Birchler T., Siegrist CA., Heumann D., Davies G, et al. Expression of MHC class II molecules contributes to lipopolysaccharide responsiveness. Eur J Immunol. 2000. 30:3140–6.6). Sanchez PJ., McWilliams JA., Haluszczak C., Yagita H., Kedl RM. Combined TLR/CD40 stimulation mediates potent cellular immunity by regulating dendritic cell expression of CD70 In vivo. J Immunol. 2007. 178:1564–72.7). Ni Gabhann J., Jefferies CA. TLR-induced activation of Btk – Role for endosomal MHC class II molecules revealed. Cell Res. 2011. 21:998–1001.
Article8). McGettrick AF., O'Neill LA. Localisation and trafficking of Toll-like receptors: an important mode of regulation. Curr Opin Immunol. 2010. 22:20–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Transcription of class II MHC gene by interferon-gamma in FRTL-5 cells
- Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Enhances Dendritic Cell Infiltration and TLR2 Expression in Rat Kidneys
- Monophosphoryl lipid A (MPL) upregulates major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I expression by increasing interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma)
- Age-Related Changes of MHC Class II-immunoreactive Dendritic Cells in Rat Brain
- Class II transactivator restricts viral replication, extending its effect to HBV: Editorial on “Novel role of MHC class II transactivator in hepatitis B virus replication and viral counteraction”