J Vet Sci.
2010 Jun;11(2):169-171. 10.4142/jvs.2010.11.2.169.
Development and characterization of stable cell lines constitutively expressing the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nucleocapsid protein
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, College of Natural Sciences, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 702-701, Korea. changhee@knu.ac.kr
- 2Animal Disease Diagnostic Center, National Veterinary Research and Quarantine Services, Anyang 430-757, Korea.
- 3Livestock Policy Division, Jeju Special Self-Governing Province, Jeju 690-700, Korea.
- KMID: 1110866
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2010.11.2.169
Abstract
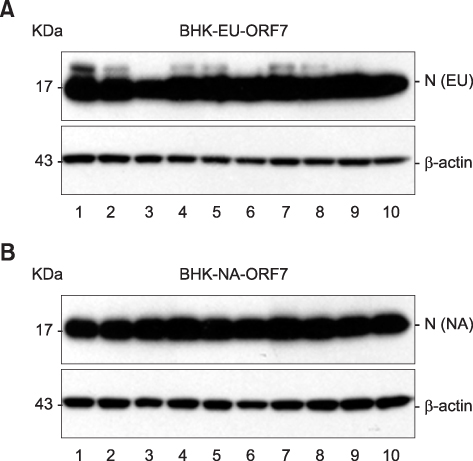
- Despite global efforts to control porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) infection, the virus continues to cause economic problems in the swine industry worldwide. In this study, we attempted to generate and characterize a panel of stable BHK cell lines that constitutively express the nucleocapsid (N) protein of type 1 or type 2 PRRSV. The established BHK cell lines were found to react well with N-specific antibodies as well as the hyperimmune serum of pigs raised against each genotype of PRRSV. Taken together, the data implicate a potential usefulness for the newly generated stable cell lines as a diagnostic reagent for PRRSV serology.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Antibodies, Viral/analysis/immunology
Blotting, Western/veterinary
Cell Line
Cricetinae
Female
Genotype
Nucleocapsid Proteins/genetics/*immunology
Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome/diagnosis/*immunology
Porcine respiratory and reproductive syndrome virus/genetics/*immunology
Swine
Transfection/veterinary
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kang SY, Yun SI, Park HS, Park CK, Choi HS, Lee YM. Molecular characterization of PL97-1, the first Korean isolate of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Virus Res. 2004. 104:165–179.
Article2. Lee YJ, Park CK, Nam E, Kim SH, Lee OS, Lee DS, Lee C. Generation of a porcine alveolar macrophage cell line for the growth of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J Virol Methods. 2010. 163:410–415.
Article3. Mounir S, Mardassi H, Dea S. Identification and characterization of the porcine reproductive and respiratory virus ORFs 7, 5 and 4 products. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1995. 380:317–320.
Article4. Nam E, Park CK, Kim SH, Joo YS, Yeo SG, Lee C. Complete genomic characterization of a European type 1 porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus isolate in Korea. Arch Virol. 2009. 154:629–638.
Article5. Nelsen CJ, Murtaugh MP, Faaberg KS. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus comparison: divergent evolution on two continents. J Virol. 1999. 73:270–280.
Article6. Nelson EA, Christopher-Hennings J, Drew T, Wensvoort G, Collins JE, Benfield DA. Differentiation of U.S. and European isolates of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus by monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1993. 31:3184–3189.
Article7. Neumann EJ, Kliebenstein JB, Johnson CD, Mabry JW, Bush EJ, Seitzinger AH, Green AL, Zimmerman JJ. Assessment of the economic impact of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome on swine production in the United States. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2005. 227:385–392.
Article8. Ropp SL, Wees CE, Fang Y, Nelson EA, Rossow KD, Bien M, Arndt B, Preszler S, Steen P, Christopher-Hennings J, Collins JE, Benfield DA, Faaberg KS. Characterization of emerging European-like porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus isolates in the United States. J Virol. 2004. 78:3684–3703.
Article9. Snijder EJ, Meulenberg JJ. The molecular biology of arteriviruses. J Gen Virol. 1998. 79:961–979.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intracellular Localization of the Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Nucleocapsid Protein
- Expression, Purification and Antiserum Production of the Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Nsp1a Protein
- Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus vaccine does not fit in classical vaccinology
- Effects of Mumps Virus Nucleocapsid Protein on the Viral Replication and Apoptosis in VeroE6 Cells
- The signal sequence of type II porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus glycoprotein 3 is sufficient for endoplasmic reticulum retention