Korean J Lab Med.
2008 Jun;28(3):230-238. 10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.3.230.
Role of STAT3 as a Negative Regulator in Mac2- Binding Protein Expression
- Affiliations
-
- 1Stem cell Research Center, Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB), Daejeon, Korea. hglee@kribb.re.kr
- 2Department of Biological Sciences and the Research Center for Women's Diseases, Sookmyung Women's University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Institute of Biomedical Science and Technology, Konkuk University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- KMID: 854872
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.3.230
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Mac-2 binding protein (Mac-2BP) is a secreted glycoprotein from the culture fluid of several human cancer cells, especially breast, lung, and gastric cells. Mac-2BP plays a role in immune response and cell adhesion activity in patients with various cancer and infectious diseases. In this study, we attempted to identify the regulators of Mac-2BP expression at the transcriptional level.
METHODS
To determine the effect of epidermal growth factor (EGF) to Mac-2BP expression in gastric cancers, we constructed the different lengths of Mac-2BP promoter plasmids and measured the promoter activity and Mac-2BP expression. In addition to investigating the role of signal transducer and activator of transcription3 (STAT3) or human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) as a regulator of Mac-2BP, we transfected the small interfering RNA (siRNA) specific for STAT3 or hTERT, and Mac-2BP level was observed by a quantitative ELISA.
RESULTS
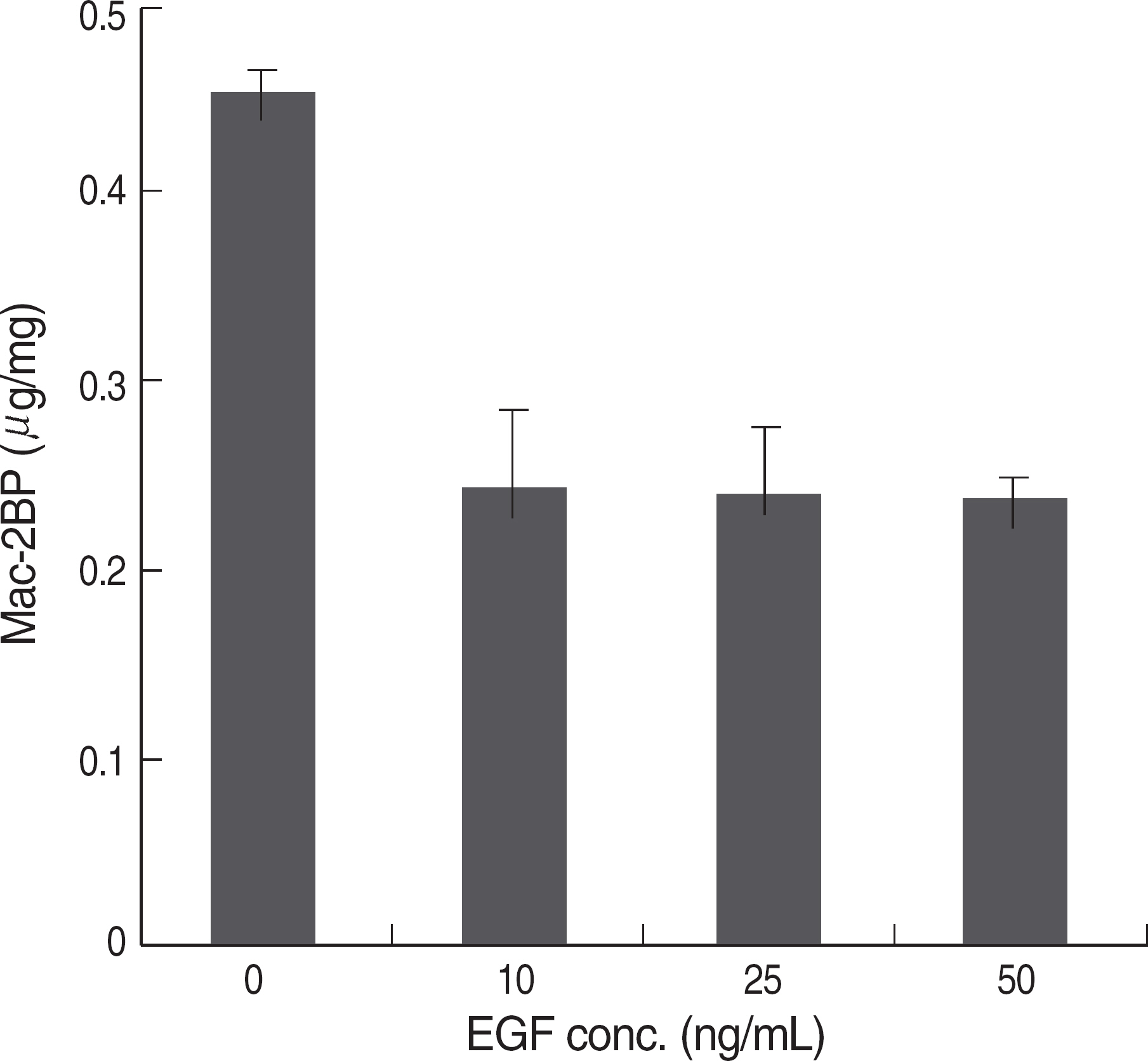
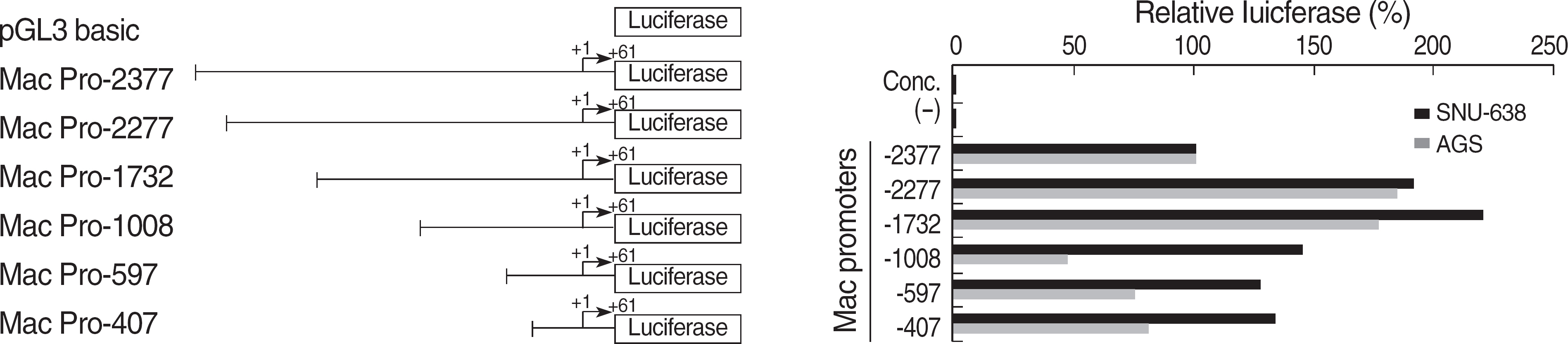
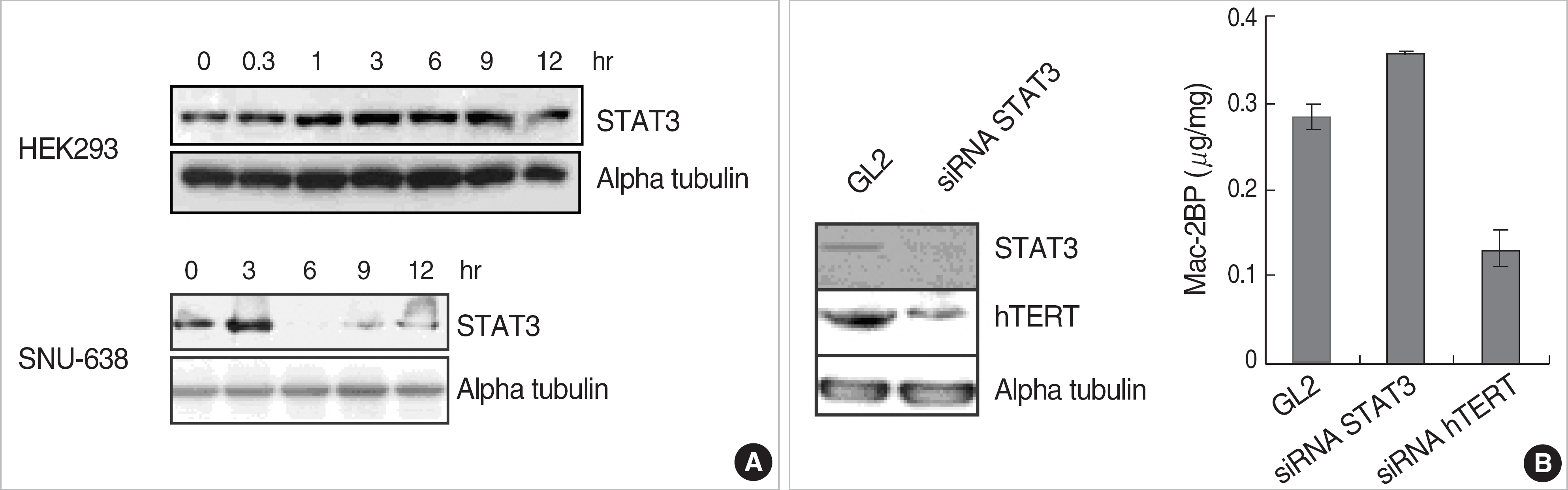
EGF treatment could suppress the Mac-2BP transcription in HEK293 or gastric cancer cell lines (SNU-638 or AGS). In 5'-deleted promoter experiment, pGL3-Mac Pro-2377 transfected cells showed a decreased luciferase activity compared to pGL3-Mac Pro-2277. We also identified that (-2,366/-2,356) on Mac-2BP promoter is a putative STAT3 binding site and suppression of STAT3 with STAT3 specific siRNA increased the Mac-2BP level, suggesting the role of STAT3 as a negative regulator, in contrast to hTERT, which is known as a positive regulator.
CONCLUSIONS
EGF signal is critical for the Mac-2BP expression, and more importantly, STAT3 could work as a negative regulator, while hTERT as a positive regulator in Mac-2BP transcription.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Levy DE., Darnell JE Jr. Stats: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002. 3:651–2.
Article2.Konnikova L., Simeone MC., Kruger MM., Kotecki M., Cochran BH. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) regulates human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) expression in human cancer and primary cells. Cancer Res. 2005. 65:6516–20.
Article3.Liu L., McBride KM., Reich NC. STAT3 nuclear import is independent of tyrosine phosphorylation and mediated by importin-alpha3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005. 102:8150–5.4.Bromberg J. Stat proteins and oncogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2002. 109:1139–42.
Article5.Bromberg JF., Wrzeszczynska MH., Devgan G., Zhao Y., Pestell RG., Albanese C, et al. Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell. 1999. 98:295–303.
Article6.Catlett-Falcone R., Landowski TH., Oshiro MM., Turkson J., Levitzki A., Savino R, et al. Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity. 1999. 10:105–15.
Article7.Bowman T., Garcia R., Turkson J., Jove R. STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene. 2000. 19:2474–88.
Article8.Bowman T., Broome MA., Sinibaldi D., Wharton W., Pledger WJ., Sedivy JM, et al. Stat3-mediated Myc expression is required for Src transformation and PDGF-induced mitogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001. 98:7319–24.
Article9.Epling-Burnette PK., Zhong B., Bai F., Jiang K., Bailey RD., Garcia R, et al. Cooperative regulation of Mcl-1 by Janus kinase/stat and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase contribute to granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-delayed apoptosis in human neutrophils. J Immunol. 2001. 166:7486–95.
Article10.Gong W., Wang L., Yao JC., Ajani JA., Wei D., Aldape KD, et al. Expression of activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 predicts expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in and angiogenic phenotype of human gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. 11:1386–93.
Article11.Bowman T., Broome MA., Sinibaldi D., Wharton W., Pledger WJ., Sedivy JM, et al. Stat3-mediated Myc expression is required for Src transformation and PDGF-induced mitogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001. 98:7319–24.
Article12.Maehara Y., Kabashima A., Koga T., Tokunaga E., Takeuchi H., Kakeji Y, et al. Vascular invasion and potential for tumor angiogenesis and metastasis in gastric carcinoma. Surgery. 2000. 128:408–16.
Article13.Iacobelli S., Arno E., D'Orazio A., Coletti G. Detection of antigens recognized by a novel monoclonal antibody in tissue and serum from patients with breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1986. 46:3005–10.14.Iacobelli S., Arno E., Sismondi P., Natoli C., Gentiloni N., Scambia G, et al. Measurement of a breast cancer associated antigen detected by monoclonal antibody SP-2 in sera of cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1988. 11:19–30.
Article15.Park YP., Choi SC., Kim JH., Song EY., Kim JW., Yoon DY, et al. Up-regulation of Mac-2 binding protein by hTERT in gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007. 120:813–20.
Article16.Resnick D., Pearson A., Krieger M. The SRCR superfamily: a family reminiscent of the Ig superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994. 19:5–8.
Article17.Akira S., Nishio Y., Inoue M., Wang XJ., Wei S., Matsusaka T, et al. Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell. 1994. 77:63–71.
Article18.Zhong Z., Wen Z., Darnell JE Jr. Stat3: a STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science. 1994. 264:95–8.
Article19.Yu LF., Cheng Y., Qiao MM., Zhang YP., Wu YL. Activation of STAT3 signaling in human stomach adenocarcinoma drug-resistant cell line and its relationship with expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. 11:875–9.
Article20.Darnell JE Jr. STATs and gene regulation. Science. 1997. 277:1630–5.
Article21.Horvath CM., Wen Z., Darnell JE Jr. A STAT protein domain that determines DNA sequence recognition suggests a novel DNA-binding domain. Genes Dev. 1995. 9:984–94.
Article22.Sasse J., Hemmann U., Schwartz C., Schniertshauer U., Heesel B., Landgraf C, et al. Mutational analysis of acute-phase response factor/Stat3 activation and dimerization. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. 17:4677–86.
Article23.Kanda N., Seno H., Konda Y., Marusawa H., Kanai M., Nakajima T, et al. STAT3 is constitutively activated and supports cell survival in association with survivin expression in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 2004. 23:4921–9.
Article24.Kube D., Holtick U., Vockerodt M., Ahmadi T., Haier B., Behrmann I, et al. STAT3 is constitutively activated in Hodgkin cell lines. Blood. 2001. 98:762–70.
Article25.Mora LB., Buettner R., Seigne J., Diaz J., Ahmad N., Garcia R, et al. Constitutive activation of Stat3 in human prostate tumors and cell lines: direct inhibition of Stat3 signaling induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2002. 62:6659–66.26.Song JI., Grandis JR. STAT signaling in head and neck cancer. Oncogene. 2000. 19:2489–95.
Article27.Buettner R., Mora LB., Jove R. Activated STAT signaling in human tumors provides novel molecular targets for therapeutic intervention. Clin Cancer Res. 2002. 8:945–54.28.Burke WM., Jin X., Lin HJ., Huang M., Liu R., Reynolds RK, et al. Inhibition of constitutively active Stat3 suppresses growth of human ovarian and breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2001. 20:7925–34.
Article29.Wennström S., Downward J. Role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in activation of ras and mitogen-activated protein kinase by epidermal growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. 19:4279–88.
Article30.Arteaga C. Targeting HER1/EGFR: a molecular approach to cancer therapy. Semin Oncol. 2003. 30:3–14.
Article31.Fombonne J., Reix S., Rasolonjanahary R., Danty E., Thirion S., Laforge-Anglade G, et al. Epidermal growth factor triggers an original, caspase-independent pituitary cell death with heterogeneous pheno-type. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. 15:4938–48.
Article32.Chen KY., Huang LM., Kung HJ., Ann DK., Shih HM. The role of tyro-sine kinase Etk/Bmx in EGF-induced apoptosis of MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2004. 23:1854–62.
Article33.Song K., Krebs TL., Danielpour D. Novel permissive role of epidermal growth factor in transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) signaling and growth suppression. Mediation by stabilization of TFG-beta receptor type II. J Biol Chem. 2006. 24:7765–74.34.Braunstein J., Brutsaert S., Olson R., Schindler C. STATs dimerize in the absence of phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:34133–40.
Article35.Pranada AL., Metz S., Herrmann A., Heinrich PC., Muller-Newen G. Real time analysis of STAT3 nucleocytoplasmic shuttling. J Biol Chem. 2004. 279:15114–23.
Article36.Chatterjee-Kishore M., Wright KL., Ting JP., Stark GR. How Stat1 mediates constitutive gene expression: a complex of unphosphorylated Stat1 and IRF1 supports transcription of the LMP2 gene. EMBO J. 2000. 19:4111–22.
Article37.Yang J., Chatterjee-Kishore M., Staugaitis SM., Nguyen H., Schlessinger K., Levy DE, et al. Novel roles of unphosphorylated STAT3 in oncogenesis and transcriptional regulation. Cancer Res. 2005. 65:939–47.38.Iacobelli S., Arno E., Sismondi P., Natoli C., Gentiloni N., Scambia G, et al. Measurement of a breast cancer associated antigen detected by monoclonal antibody SP-2 in sera of cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1988. 11:19–30.
Article39.Marchetti A., Tinari N., Buttitta F., Chella A., Angeletti CA., Sacco R, et al. Expression of 90K (Mac-2 BP) correlates with distant metastasis and predicts survival in stage I non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2002. 62:2535–9.40.Matarrese P., Fusco O., Tinari N., Natoli C., Liu FT., Semeraro ML, et al. Galectin-3 overexpression protects from apoptosis by improving cell adhesion properties. Int J Cancer. 2000. 85:545–54.
Article41.Sasaki T., Brakebusch C., Engel J., Timpl R. Mac-2 binding protein is a cell-adhesive protein of the extracellular matrix which self-assembles into ring-like structures and binds beta1 integrins, collagens and fibronectin. EMBO J. 1998. 17:1606–13.42.Fornarini B., D'Ambrosio C., Natoli C., Tinari N., Silingardi V., Iacobelli S. Adhesion to 90K (Mac-2 BP) as a mechanism for lymphoma drug resistance in vivo. Blood. 2000. 96:3282–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Enhanced Protein Expression of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 and Protein Kinase Substrate p36 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Role of STAT3-Interacting Protein (STIP1) in delta12-Prostaglandin J2-Induced Cell Death
- STAT3 inhibits the degradation of HIF-1alpha by pVHL-mediated ubiquitination
- STAT3 expression is associated with poor survival in non-elderly adult patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
- A mechanism of differential expression of GLUT2 in hepatocyte and pancreatic beta-cell line