Lab Med Online.
2020 Oct;10(4):283-294. 10.47429/lmo.2020.10.4.283.
Comparison of IRIS Iq200, UF-1000i, and Cobas u701 Module Automated Urine Sediment Analyzers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Busan, Korea
- 2Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 3Department of Orthopedics, Gangneung Asan Medical Center, Gangneung, Korea
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2512267
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.47429/lmo.2020.10.4.283
Abstract
- Background
We sought to compare the performance of three commercially available automated urine sediment analyzers that represent the current urine sediment analysis technology.
Methods
A total of 232 patient samples were analyzed using manual microscopy and three automated analyzers: IRIS Iq200 (Beckman Coulter, USA), UF-1000i (Sysmex, Japan), and Cobas u701 (Roche, Switzerland). We analyzed precision, linearity, carry-over, concordance rate, and agreement between the three analyzers and manual microscopy.
Results
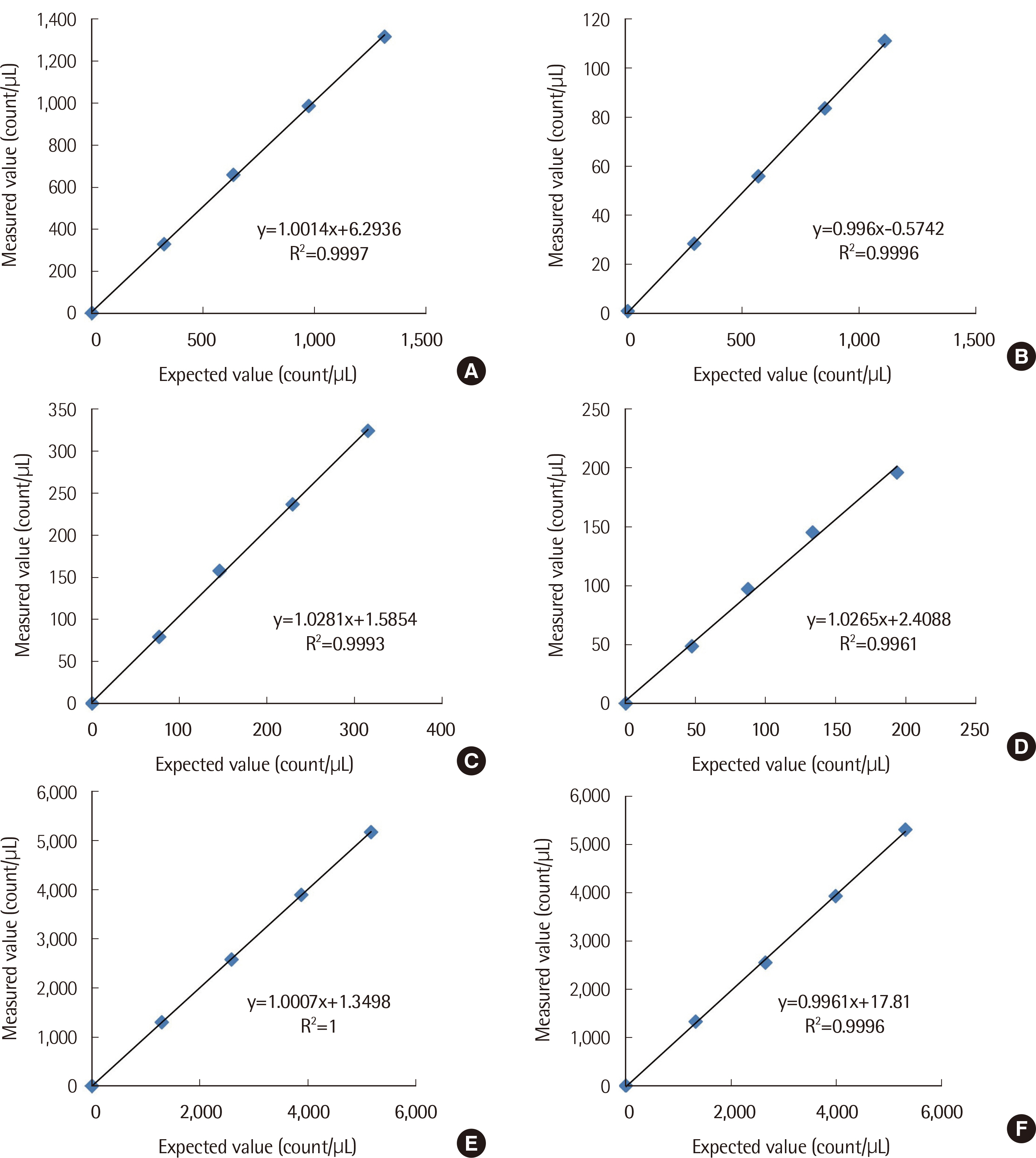
The repeatability and within-laboratory precision showed results similar to those of previous studies. All analyzers showed excellent linearity. The carry-over rates were within 1%. The correlation coefficient (r) between the three analyzers and manual microscopy was good. Regarding red blood cell (RBC), the UF-1000i showed a better concordance rate (90.52%) with manual microscopy than the other two analyzers and the agreement was substantial for UF-1000i (κ=0.63) and IRIS Iq200 (κ=0.61). Regarding white blood cell (WBC), Cobas u701 showed the best concordance rate (96.55%) and the agreement was moderate for IRIS Iq200 (κ=0.57) and Cobas u701 (κ=0.56), and fair for UF-1000i (κ=0.47). Regarding epithelial cell (EPI), IRIS Iq200 showed the highest concordance rate (99.2%) and the agreement was moderate for IRIS Iq200 (κ=0.59) and Cobas u701 (κ=0.54), and fair for UF-1000i (κ=0.40).
Conclusions
IRIS Iq200 offered the best agreement with manual microscopy for WBC and EPI count, while UF-1000i showed a better agreement for RBC count. The agreement is insufficient for fully replacing the manual microscopy.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2009. Urinalysis; Approved Guideline-Third Edition. CLSI Document GP16-A3. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:2. McPherson RA, Ben-Ezra J, et al. McPherson RA, Pincus MR, editors. 2017. Basic examination of urine. Henry's clinical diagnosis and management by laboratory methods. 23rd ed. Elsevier-Saunders;Philadelphia: p. 442.
Article3. Perazella MA. 2015; The urine sediment as a biomarker of kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 66:748–55. DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.02.342. PMID: 25943719. PMCID: PMC7446794.
Article4. Becker GJ, Garigali G, Fogazzi GB. 2016; Advances in urine microscopy. Am J Kidney Dis. 67:954–64. DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.11.011. PMID: 26806004. PMCID: PMC7466446.
Article5. Manoni F, Gessoni G, Caleffi A, Alessio MG, Rosso R, Menozzi P, et al. 2013; Pediatric reference values for urine particle quantification by using automated flow cytometer: results of a multicenter study of Italian urinalysis group. Clin Biochem. 46:1820–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2013.09.005. PMID: 24051212.
Article6. Kouri TT, Gant VA, Fogazzi GB, Hofmann W, Hallander HO, Guder WG. 2000; Towards European urinalysis guidelines. Introduction of a project under European Confederation of Laboratory Medicine. Clin Chim Acta. 297:305–11. DOI: 10.1016/S0009-8981(00)00256-4. PMID: 10841931.7. Du J, Xu J, Wang F, Guo Y, Zhang F, Wu W, et al. 2015; Establishment and development of the personalized criteria for microscopic review following multiple automated routine urinalysis systems. Clin Chim Acta. 444:221–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2015.02.022. PMID: 25701652.
Article8. Winkel P, Statland BE, Jørgensen K. 1974; Urine microscopy, an Ⅲ-defined method, examined by a multifactorial technique. Clin Chem. 20:436–9. DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/20.4.436. PMID: 4818195.9. Chase J, Hammond J, Bilbrough G, DeNicola DB. 2018; Urine sediment examination: Potential impact of red and white blood cell counts using different sediment methods. Vet Clin Pathol. 47:608–16. DOI: 10.1111/vcp.12674. PMID: 30537173.
Article10. Wargotz ES, Hyde JE, Karcher DS, Hitlan JP, Wilkinson DS. 1987; Urine sediment analysis by the Yellow IRIS automated urinalysis workstation. Am J Clin Pathol. 88:746–8. PMID: 3687846.11. Deindoerfer FH, Gangwer JR, Laird CW, Ringold RR. 1985; "The Yellow IRIS" urinalysis workstation--the first commercial application of "automated intelligent microscopy". Clin Chem. 31:1491–9. DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/31.9.1491. PMID: 4028398.
Article12. Roe CE, Carlson DA, Daigneault RW, Statland BE. 1986; Evaluation of the Yellow IRIS®: an automated method for urinalysis. Am J Clin Pathol. 86:661–5. DOI: 10.1093/ajcp/86.5.661. PMID: 3776920.13. Mayo S, Acevedo D, Quiñones-Torrelo C, Canós I, Sancho M. 2008; Clinical laboratory automated urinalysis: comparison among automated microscopy, flow cytometry, two test strips analyzers, and manual microscopic examination of the urine sediments. J Clin Lab Anal. 22:262–70. DOI: 10.1002/jcla.20257. PMID: 18623125. PMCID: PMC6649239.
Article14. Chien TI, Kao JT, Liu HL, Lin PC, Hong JS, Hsieh HP, et al. 2007; Urine sediment examination: a comparison of automated urinalysis systems and manual microscopy. Clin Chim Acta. 384:28–34. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2007.05.012. PMID: 17604012. PMCID: PMC6039169.
Article15. Lee W, Ha JS, Ryoo NH. 2016; Comparison of the automated cobas u701 urine microscopy and UF-1000i flow cytometry systems and manual microscopy in the examination of urine sediments. J Clin Lab Anal. 30:663–71. DOI: 10.1002/jcla.21919. PMID: 26842372. PMCID: PMC6807231.16. Cho J, Oh KJ, Jeon BC, Lee SG, Kim JH. 2019; Comparison of five automated urine sediment analyzers with manual microscopy for accurate identification of urine sediment. Clin Chem Lab Med. 57:1744–53. DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2019-0211. PMID: 31280239.
Article17. Wang J, Zhang Y, Xu D, Shao W, Lu Y. 2010; Evaluation of the Sysmex UF-1000i for the diagnosis of urinary tract infection. Am J Clin Pathol. 133:577–82. DOI: 10.1309/AJCP1GT2JXOCQBCZ. PMID: 20231611.
Article18. Manoni F, Tinello A, Fornasiero L, Hoffer P, Temporin V, Valverde S, et al. 2010; Urine particle evaluation: a comparison between the UF-1000i and quantitative microscopy. Clin Chem Lab Med. 48:1107–11. DOI: 10.1515/CCLM.2010.233. PMID: 20482296.
Article19. Manoni F, Fornasiero L, Ercolin M, Tinello A, Ferrian M, Hoffer P, et al. 2009; Cutoff values for bacteria and leukocytes for urine flow cytometer Sysmex UF-1000i in urinary tract infections. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 65:103–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2009.06.003. PMID: 19748419.
Article20. Bakan E, Ozturk N, Baygutalp NK, Polat E, Akpinar K, Dorman E, et al. 2016; Comparison of Cobas 6500 and Iris IQ200 fully-automated urine analyzers to manual urine microscopy. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 26:365–75. DOI: 10.11613/BM.2016.040. PMID: 27812305. PMCID: PMC5082210.
Article21. Bakan E, Bayraktutan Z, Baygutalp NK, Gul MA, Umudum FZ, Bakan N. 2018; Evaluation of the analytical performances of Cobas 6500 and Sysmex UN series automated urinalysis systems with manual microscopic particle counting. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 28:020712. DOI: 10.11613/BM.2018.020712. PMID: 30022887. PMCID: PMC6039169.
Article22. Wesarachkitti B, Khejonnit V, Pratumvinit B, Reesukumal K, Meepanya S, Pattanavin C, et al. 2016; Performance evaluation and comparison of the fully automated urinalysis analyzers UX-2000 and Cobas 6500. Lab Med. 47:124–33. DOI: 10.1093/labmed/lmw002. PMID: 27069030.
Article23. Linko S, Kouri TT, Toivonen E, Ranta PH, Chapoulaud E, Lalla M. 2006; Analytical performance of the Iris iQ200 automated urine microscopy analyzer. Clin Chim Acta. 372:54–64. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2006.03.015. PMID: 16696963.
Article24. Wah DT, Wises PK, Butch AW. 2005; Analytic performance of the iQ200 automated urine microscopy analyzer and comparison with manual counts using Fuchs-Rosenthal cell chambers. Am J Clin Pathol. 123:290–6. DOI: 10.1309/VNGU9Q5V932D74NU. PMID: 15842056.
Article25. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2004. Evaluation of precision performance of quantitative measurement methods; Approved guideline. CLSI document EP05-A2. 2nd ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:26. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2003. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative measurement procedures: A statistical approach; Approved guideline. CLSI document EP06-A. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:27. 2003. Laboratory automation. Clinical chemistry: theory, analysis, correlation. 4th ed. Mosby;Baltimore: p. 294.28. Landis JR, Koch GG. 1977; The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 33:159–74. DOI: 10.2307/2529310. PMID: 843571.
Article29. Budak YU, Huysal K. 2011; Comparison of three automated systems for urine chemistry and sediment analysis in routine laboratory practice. Clin Lab. 57:47–52. PMID: 21391464.30. Cui M, Ju S, Shi Y, Jing R. 2017; Performance verification of the Iris iQ200 Sprint automated urine microscopy analyzer in a hospital routine laboratory. Clin Lab. 63:1607–12. DOI: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2017.170318. PMID: 29035449.
Article31. Park J, Kim J. 2008; Evaluation of iQ200 automated urine microscopy analyzer. Korean J Lab Med. 28:267–73. DOI: 10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.4.267. PMID: 18728375. PMCID: PMC6804654.
Article32. Altekin E, Kadiçesme O, Akan P, Kume T, Vupa O, Ergor G, et al. 2010; New generation IQ-200 automated urine microscopy analyzer compared with KOVA cell chamber. J Clin Lab Anal. 24:67–71. DOI: 10.1002/jcla.20319. PMID: 20333768. PMCID: PMC6647716.
Article33. Ottiger C, Huber AR. 2003; Quantitative urine particle analysis: integrative approach for the optimal combination of automation with UF-100 and microscopic review with KOVA cell chamber. Clinl Chem. 49:617–23. DOI: 10.1373/49.4.617. PMID: 12651815.
Article34. Langlois MR, Delanghe JR, Steyaert SR, Everaert KC, De Buyzere ML. 1999; Automated flow cytometry compared with an automated dipstick reader for urinalysis. Clin Chem. 45:118–22. DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/45.1.118. PMID: 9895347.
Article35. Ben-Ezra J, Bork L, McPherson RA. 1998; Evaluation of the Sysmex UF-100 automated urinalysis analyzer. Clin Chem. 44:92–5. DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/44.1.92. PMID: 9550564.
Article36. Zaman Z, Fogazzi GB, Garigali G, Croci MD, Bayer G, Kránicz T. 2010; Urine sediment analysis: Analytical and diagnostic performance of sediMAX® - A new automated microscopy image-based urine sediment analyser. Clin Chima Acta. 411:147–54. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2009.10.018. PMID: 19861122.
Article37. Enko D, Stelzer I, Böckl M, Derler B, Schnedl WJ, Anderssohn P, et al. 2020; Comparison of the diagnostic performance of two automated urine sediment analyzers with manual phase-contrast microscopy. Clin Chem Lab Med. 58:268–73. DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2019-0919. PMID: 31605578.
Article38. Bartosova K, Kubicek Z, Franekova J, Louzensky G, Lavrikova P, Jabor A. 2016; Analysis of four automated urinalysis systems compared to reference methods. Clin Lab. 62:2115–23. DOI: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2016.160316. PMID: 28164659.
Article39. Cao Y, Cheng M, Hu C. 2012; UrineCART, a machine learning method for establishment of review rules based on UF-1000i flow cytometry and dipstick or reflectance photometer. Clin Chem Lab Med. 50:2155–61. DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2012-0272. PMID: 23093270.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Analytical Performance between the Sysmex UF-100 flow cytometer and the Iris iQ200 Urine Microscopy System
- Comparison of YD URiSCAN PluScope Urine Microscopic Analyzer and Sysmex UF-1000i Flow Cytometry Systems
- Evaluation of iQ200 Automated Urine Microscopy Analyzer
- Age-Specific Cutoffs of the Sysmex UF-1000i Automated Urine Analyzer for Rapid Screening of Urinary Tract Infections in Outpatients
- Small Red Blood Cell Fraction on the UF-1000i Urine Analyzer as a Screening Tool to Detect Dysmorphic Red Blood Cells for Diagnosing Glomerulonephritis