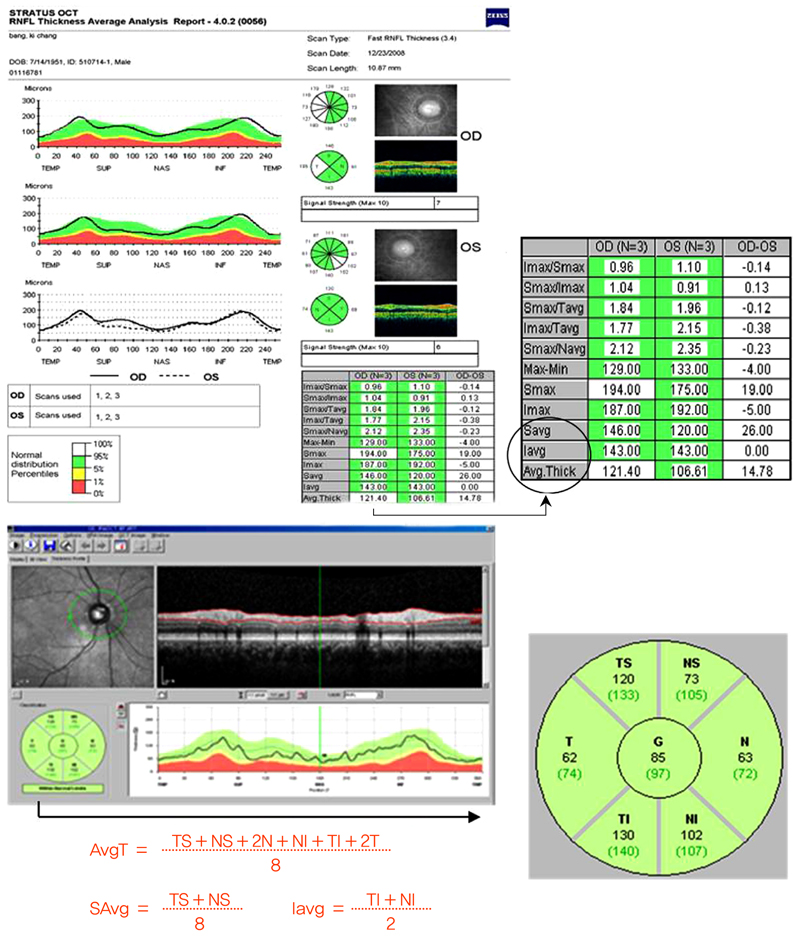
Korean J Ophthalmol.
2011 Jun;25(3):166-173. 10.3341/kjo.2011.25.3.166.
Comparison of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness between Stratus and Spectralis OCT
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bjcho@kuh.ac.kr
- KMID: 1010023
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2011.25.3.166
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness of normal patients and those with various glaucoma diseases by time domain (Stratus) and spectral domain (Spectralis) optical coherence tomography (OCT).
METHODS
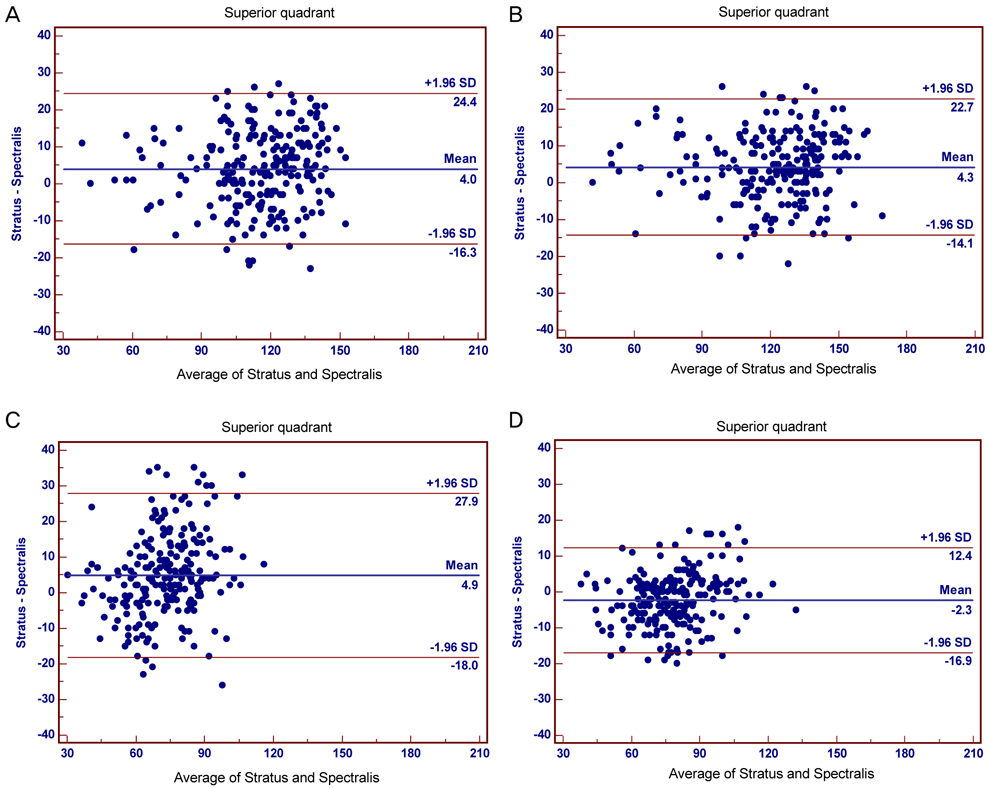
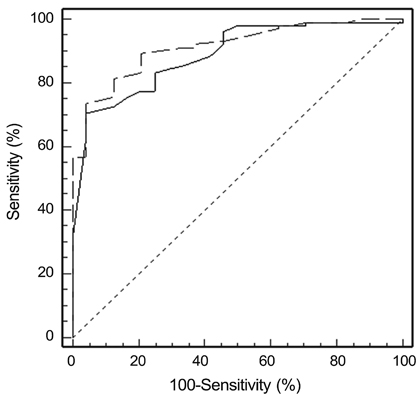
The RNFL thickness as measured by the Stratus and Spectral OCT was compared (paired t-test). The relationship and agreement of RNFL thickness between the two OCT modalities were evaluated by Pearson correlation, Bland-Altman plot, and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.
RESULTS
Two-hundred seventeen eyes of 217 patients, including twenty-four normal eyes, ninety-one glaucoma suspects, seventy-six normal tension glaucoma cases, and twenty-six primary open angle glaucoma cases (POAG) were analyzed. The peripapillary RNFL thicknesses as measured by Stratus OCT were significantly greater than those measured by Spectralis OCT. However, in quadrant comparisons, the temporal RNFL thickness obtained using Stratus OCT were significantly less than those obtained using Spectralis OCT. Correlations between RNFL parameters were strong (Pearson correlation coefficient for mean RNFL thickness = 0.88); a high degree of correlation was found in the POAG group. Bland-Altman plotting demonstrated that agreement in the temporal quadrant was greater than any other quadrant.
CONCLUSIONS
Both OCT systems were highly correlated and demonstrated strong agreement. However, absolute measurements of peripapillary RNFL thickness differed between Stratus OCT and Spectralis OCT. Thus, measurements with these instruments should not be considered interchangeable. The temporal quadrant was the only sector where RNFL thickness as measured by Spectralis OCT was greater than by Stratus OCT; this demonstrated greater agreement than other sectors.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Comparison of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measured Using Five Different Optical Coherence Tomography Devices
Youn Gon Lee, Young Hoon Hwang
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(3):261-267. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.3.261.
Reference
-
1. Bowd C, Zangwill LM, Berry CC, et al. Detecting early glaucoma by assessment of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and visual function. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001. 42:1993–2003.2. Huang D, Swanson EA, Lin CP, et al. Optical coherence tomography. Science. 1991. 254:1178–1181.3. Budenz DL, Chang RT, Huang X, et al. Reproducibility of retinal nerve fiber thickness measurements using the stratus OCT in normal and glaucomatous eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. 46:2440–2443.4. Paunescu LA, Schuman JS, Price LL, et al. Reproducibility of nerve fiber thickness, macular thickness, and optic nerve head measurements using Stratus OCT. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004. 45:1716–1724.5. Schuman JS, Pedut-Kloizman T, Pakter H, et al. Optical coherence tomography and histologic measurements of nerve fiber layer thickness in normal and glaucomatous monkey eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007. 48:3645–3654.6. Blumenthal EZ, Parikh RS, Pe'er J, et al. Retinal nerve fibre layer imaging compared with histological measurements in a human eye. Eye (Lond). 2009. 23:171–175.7. Bowd C, Weinreb RN, Williams JM, Zangwill LM. The retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in ocular hypertensive, normal, and glaucomatous eyes with optical coherence tomography. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000. 118:22–26.8. Williams ZY, Schuman JS, Gamell L, et al. Optical coherence tomography measurement of nerve fiber layer thickness and the likelihood of a visual field defect. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002. 134:538–546.9. Chen TC, Cense B, Pierce MC, et al. Spectral domain optical coherence tomography: ultra-high speed, ultra-high resolution ophthalmic imaging. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005. 123:1715–1720.10. de Boer JF, Cense B, Park BH, et al. Improved signal-to-noise ratio in spectral-domain compared with time-domain optical coherence tomography. Opt Lett. 2003. 28:2067–2069.11. Ray R, Stinnett SS, Jaffe GJ. Evaluation of image artifact produced by optical coherence tomography of retinal pathology. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005. 139:18–29.12. Jaffe GJ, Caprioli J. Optical coherence tomography to detect and manage retinal disease and glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004. 137:156–169.13. Cense B, Chen TC, Nassif N, et al. Ultra-high speed and ultra-high resolution spectral-domain optical coherence tomography and optical Doppler tomography in ophthalmology. Bull Soc Belge Ophtalmol. 2006. (302):123–132.14. Nassif N, Cense B, Park BH, et al. In vivo human retinal imaging by ultrahigh-speed spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Opt Lett. 2004. 29:480–482.15. Knight OJ, Chang RT, Feuer WJ, Budenz DL. Comparison of retinal nerve fiber layer measurements using time domain and spectral domain optical coherent tomography. Ophthalmology. 2009. 116:1271–1277.16. Sung KR, Kim DY, Park SB, Kook MS. Comparison of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by Cirrus HD and Stratus optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2009. 116:1264–1270. 1270.e117. Han IC, Jaffe GJ. Comparison of spectral- and time-domain optical coherence tomography for retinal thickness measurements in healthy and diseased eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009. 147:847–858. 858.e118. Wu Z, Vazeen M, Varma R, et al. Factors associated with variability in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements obtained by optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2007. 114:1505–1512.19. Cheung CY, Leung CK, Lin D, et al. Relationship between retinal nerve fiber layer measurement and signal strength in optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2008. 115:1347–1351. 1351.e1–1351.e2.20. Bendschneider D, Tornow RP, Horn FK, et al. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normals measured by spectral domain OCT. J Glaucoma. 2010. 19:475–482.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Time Domain OCT and Spectrum Domain OCT for Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Assessment
- Comparison of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measured by Spectral-Domain and Time-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
- Comparison of Diagnostic Ability of 3D and Stratus Optical Coherence Tomography in Early Glaucoma
- Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measured with Two Different Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Devices
- Usefulness of Table Parameters of Stratus OCT in Detection of Localized Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Defects