J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Apr;20(2):291-296. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.2.291.
Neuroprotective Effect of Ginseng Total Saponins in Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea. ybkim1218@cau.ac.kr
- KMID: 1095206
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.2.291
Abstract
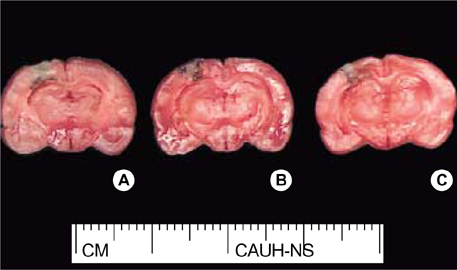
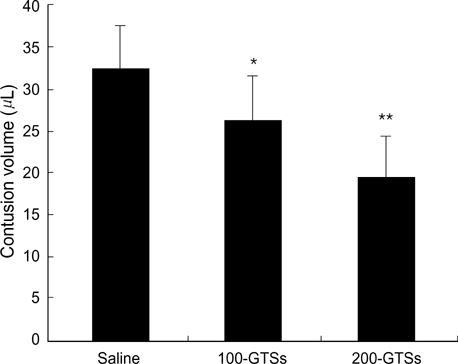
- In the present study, we investigated whether ginseng total saponins (GTSs) protect hippocampal neurons after experimental traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rats. A moderate-grade TBI was made with the aid of a controlled cortical impact (CCI) device set at a velocity of 3.0 m/sec, a deformation of 3.0 mm, and a compression time of 0.2 sec at the right parietal area for adult male Sprague-Dawley rats. Shamoperated rats that underwent craniectomy without impact served as controls. GTSs (100 and 200 mg/kg) or saline was injected intraperitoneally into the rats immediately post-injury. Twenty-four hours after the injury, the rats underwent neurological evaluation. Contusion volume and the number of hippocampal neurons were calculated with apoptosis evaluated by TUNEL staining. 24 hr post-injury, salineinjected rats showed a significant loss of neuronal cells in the CA2 region of the right hippocampus (53.4%, p<0.05) and CA3 (34.6%, p<0.05) compared with contralateral hippocampal region, a significant increase in contusion volume (34 +/-8microliter), and significant increase in neurologic deficits compared with the GTSs groups. Treating rats with GTSs seemed to protect the CCI-induced neuronal loss in the hippocampus, decrease cortical contusion volume, and improve neurological deficits.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Attele AS, Wu JA, Yuan CS. Ginseng pharmacology: multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999. 58:1685–1693.2. Kim S, Ahn K, Oh TH, Nah SY, Rhim H. Inhibitory effect of ginsenosides on NMDA receptor-mediated signals in rat hippocampal neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002. 296:247–254.
Article3. Lee JH, Kim SR, Bae CS, Kim DH, Hong HN, Nah SY. Protective effect of ginsenosides, active ingredients of Panax ginseng, on kainic acid-induced neurotoxicity in rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 2002. 325:129–133.
Article4. Kim HE, Oh JH, Lee SK, Oh YJ. Ginsenoside RH-2 induces apoptotic cell death in rat C6 glioma via a reactive oxygen- and caspase-dependent but Bcl-X(L)-independent pathway. Life Sci. 1999. 65:PL33–PL40.
Article5. Shibata S. Chemistry and cancer preventing activities of ginseng saponins and some related triterpenoid compounds. J Korean Med Sci. 2001. 16:Suppl. S28–S37.
Article6. Faden AI. Neuroprotection and traumatic brain injury: the search continues. Arch Neurol. 2001. 58:1553–1555.7. Choi SM, Suk JS, Kwon JT, Min BK, Kim YB, Hwang SN, Choi DY, Kim JH, Lee SM, Earmme YY. Development of upgraded cortical impact model (Part I: Mechanics). J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2002. 32:29–34.8. Choi SM, Suk JS, Min BK, Hwang SN, Kim YB, Kim JH. Development of upgraded cortical impact model (Part II: Functional outcome). J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2002. 32:458–462.9. Wang LJ, Lu YY, Muramatsu S, Ikeguchi K, Fujimoto KI, Okada T, Mizukami H, Matsushita T, Hanazono Y, Kume A, Nagatsu T, Ozawa K, Nakano I. Neuroprotective effects of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor mediated by an adeno-associated virus vector in a transgenic animal model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci. 2002. 22:6920–6928.
Article10. Wennersten A, Holmin S, Mathiesen T. Characterization of Bax and Bcl-2 in apoptosis after experimental traumatic brain injury in the rat. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 2003. 105:281–288.
Article11. Stelmasiak Z, Dudkowska-Konopa A, Rejdak K. Head trauma and neuroprotection. Med Sci Monit. 2000. 6:426–432.12. Faden AI. Neuroprotection and traumatic brain injury: theoretical option or realistic proposition. Curr Opin Neurol. 2002. 15:707–712.
Article13. Lighthall JW. Controlled cortical impact: a new experimental brain injury model. J Neurotrauma. 1988. 5:1–15.
Article14. Lighthall JW, Dixon CE, Anderson TE. Experimental models of brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 1989. 6:83–97.
Article15. Goodman JC, Cherian L, Bryan RM Jr, Robertson CS. Lateral cortical impact injury in rats: pathologic effects of varying cortical compression and impact velocity. J Neurotrauma. 1994. 11:587–597.
Article16. Baskaya MK, Dogan A, Temiz C, Dempsey RJ. Application of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining to evaluate injury volume after controlled cortical impact brain injury: role of brain edema in evolution of injury volume. J Neurotrauma. 2000. 17:93–99.17. Hamm RJ, Pike BR, O'Dell DM, Lyeth BG, Jenkins LW. The rotarod test: an evaluation of its effectiveness in assessing motor deficits following traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 1994. 11:187–196.
Article18. Liao B, Newmark H, Zhou R. Neuroprotective effects of Ginseng total saponin and ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 on spinal cord neurons in vitro. Exp Neurol. 2002. 173:224–234.
Article19. Lim JH, Wen TC, Matsuda S, Tanaka J, Maeda N, Peng H, Aburaya J, Ishihara K, Sakanaka M. Protection of ischemic hippocampal neurons by ginsenoside Rb1, a main ingredient of ginseng root. Neurosci Res. 1997. 28:191–200.
Article20. Shen L, Zhang J. Ginsenoside Rg1 increases ischemia-induced cell proliferation and survival in the dentate gyrus of adult gerbils. Neurosci Lett. 2003. 344:1–4.
Article21. Lee YJ, Chung E, Lee KY, Lee YH, Hur B, Lee SK. Ginsenoside-Rg1, one of the major active molecules from Panax ginseng, is a functional ligand of glucocorticoid receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1997. 133:135–140.
Article22. Chen XC, Chen Y, Zhu YG, Fang F, Chen LM. Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 against MPTP-induced apoptosis in mouse substantia nigra neurons. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2002. 23:829–834.23. Chen XC, Zhu YG, Zhu LA, Huang C, Chen Y, Chen LM, Fang F, Zhou YC, Zhao CH. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates dopamine-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by suppressing oxidative stress. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003. 473:1–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Ginseng Saponins on Nicotine-Induced Dopamine Release in the Rat Nucleus Accumbens and Striatum
- The Comparison of Seasonal Ginsenoside Composition Contents in Korean Wild Simulated Ginseng (Panax ginseng) which were Cultivated in Different Areas and Various Ages
- Inhibitory effects of ginseng saponins on c-fos mRNA expression and the proliferation of rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells stimulated by angiotensin II
- Therapeutic Effect of 10 % Ginseng Saponin Ointment for Recurrent Herpes Simplex Virus Infections
- The Effect of Ginseng Saponin on the Dopaminergic Neurons in the Parkinson's Disease Model in Mice