J Vet Sci.
2008 Jun;9(2):203-205. 10.4142/jvs.2008.9.2.203.
Aquaporin 1 expression in tissues of canines possessing inherited high K+ erythrocytes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Institute of Biosciences, Azabu University, Kanagawa 229-8501, Japan. ochiaih@azabu-u.ac.jp
- 2Laboratory of Pathobiochemistry, School of Veterinary Medicine, Azabu University, Kanagawa 229-8501, Japan.
- 3Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry, College of Environmental Health, Azabu University, Kanagawa 229-8501, Japan.
- 4Veterinary Teaching Hospital, Azabu University, Kanagawa 229-8501, Japan.
- KMID: 1106237
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2008.9.2.203
Abstract
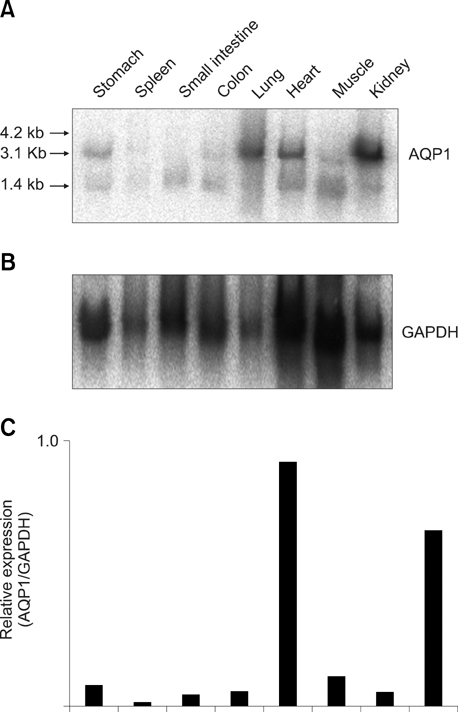
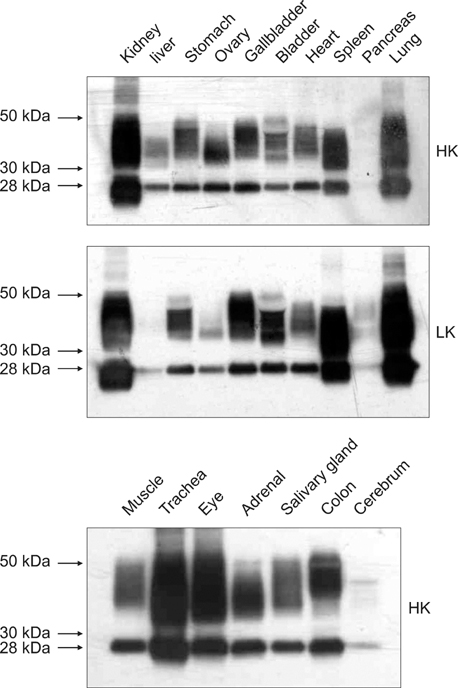
- We investigated the expression of aquaporin 1 (AQP1) in tissues from canines with an inherited anomaly that causes their erythrocytes to have high K+. Northern blot analysis revealed abundant AQP1 expression in lung and kidney, though little expression was found in spleen. Using anti-C-terminus for dog AQP1, abundant expression was shown in kidney, trachea, and eye, but little expression was shown in pancreas and cerebrum, indicating that AQP1 expression in canine tissues is similar to that noted in other mammals.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Burg MB, Kwon ED, Kültz D. Regulation of gene expression by hypertonicity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1997. 59:437–455.
Article2. Denker BM, Smith BL, Kuhajda FP, Agre P. Identification, purification, and partial characterization of a novel Mr 28,000 integral membrane protein from erythrocytes and renal tubules. J Biol Chem. 1988. 263:15634–15642.
Article3. Fujise H, Higa K, Kanemaru T, Fukuda M, Adragna NC, Lauf P. GSH depletion, K-Cl cotransport, and regulatory volume decrease in high-K/high-GSH dog red blood cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001. 281:C2003–C2009.4. Fujise H, Higa K, Nakayama T, Wada K, Ochiai H, Tanabe Y. Incidence of dogs possessing red blood cells with high K in Japan and East Asia. J Vet Med Sci. 1997. 59:495–497.
Article5. Higa K, Ochiai H, Fujise H. Molecular cloning and expression of aquaporin 1 (AQP1) in dog kidney and erythroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. 1463:374–382.
Article6. Inaba M, Maede Y. Increase of Na+ gradient-dependent L-glutamate and L-aspartate transport in high K+ dog erythrocytes associated with high activity of (Na+, K+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984. 259:312–317.
Article7. Inaba M, Maede Y. Inherited persistence of immature type pyruvate kinase and hexokinase isozymes in dog erythrocytes. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1989. 92:151–156.
Article8. Jenq W, Cooper DR, Bittle P, Ramirez G. Aquaporin-1 expression in proximal tubule epithelial cells of human kidney is regulated by hyperosmolarity and contrast agents. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. 256:240–248.
Article9. Maede Y, Inaba M. Energy metabolism in canine erythrocytes associated with inherited high Na+- and K+-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase activity. Am J Vet Res. 1987. 48:114–118.10. Maede Y, Inaba M, Taniguchi N. Increase of Na-K-ATPase activity, glutamate, and aspartate uptake in dog erythrocytes associated with hereditary high accumulation of GSH, glutamate, glutamine, and aspartate. Blood. 1983. 61:493–499.
Article11. Maede Y, Kasai N, Taniguchi N. Hereditary high concentration of glutathione in canine erythrocytes associated with high accumulation of glutamate, glutamine, and aspartate. Blood. 1982. 59:883–889.
Article12. Moon C, King LS, Agre P. Aqp1 expression in erythroleukemia cells: genetic regulation of glucocorticoid and chemical induction. Am J Physiol. 1997. 273:C1562–C1570.13. Moon C, Preston GM, Griffin CA, Jabs EW, Agre P. The human aquaporin-CHIP gene. Structure, organization, and chromosomal localization. J Biol Chem. 1993. 268:15772–15778.
Article14. Nielsen S, Smith BL, Christensen EI, Agre P. Distribution of the aquaporin CHIP in secretory and resorptive epithelia and capillary endothelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993. 90:7275–7279.
Article15. Preston GM, Carroll TP, Guggino WB, Agre P. Appearance of water channels in Xenopus oocytes expressing red cell CHIP28 protein. Science. 1992. 256:385–387.
Article16. Umenishi F, Verkman AS. Isolation of the human aquaporin-1 promoter and functional characterization in human erythroleukemia cell lines. Genomics. 1998. 47:341–349.
Article17. Yamamoto T, Sasaki S. Aquaporins in the kidney: Emerging new aspects. Kidney Int. 1998. 54:1041–1054.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of Aquaporin-4 in Placenta of Preeclampsia
- Loss of Caveolin 1 is Associated With the Expression of Aquaporin 1 and Bladder Dysfunction in Mice
- Loss of aquaporin-1 expression is associated with worse clinical outcomes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study
- Expression of Aquaporin-8 in Placenta of Preeclampsia
- Altered Renal Expression of Aquaporin-2 Water Channels in Two-Kidney, One Clip Hypertension in Rats