Lab Med Online.
2016 Jul;6(3):147-151. 10.3343/lmo.2016.6.3.147.
Performance Evaluation of the CLINITEK Novus Automated Urine Chemistry Analyzer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jeongho@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2308729
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2016.6.3.147
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
We aimed to evaluate the performance of the CLINITEK Novus urine chemistry analyzer (Siemens, UK).
METHODS
The precision, correlation, and carryover study were performed using two kinds of commercial quality control materials and 40-55 freshly collected patient specimens. We calculated exact and within-1-block agreement, along with kappa agreement, to compare the semi-quantitative results between urine chemistry analyzers. The urine specific gravity taken by a refractometer was compared with the analyzer results. Moreover, we analyzed additional urine specimens for protein to evaluate the agreement of results between those of the CLINITEK Novus and the AU680 analyzers (Beckman Coulter, Japan).
RESULTS
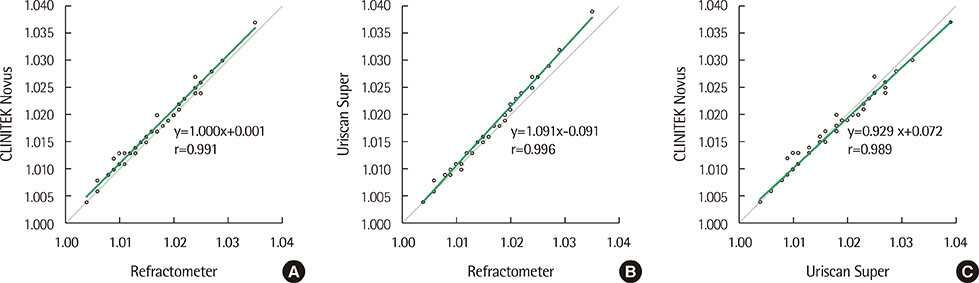
The precision study showed acceptable results; within-1-block agreement was 100% in all tested items. The urine chemistry results from the CLNITEK Novus analyzer demonstrated ≥85.1% within-1-block agreements with those of the Uriscan Super, and the kappa test results were ≥0.81. The comparison of specific gravity with manual refractometer showed a good correlation (r=0.991), and the protein comparison with the AU680 analyzer also showed a good correlation (with exact and within-1-block agreements being 75.9% and 100.0%, respectively). The carryover rates were 0% in all tested items, except specific gravity and heavy blood tests.
CONCLUSIONS
The CLINITEK Novus analyzer showed good performance in terms of precision, comparison, and carryover in this study. Therefore, the CLINITEK Novus automated urine analysis is expected to be useful for routine urinalysis in a clinical laboratory.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim KD. Urinalysis. In : Kang , editor. The Korean Society for Laboratory Medicine. Laboratory medicine. 5th ed. Seoul: E*PUBLIC;2014. p. 497–508.2. McPherson RA, Ben-Ezra J. Basic examination of the urine. In : Henry JB, editor. Clinical diagnosis and management by laboratory methods. 22nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;2011. p. 445–479.3. Han TH. Urinalysis: the usefulness and limitations of urine dipstick testing. J Korean Soc Pediatr Nephrol. 2013; 17:42–48.
Article4. Park HR, Jeong BK, Park NW. Comparative evaluation of dipstick urinalysis by dipstick readers. J Clin Pathol Qual Control. 2001; 23:239–246.5. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. User verification of precision and estimation of bias; Approved guideline-Third Edition. EP15-A3. Third Edition. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2014.6. Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute. Urinalysis; Approved Guideline-Third Edition. GP16-A3. Wayne, PA: Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute;2012.7. Skitek M. Imprecision and instability of common analytes in urine analysed by semi-automated dipstick urinalysis. Accred Qual Assur. 2004; 9:700–703.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Performance Evaluation of Beckman Coulter AU5822 Automated Clinical Chemistry Analyzer
- Comparison of three types of analyzers for urine protein-tocreatinine ratios in dogs
- Performance Evaluation of Automated Chemistry Analyser for Urine Chemistry Test
- Evaluation of the Analytical Performance of Atellica CH 930 Automated Chemistry Analyzer
- Diagnostic Utility of the URiSCAN 2 ACR Strip as a Point-of-care Test for Estimating Urine Albumin-Creatinine Ratios