Korean J Lab Med.
2008 Aug;28(4):267-273. 10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.4.267.
Evaluation of iQ200 Automated Urine Microscopy Analyzer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. wan1818@paran.com
- KMID: 854888
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.4.267
Abstract
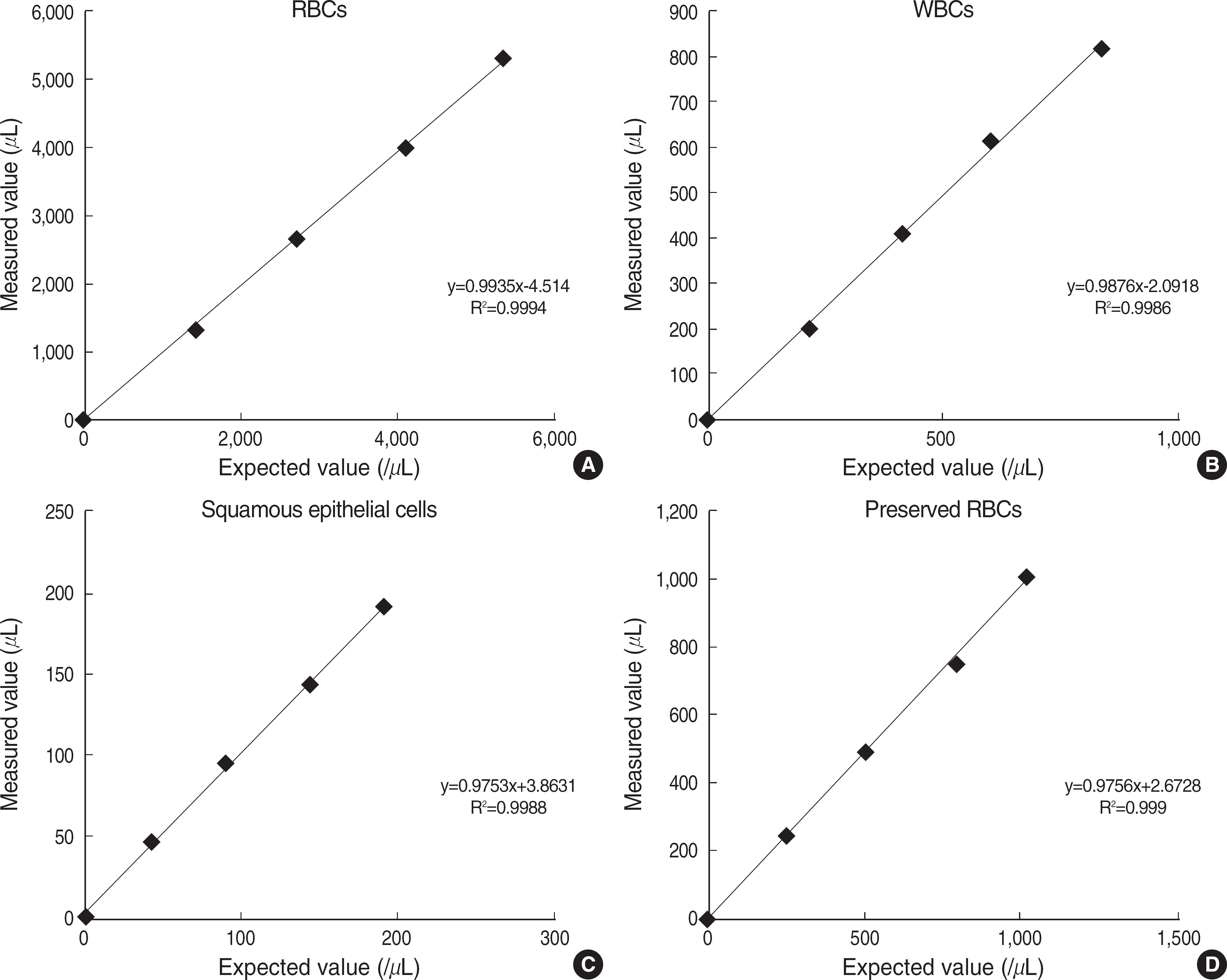
- BACKGROUND: Microscopic examination of urine sediment is one of the most commonly performed tests in the clinical laboratory. However, manual microscopic sediment examination is labor-intensive, time-consuming and imprecise. In this study, we evaluated the analytical performance and clinical usefulness of a recently introduced image-based automated urinalysis system, Iris iQ200 (Iris Diagnostics, USA). METHODS: We assessed the iQ200 for linearity, precision and carryover rate using patient's samples and quality control materials. On 337 urine samples, urine sediment analyses performed by the iQ200 were compared with manual microscopy results. RESULTS: The iQ200 showed a good linearity (r2>0.99) for all cellular components analyzed. Within-run and total CVs on urine specimens and quality control samples were less than 10% except for within-run CV for the samples with low concentration of the squamous epithelial cells. The carryover rates were 0.21% for RBCs and 1.92% for WBCs. The agreement rates within one grade between the iQ200 and manual microscopy for RBCs, WBCs, and squamous epithelial cells were 93.8%, 94.2% and 96.9%, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: Since the iQ200 showed a reliable analytical performance and good concordance with manual microscopy, it could be useful in the clinical practice as a screening procedure.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
IRIS Iq200, UF-1000i, Cobas u701 자동요침사분석장비의 비교 평가
Hyunji Choi, Dahae Yang, Sun Ja Kwon,, Poo Reum Kang, Hasung Park, Teayun Kim, Hyunyong Hwang
Lab Med Online. 2020;10(4):283-294. doi: 10.47429/lmo.2020.10.4.283.Selection of Unnecessary Urine Culture Specimens Using Sysmex UF-5000 Urine Flow Cytometer
Duyeal Song, Hyun-Ji Lee, Su Yeon Jo, Sun Min Lee, Chulhun L. Chang
Ann Clin Microbiol. 2018;21(4):75-79. doi: 10.5145/ACM.2018.21.4.75.
Reference
-
1.Fuller CE., Threatte GA., Henry JB. Basic examination of urine. Henry JB, editor. Clinical diagnosis and management by laboratory methods. 20th ed.Philadelphia: WB Saunders;;2001. p. 367–402.2.Ferris JA. Comparison and standardization of the urine microscopic examination. Lab Med. 1983. 14:659–62.
Article3.Huussen J., Koene RA., Hilbrands LB. The (fixed) urinary sediment, a simple and useful diagnostic tool in patients with haematuria. Neth J Med. 2004. 62:4–9.4.Elin RJ., Hosseini JM., Kestner J., Rawe M., Ruddel M., Nishi HH. Comparison of automated and manual methods for urinalysis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986. 86:731–7.
Article5.Carlson DA., Statland BE. Automated urinalysis. Clin Lab Med. 1988. 8:449–61.
Article6.Wah DT., Wises PK., Butch AW. Analytic performance of the iQ200 automated urine microscopy analyzer and comparison with manual counts using Fuchs-Rosenthal cell chambers. Am J Clin Pathol. 2005. 123:290–6.
Article7.Lamchiagdhase P., Preechaborisutkul K., Lomsomboon P., Srisuchart P., Tantiniti P., Khan-u-Ra N, et al. Urine sediment examination: a comparison between the manual method and the iQ200 automated urine microscopy analyzer. Clin Chim Acta. 2005. 358:167–74.
Article8.Chien TI., Kao JT., Liu HL., Lin PC., Hong JS., Hsieh HP, et al. Urine sediment examination: a comparison of automated urinalysis systems and manual microscopy. Clin Chim Acta. 2007. 384:28–34.
Article9.Shayanfar N., Tobler U., von Eckardstein A., Bestmann L. Automated urinalysis: first experiences and a comparison between the Iris iQ200 urine microscopy system, the Sysmex UF-100 flow cytometer and manual microscopic particle counting. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2007. 45:1251–6.
Article10.Okada H., Sakai Y., Kawabata G., Fujisawa M., Arakawa S., Hamaguchi Y, et al. Automated urinalysis. Evaluation of the Sysmex UF-50. Am J Clin Pathol. 2001. 115:605–10.11.National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative measurement procedures: a statistical approach; approved guideline. NCCLS document EP6-A. Wayne, PA: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards;2003.12.National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Evaluation of the precision performance of clinical chemistry devices; approved guideline. NCCLS document EP5-A. Wayne, PA: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards;1999.13.Pesce MA. Laboratory automation. Kaplan LA, Pesce AJ, editors. Clinical Chemistry. 4th ed.Baltimore: Mosby;2003. p. 294.14.Ottiger C., Huber AR. Quantitative urine particle analysis: integrative approach for the optimal combination of automation with UF-100 and microscopic review with KOVA cell chamber. Clin Chem. 2003. 49:617–23.
Article15.Roe CE., Carlson DA., Daigneault RW., Statland BE. Evaluation of the Yellow IRIS. An automated method for urinalysis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986. 86:661–5.
Article16.Deindoerfer FH., Gangwer JR., Laird CW., Ringold RR. “The Yellow IRIS” urinalysis workstation–the first commercial application of “automated intelligent microscopy”. Clin Chem. 1985. 31:1491–9.
Article17.Wargotz ES., Hyde JE., Karcher DS., Hitlan JP., Wilkinson DS. Urine sediment analysis by the Yellow IRIS automated urinalysis workstation. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987. 88:746–8.18.Kim DC., Yoo MY., Jo SS., Park J., Yoon Y., Kim JQ. Laboratory evaluation of fully automated urine cell analyzer Sysmex UF-100. J Clin Pathol & Quality Control. 2001. 23:299–306. (김동찬, 유영미, 조성석, 박준완, 윤여민, 김진규. 자동요침사분석기 UF-100의평가. 임상병리와정도관리 2001;23: 299-306.).
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of IRIS Iq200, UF-1000i, and Cobas u701 Module Automated Urine Sediment Analyzers
- Comparison of Analytical Performance between the Sysmex UF-100 flow cytometer and the Iris iQ200 Urine Microscopy System
- Evaluation and Establishment of Reference Range of Automated Urine Cell Analyzer UF-100
- Performance Evaluation of the CLINITEK Novus Automated Urine Chemistry Analyzer
- Comparison of YD URiSCAN PluScope Urine Microscopic Analyzer and Sysmex UF-1000i Flow Cytometry Systems