J Korean Rheum Assoc.
2008 Sep;15(3):197-203. 10.4078/jkra.2008.15.3.197.
Glucosamine Sulfate and Chondroitin Sulfate for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea. lyhcgh@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 1270197
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jkra.2008.15.3.197
Abstract
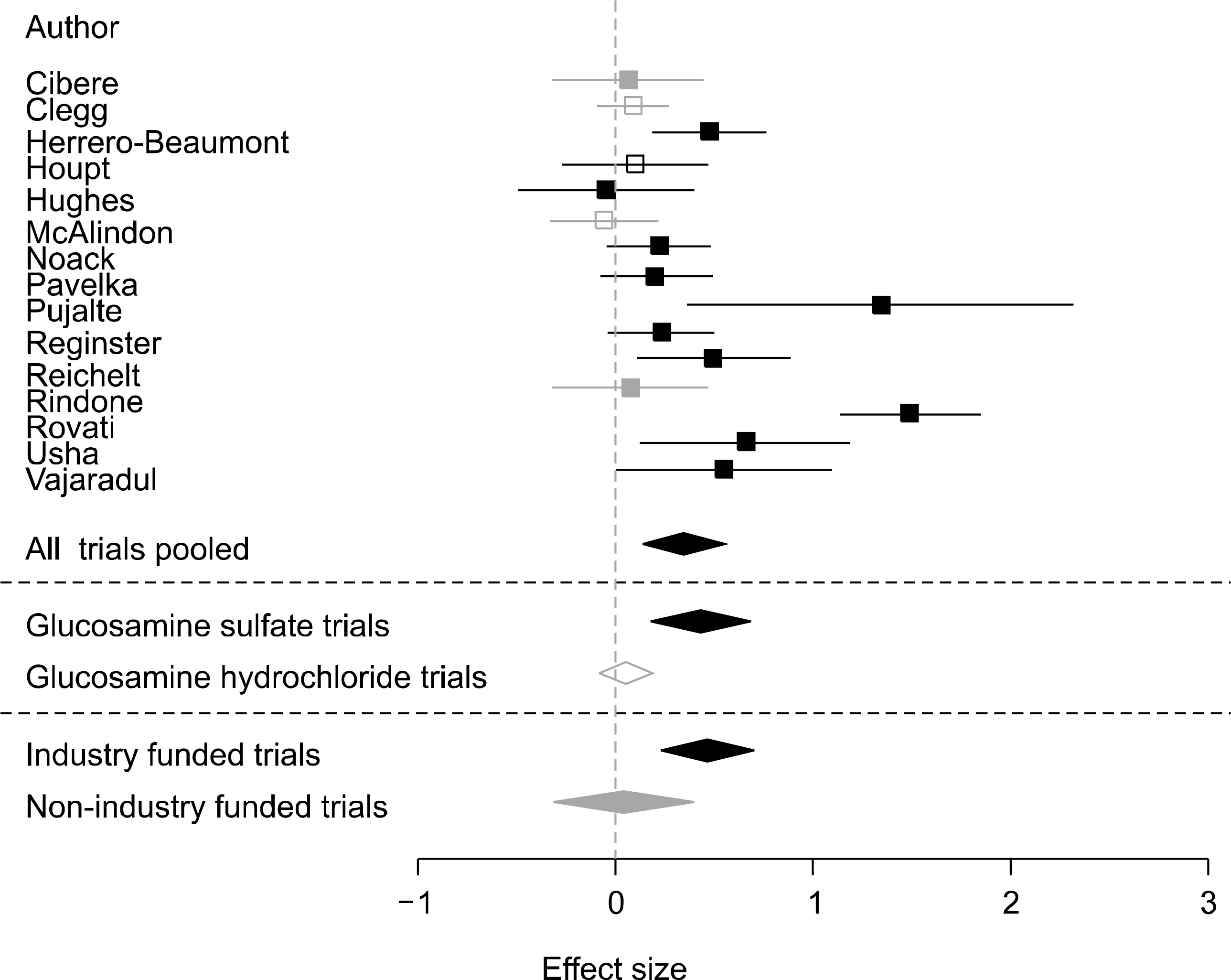
- Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis often associated with morbidity, disability, functional impairment and impaired quality of life. A new perspective in OA management is to delay disease progression by modifying joint structure. Glucosamine sulfate (GS) and chondroitin sulfate (CS) have attracted a lot of interest as a specific drug for OA. Glucosamine is a constituent of glcosaminoglycans in cartilage matrix and synovial fluid and is involved in cartilage formation. Chondroitin sulfate (CS) belongs to the glycosaminoglycan group and is a major component of the articular cartilage. The meta-analyses have shown that GS (but not glucosamine hydrochloride) and CS have small-to-moderate symptomatic efficacy in OA. With respect to the structure-modifying effect, there is some evidence that GS and CS may interfere with structural progression of OA.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Jinks C, Jordan K, Croft P. Osteoarthritis as a public health problem: the impact of developing knee pain on physical function in adults living in the community: (KNEST 3). Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007; 46:877–81.
Article2. Vlad SC, LaValley MP, McAlindon TE, Felson DT. Glucosamine for pain in osteoarthritis: why do trial results differ? Arthritis Rheum. 2007; 56:2267–77.
Article3. Bruyere O, Reginster JY. Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate as therapeutic agents for knee and hip osteoarthritis. Drugs Aging. 2007; 24:573–80.
Article4. Setnikar I, Cereda R, Pacini MA, Revel L. Antireactive properties of glucosamine sulfate. Arzneimittelforschung. 1991; 41:157–61.5. Largo R, Alvarez-Soria MA, Diez-Ortego I, Calvo E, Sanchez-Pernaute O, Egido J, et al. Glucosamine inhibits IL-1beta-induced NFkappaB activation in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2003; 11:290–8.6. Altman RD, Abramson S, Bruyere O, Clegg D, Herrero-Beaumont G, Maheu E, et al. Commentary: osteoarthritis of the knee and glucosamine. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14:963–6.
Article7. Bali JP, Cousse H, Neuzil E. Biochemical basis of the pharmacologic action of chondroitin sulfates on the osteoarticular system. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2001; 31:58–68.
Article8. Reginster JY. The efficacy of glucosamine sulfate in osteoarthritis: financial and nonfinancial conflict of interest. Arthritis Rheum. 2007; 56:2105–10.
Article9. Drenth JP, Verheugt FW. Do COX-2 inhibitors give enough gastrointestinal protection? Lancet. 2007; 369:439–40.
Article10. Towheed TE, Maxwell L, Anastassiades TP, Shea B, Houpt J, Robinson V, et al. Glucosamine therapy for treating osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. CD002946.11. Clegg DO, Reda DJ, Harris CL, Klein MA, O'Dell JR, Hooper MM, et al. Glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, and the two in combination for painful knee osteoarthritis. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:795–808.12. Herrero-Beaumont G, Ivorra JA, Del Carmen TM, Blanco FJ, Benito P, Martin-Mola E, et al. Glucosamine sulfate in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis symptoms: a randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled study using acetaminophen as a side comparator. Arthritis Rheum. 2007; 56:555–67.
Article13. Reginster JY, Deroisy R, Rovati LC, Lee RL, Lejeune E, Bruyere O, et al. Long-term effects of glucosamine sulphate on osteoarthritis progression: a randomised, placebocontrolled clinical trial. Lancet. 2001; 357:251–6.
Article14. Pavelka K, Gatterova J, Olejarova M, Machacek S, Giacovelli G, Rovati LC, et al. Glucosamine sulfate use and delay of progression of knee osteoarthritis: a 3-year, randomized, placebocontrolled, double-blind study. Arch Intern Med. 2002; 162:2113–23.15. Towheed TE, Anastassiades TP. Glucosamine therapy for osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 1999; 26:2294–7.16. Tapadinhas MJ, Rivera IC, Bignamini AA. Oral glucosamine sulphate in the management of arthrosis: report on a multi-centre open investigation in Portugal. Pharmatherapeutica. 1982; 3:157–68.17. Rovati LC, Annefeld M, Giacovelli G, Schmid K, Setnikar I. Glucosamine in osteoarthritis. Lancet. 1999; 354:1640–2.
Article18. Reichenbach S, Sterchi R, Scherer M, Trelle S, Burgi E, Burgi U, et al. Meta-analysis: chondroitin for osteoarthritis of the knee or hip. Ann Intern Med. 2007; 146:580–90.
Article19. Clegg DO, Reda DJ, Harris CL, Klein MA, O'Dell JR, Hooper MM, et al. Glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, and the two in combination for painful knee osteoarthritis. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:795–8.20. Kahan A. STOPP (Study on Osteoarthritis Progression Prevention): a new two-year trial with condroitin 4 & 6 sulfate (CS). Accessed at. www.ibsa-ch.com/eular_2006_amsterdam_vignon-2.pdf. on 18 september. 2006.21. Michel BA, Stucki G, Frey D, De Vathaire F, Bignon E, Buehlmann P, et al. Chondroitins 4 and 6 sulfate in osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:779–86.
Article22. Uebelhart D, Thonar EJ, Delmas PD, Chantraine A, Vignon E. Effects of oral chondroitin sulfate on the progression of knee osteoarthritis: a pilot study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1998; 6(Suppl A):39–46S.
Article23. Uebelhart D, Malaise M, Marcolongo R, de Vathaire F, Piperno M, Mailleux E, et al. Intermittent treatment of knee osteoarthritis with oral chondroitin sulfate: a one-year, randomized, double-blind, multicenter study versus placebo. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004; 12:269–76.24. Hathcock JN, Shao A. Risk assessment for glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2007; 47:78–83.
Article25. Zhang W, Moskowitz RW, Nuki G, Abramson S, Altman RD, Arden N, et al. OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis, Part II: OARSI evidencebased, expert consensus guidelines. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008; 16:137–62.
Article26. Jordan KM, Arden NK, Doherty M, Bannwarth B, Bijlsma JW, Dieppe P, et al. EULAR Recommendations 2003: an evidence based approach to the management of knee osteoarthritis: Report of a Task Force of the Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutic Trials (ESCISIT). Ann Rheum Dis. 2003; 62:1145–55.
Article27. Russell AS, Aghazadeh-Habashi A, Jamali F. Active ingredient consistency of commercially available glucosamine sulfate products. J Rheumatol. 2002; 29:2407–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pharmacological Therapy in Osteoarthritis
- Chondroitin sulfate in Corneal Preaervation Media Assessed by monitoring the Transendothelial Electrical Potential Difference
- Measurement of Transendothelial Potential Difference to Evaluate the Chondroitin Sulfate Effect in TC-l99 Cornea Preservation Media
- Effects of Glycosaminoglycan on the Growth of Human Gingival Fibroblast
- The Evaluation of Neurotoxicity after Intrathecal Restorative Fluid Injection in the Rat