Yonsei Med J.
2007 Oct;48(5):765-772. 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.5.765.
Expression and Regulation of Osteoprotegerin in Adipose Tissue
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. lsk@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Institute of Endocrine Research, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1122612
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2007.48.5.765
Abstract
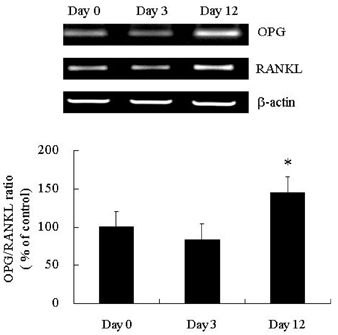
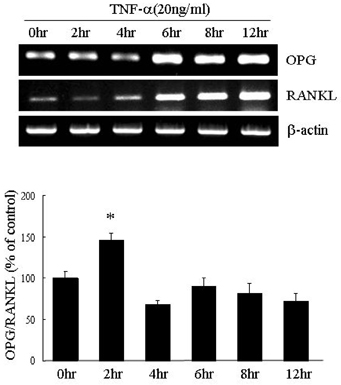
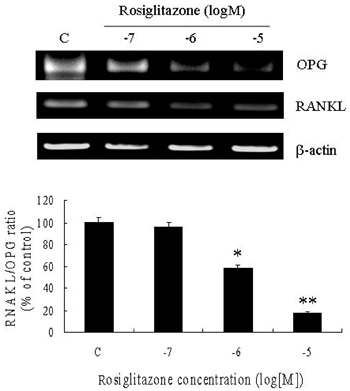
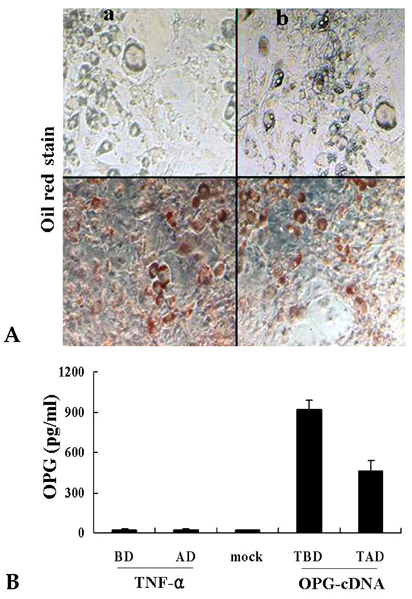
- PURPOSE: Osteoprotegerin (OPG), a potent inhibitor of osteoclastic bone resorption, has a variety of biological functions that include anti-inflammatory effects. Adipocytes and osteoblasts share a common origin, and the formation of new blood vessels often precedes adipogenesis in developing adipose tissue microvasculature. We examined whether OPG is secreted from adipocytes, therefore contributing to the prevention of neovascularization and protecting the vessels from intimal inflammation and medial calcification. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The mRNA expression of OPG and receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) was measured in differentiated 3T3L1 adipocytes and adipose tissues. RESULTS: OPG mRNA expression increased with the differentiation of 3T3L1 adipocytes, while RANKL expression was not significantly altered. OPG mRNA was expressed at higher levels in white adipose tissue than in brown adipose tissue and was most abundant in the epididymal portion. In differentiated 3T3L1 adipocytes, Rosiglitazone and insulin reduced the OPG/RANKL expression ratio in a dose- and time- dependent manner. In contrast, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) increased the expression of both OPG and RANKL in a time-dependent manner. The OPG/RANKL ratio was at a maximum two hours after TNF-alpha treatment and then returned to control levels. Furthermore, OPG was abundantly secreted into the media after transfection of OPG cDNA with Phi C31 integrase into 3T3L1 cells. CONCLUSION: Our results indicate that OPG mRNA is expressed and regulated in the adipose tissue. Considering the role of OPG in obesity-associated inflammatory changes in adipose tissue and vessels, we speculate that OPG may have both a protective function against inflammation and anti-angiogenic effects on adipose tissue.
MeSH Terms
-
3T3-L1 Cells
Adipocytes/cytology/drug effects/metabolism
Adipogenesis/genetics
Adipose Tissue/cytology/*metabolism
Animals
Cell Differentiation
*Gene Expression Regulation/drug effects
Hypoglycemic Agents/pharmacology
Insulin/pharmacology
Male
Mice
Osteoprotegerin/genetics/*metabolism
RANK Ligand/metabolism
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Thiazolidinediones/pharmacology
Transfection
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha/pharmacology
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ, Dunstan CR, Burgess T, et al. Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell. 1998. 93:165–176.
Article2. Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley M, Chang MS, Lüthy R, et al. Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell. 1997. 89:309–319.
Article3. Bucay N, Sarosi I, Dunstan CR, Morony S, Tarpley J, Capparelli C, et al. Osteoprotegerin-deficient mice develop early onset osteoporosis and arterial calcification. Genes Dev. 1998. 12:1260–1268.
Article4. Emery JG, McDonnell P, Burke MB, Deen KC, Lyn S, Silverman C, et al. Osteoprotegerin is a receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. J Biol Chem. 1998. 273:14363–14367.
Article5. Malyankar UM, Scatena M, Suchland KL, Yun TJ, Clark EA, Giachelli CM. Osteoprotegerin is an alpha vbeta 3-induced, NF-kappa B-dependent survival factor for endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:20959–20962.
Article6. Collin-Osdoby P, Rothe L, Anderson F, Nelson M, Maloney W, Osdoby P. Receptor activator of NF-kappa B and osteoprotegerin expression by human microvascular endothelial cells, regulation by inflammatory cytokines, and role in human osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:20659–20672.
Article7. Sattler AM, Schoppet M, Schaefer JR, Hofbauer LC. Novel aspects on RANK ligand and osteoprotegerin in osteoporosis and vascular disease. Calcif Tissue Int. 2003. 74:103–106.
Article8. Min JK, Kim YM, Kim YM, Kim EC, Gho YS, Kang IJ, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulates expression of receptor activator of NF-kappa B (RANK) in endothelial cells. Concomitant increase of angiogenic responses to RANK ligand. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:39548–39557.
Article9. Price PA, June HH, Buckley JR, Williamson MK. Osteoprotegerin inhibits artery calcification induced by warfarin and by vitamin D. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001. 21:1610–1616.
Article10. Browner WS, Lui LY, Cummings SR. Associations of serum osteoprotegerin levels with diabetes, stroke, bone density, fractures, and mortality in elderly women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86:631–637.
Article11. Schoppet M, Sattler AM, Schaefer JR, Herzum M, Maisch B, Hofbauer LC. Increased osteoprotegerin serum levels in men with coronary artery disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003. 88:1024–1028.
Article12. Jono S, Ikari Y, Shioi A, Mori K, Miki T, Hara K, et al. Serum osteoprotegerin levels are associated with the presence and severity of coronary artery disease. Circulation. 2002. 106:1192–1194.
Article13. Schoppet M, Schaefer JR, Hofbauer LC. Low serum levels of soluble RANK ligand are associated with the presence of coronary artery disease in men. Circulation. 2003. 107:e76.
Article14. Rasmussen LM, Ledet T. Osteoprotegerin and diabetic macroangiopathy. Horm Metab Res. 2005. 37:Suppl 1. 90–94.
Article15. Imhof BA, Aurrand-Lions M. Angiogenesis and inflammation face off. Nat Med. 2006. 12:171–172.
Article16. Nakashima T, Kobayashi Y, Yamasaki S, Kawakami A, Eguchi K, Sasaki H, et al. Protein expression and functional difference of membrane-bound and soluble receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand: modulation of the expression by osteotropic factors and cytokines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. 275:768–775.
Article17. Collin-Osdoby P, Rothe L, Anderson F, Nelson M, Maloney W, Osdoby P. Receptor activator of NF-kappa B and osteoprotegerin expression by human microvascular endothelial cells, regulation by inflammatory cytokines, and role in human osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:20659–20672.
Article18. Rupnick MA, Panigrahy D, Zhang CY, Dallabrida SM, Lowell BB, Langer R, et al. Adipose tissue mass can be regulated through the vasculature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. 99:10730–10735.
Article19. Hausman GJ, Richardson RL. Adipose tissue angiogenesis. J Anim Sci. 2004. 82:925–934.20. Groth AC, Olivares EC, Thyagarajan B, Calos MP. A phage integrase directs efficient site-specific integration in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. 97:5995–6000.
Article21. Hofbauer LC, Schoppet M. Clinical implications of the osteoprotegerin/RANKL/RANK system for bone and vascular diseases. JAMA. 2004. 292:490–495.
Article22. Trayhurn P, Wood IS. Adipokines: inflammation and the pleiotropic role of white adipose tissue. Br J Nutr. 2004. 92:347–355.
Article23. Collin-Osdoby P. Regulation of vascular calcification by osteoclast regulatory factors RANKL and osteoprotegerin. Circ Res. 2004. 95:1046–1057.
Article24. Pantouli E, Boehm MM, Koka S. Inflammatory cytokines activate p38 MAPK to induce osteoprotegerin synthesis by MG-63 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. 329:224–229.
Article25. Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ, et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2003. 112:1821–1830.
Article26. Olesen P, Ledet T, Rasmussen LM. Arterial osteoprotegerin: increased amounts in diabetes and modifiable synthesis from vascular smooth muscle cells by insulin and TNF-alpha. Diabetologia. 2005. 48:561–568.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Vitamin D regulation of adipogenesis and adipose tissue functions
- The Role of Adipose Tissue Vasculature in Energy Balance
- Human Adipose Tissue Metabolism in Obesity
- The Role of Vitamin D in Adipose Tissue Biology: Adipocyte Differentiation, Energy Metabolism, and Inflammation
- Differential Expression of RANKL and OPG by the PPAR gamma Agonist Rosiglitazone in Osteoblasts