Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2024 Nov;28(6):559-568. 10.4196/kjpp.2024.28.6.559.
Hemin attenuates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice by regulating the TGF-ββ1/MAPK and AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1αα/HO-1/ NF-κκB pathways
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Functional Experimental Training Center, Wu Hu 241002, China
- 2Department of Pathophysiology, Basic Medical College, Wannan Medical College, Wu Hu 241002, China
- 3Department of Medical Imageology, Wannan Medical College, Wu Hu 241002, China
- 4Department of Physiology, Basic Medical College, Wannan Medical College, Wu Hu 241002, China
- KMID: 2560735
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2024.28.6.559
Abstract
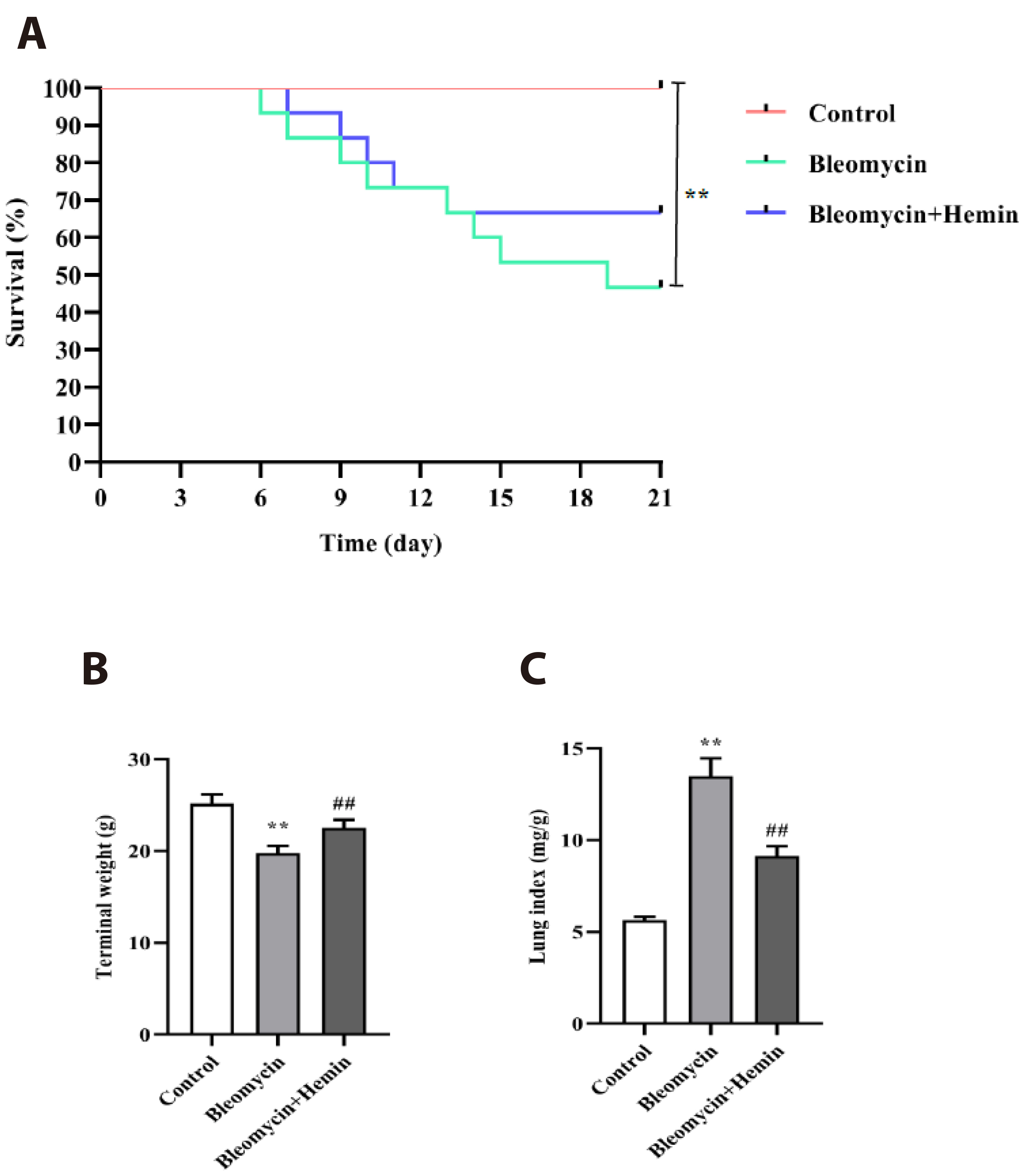
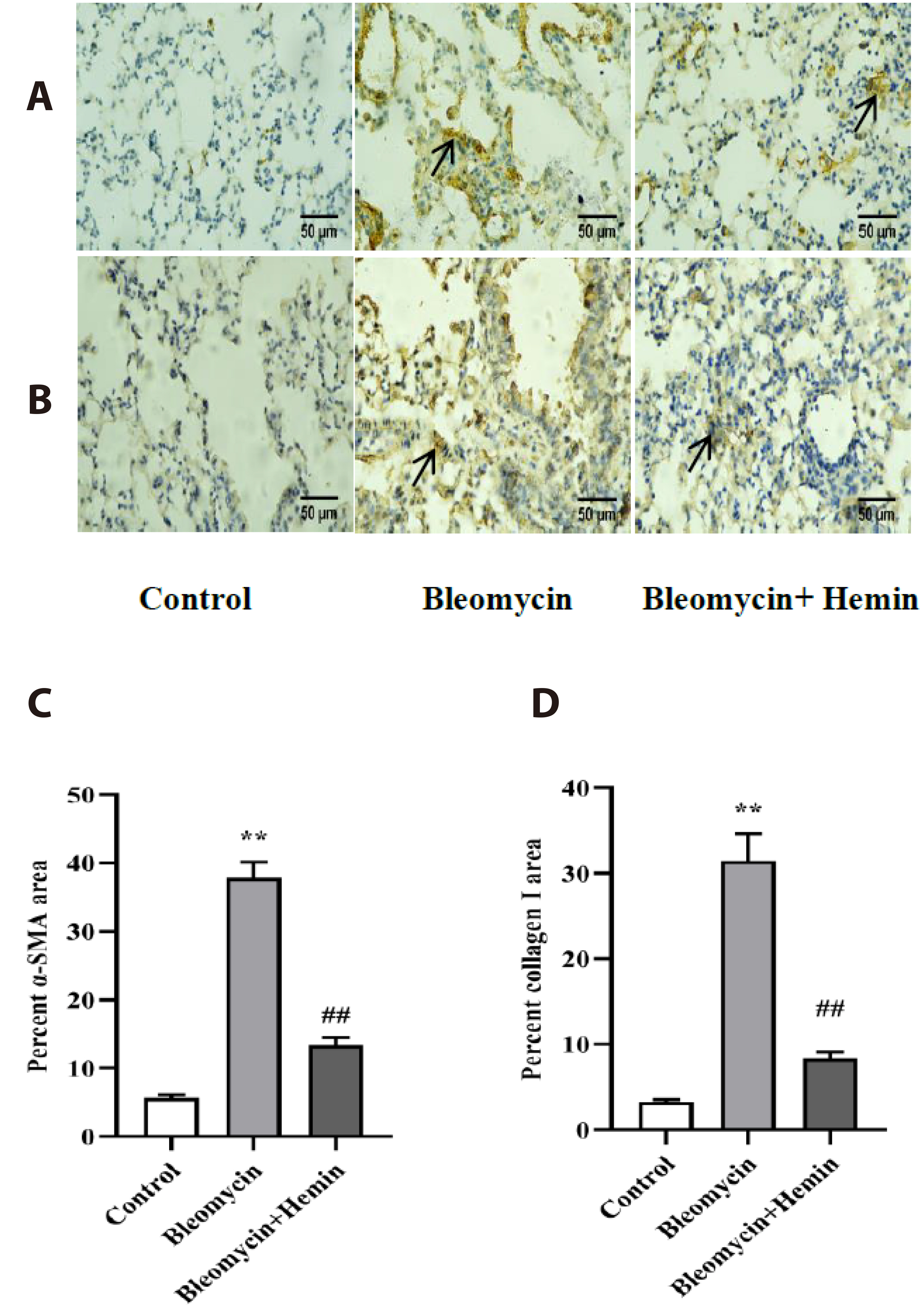
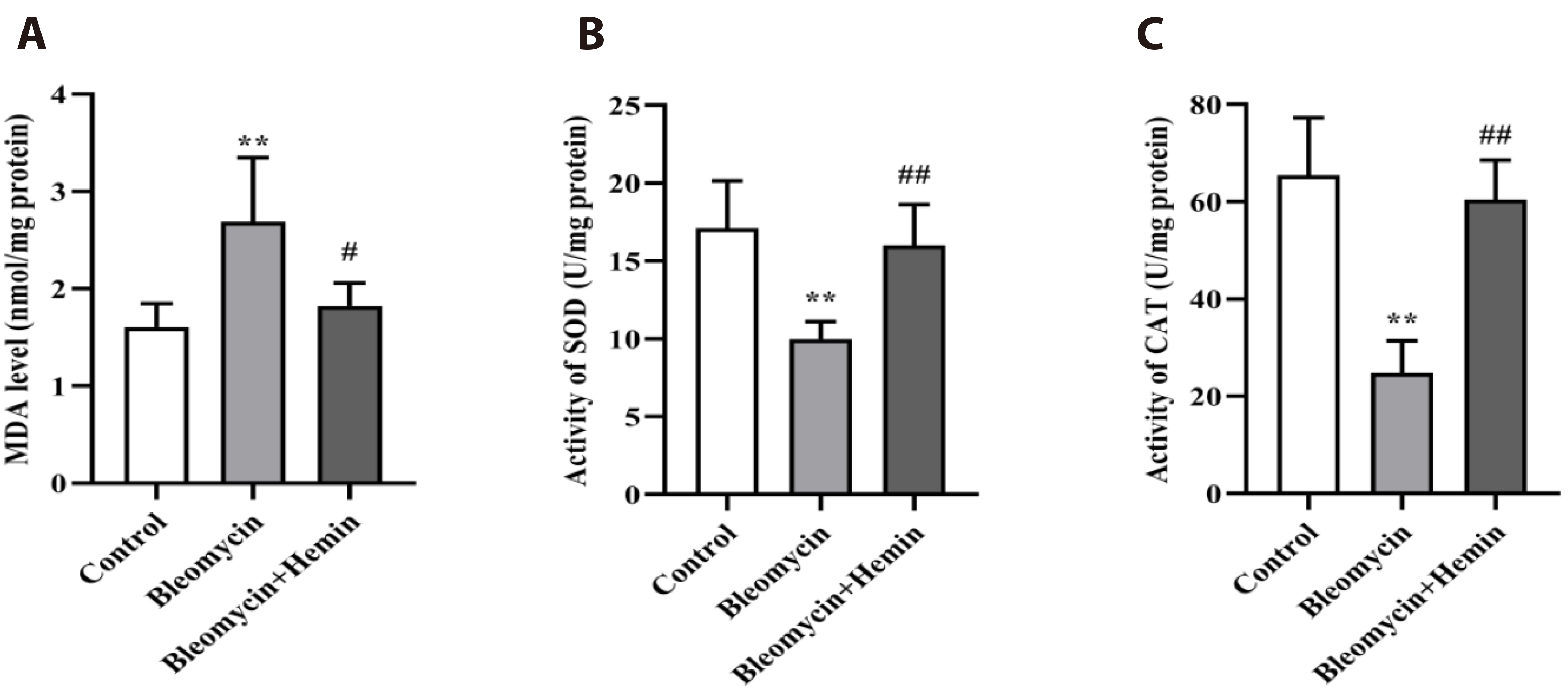
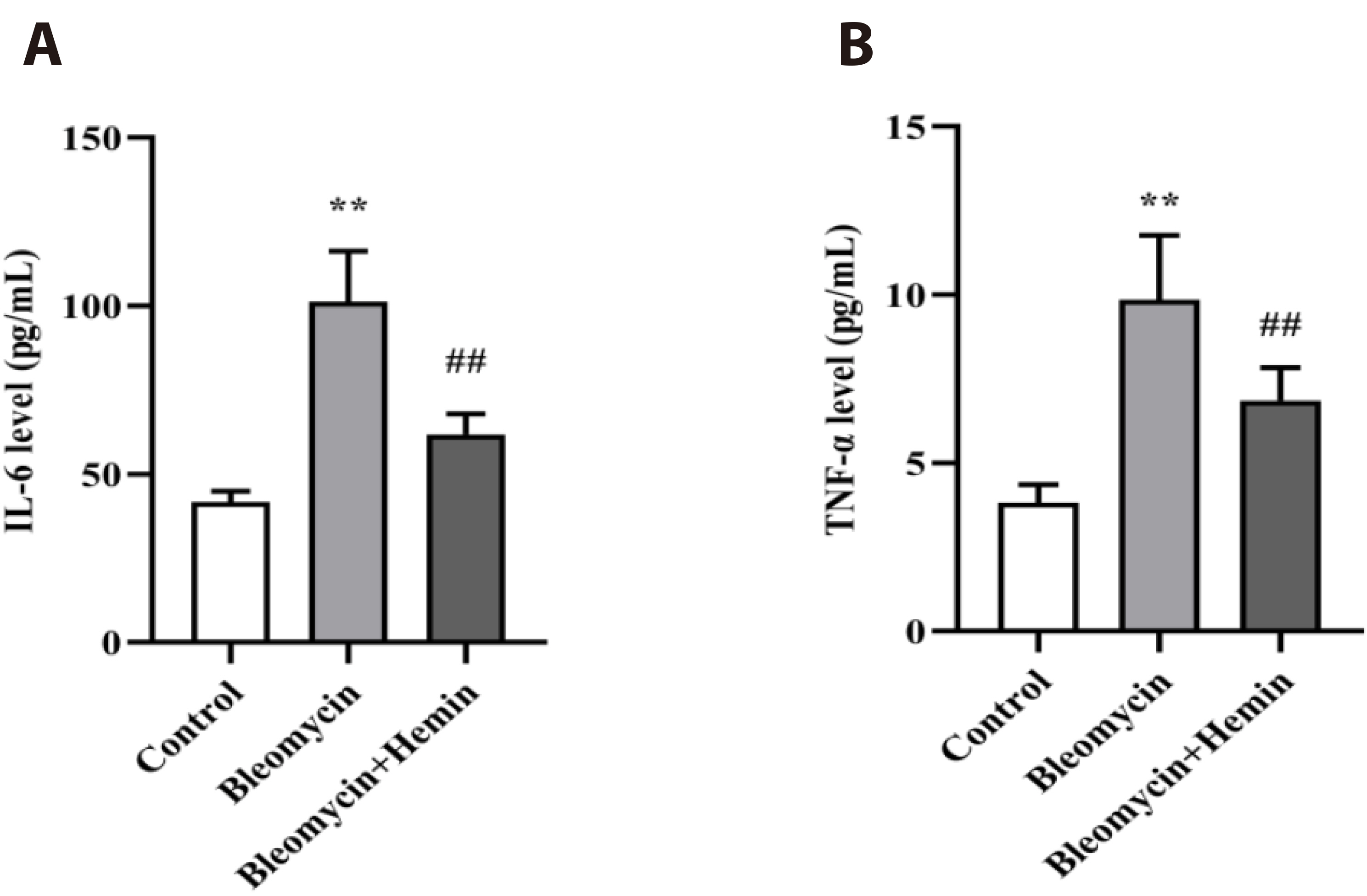
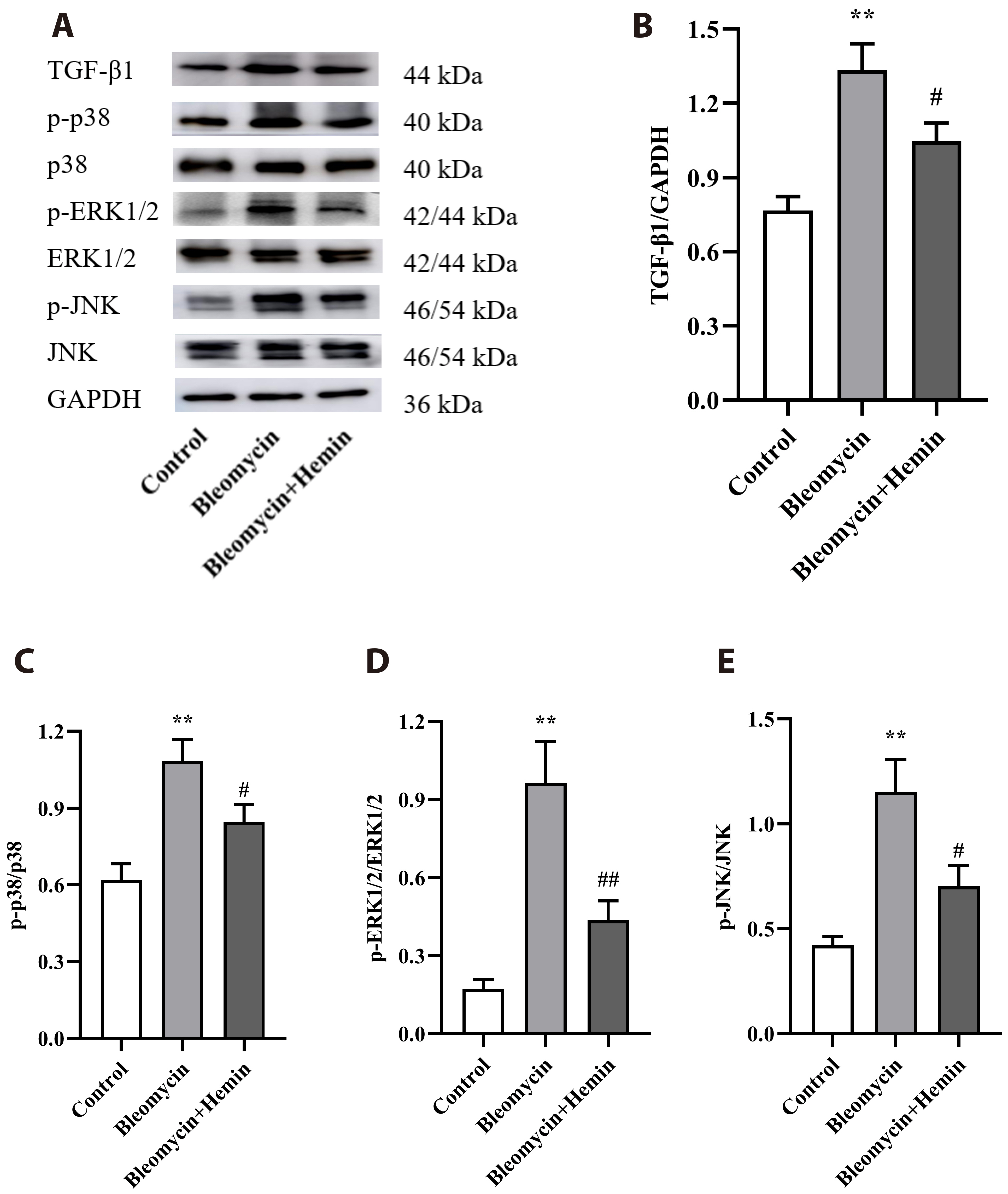
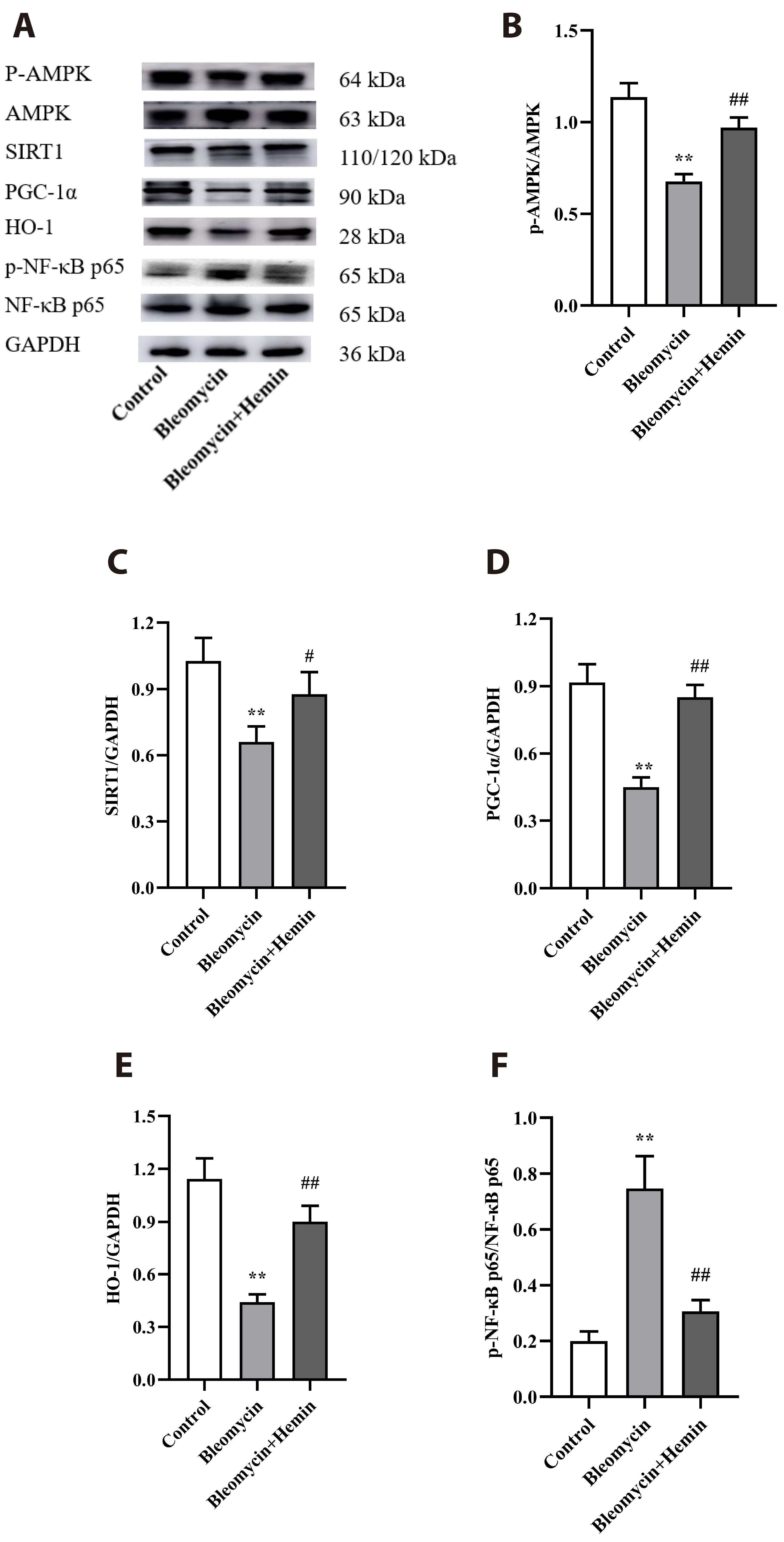
- The objective of this study was to investigate the protective effect and potential mechanism of action of hemin on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Male C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into control, bleomycin and bleomycin + hemin groups. Mice in the bleomycin and bleomycin + hemin groups were injected intratracheally with bleomycin to establish the pulmonary fibrosis model. The bleomycin + hemin group mice were injected intraperitoneally with hemin starting 7 days before modeling until the end of Day 21 after modeling. Pathological changes in lung tissue were assessed by HE and Masson staining. Malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) levels were determined in lung tissue. Immunohistochemistry was performed to assess the expression of α-SMA and collagen I. The serum levels of IL-6 and TNF-α were measured via ELISA. Western blotting was used to determine the expression of TGF-β1, SIRT1, PGC-1α and HO-1 and the phosphorylation levels of p38, ERK1/2, JNK, AMPK and NF-κB p65 in lung tissue. Hemin significantly reduced lung indices, increased terminal body weight. It also significantly increased SOD and CAT activities; decreased MDA, IL-6 and TNF-α levels; reduced the levels of α-SMA and collagen I-positive cells; upregulated SIRT1, PGC-1α and HO-1 expression; promoted AMPK phosphorylation; and downregulated TGF-β1 expression and p38, ERK1/2, JNK and NF-κB p65 phosphorylation. Hemin might attenuate oxidative damage and inflammatory responses and reduces extracellular matrix deposition by regulating the expression and phosphorylation of proteins associated with the TGF-β1/MAPK and AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α/HO-1/ NF-κB pathways, thereby alleviating bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Santos G, Fabiano A, Mota PC, Rodrigues I, Carvalho D, Melo N, Novais-Bastos H, Alexandre AT, Moura CS, Guimarães S, Pereira JM, Carvalho A, Morais A. 2023; The impact of nintedanib and pirfenidone on lung function and survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in real-life setting. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 83:102261–102267. DOI: 10.1016/j.pupt.2023.102261. PMID: 37758002.2. Chanda D, Otoupalova E, Smith SR, Volckaert T, De Langhe SP, Thannickal VJ. 2019; Developmental pathways in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis. Mol Aspects Med. 65:56–69. DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2018.08.004. PMID: 30130563. PMCID: PMC6374163.3. Canestaro WJ, Forrester SH, Raghu G, Ho L, Devine BE. 2016; Drug treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Chest. 149:756–766. DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2015.11.013. PMID: 26836914.4. Justet A, Klay D, Porcher R, Cottin V, Ahmad K, Molina Molina M, Nunes H, Reynaud-Gaubert M, Naccache JM, Manali E, Froidure A, Jouneau S, Wemeau L, Andrejak C, Gondouin A, Hirschi S, Blanchard E, Bondue B, Bonniaud P, Tromeur C, et al. ; OrphaLung Network. 2021; Safety and efficacy of pirfenidone and nintedanib in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and carrying a telomere-related gene mutation. Eur Respir J. 57:2003198–2003201. DOI: 10.1183/13993003.03198-2020. PMID: 33214205.5. Collins BF, Raghu G. 2019; Antifibrotic therapy for fibrotic lung disease beyond idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir Rev. 28:190022–190036. DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0022-2019. PMID: 31578210. PMCID: PMC9489066.6. Lancaster LH, de Andrade JA, Zibrak JD, Padilla ML, Albera C, Nathan SD, Wijsenbeek MS, Stauffer JL, Kirchgaessler KU, Costabel U. 2017; Pirfenidone safety and adverse event management in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir Rev. 26:170057–170066. DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0057-2017. PMID: 29212837. PMCID: PMC9488585.7. Spagnolo P, Kropski JA, Jones MG, Lee JS, Rossi G, Karampitsakos T, Maher TM, Tzouvelekis A, Ryerson CJ. 2021; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: disease mechanisms and drug development. Pharmacol Ther. 222:107798–107808. DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107798. PMID: 33359599. PMCID: PMC8142468.8. Mastruzzo C, Crimi N, Vancheri C. 2002; Role of oxidative stress in pulmonary fibrosis. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 57:173–176. PMID: 12619377.9. Todd NW, Luzina IG, Atamas SP. 2012; Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 5:11–34. DOI: 10.1186/1755-1536-5-11. PMID: 22824096. PMCID: PMC3443459.10. Blanc PD, Annesi-Maesano I, Balmes JR, Cummings KJ, Fishwick D, Miedinger D, Murgia N, Naidoo RN, Reynolds CJ, Sigsgaard T, Torén K, Vinnikov D, Redlich CA. 2019; The occupational burden of nonmalignant respiratory diseases. An Official American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society Statement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 199:1312–1334. DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201904-0717ST. PMID: 31149852. PMCID: PMC6543721.11. Kim KK, Kugler MC, Wolters PJ, Robillard L, Galvez MG, Brumwell AN, Sheppard D, Chapman HA. 2006; Alveolar epithelial cell mesenchymal transition develops in vivo during pulmonary fibrosis and is regulated by the extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 103:13180–13185. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0605669103. PMID: 16924102. PMCID: PMC1551904.12. Saito A, Horie M, Micke P, Nagase T. 2018; The role of TGF-β signaling in lung cancer associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 19:E3611–E3624. DOI: 10.3390/ijms19113611. PMID: 30445777. PMCID: PMC6275044.13. Yang W, Li X, Qi S, Li X, Zhou K, Qing S, Zhang Y, Gao MQ. 2017; lncRNA H19 is involved in TGF-β1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in bovine epithelial cells through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. PeerJ. 5:e3950–e3964. DOI: 10.7717/peerj.3950. PMID: 29062612. PMCID: PMC5649593.14. Arthur JS, Ley SC. 2013; Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:679–692. DOI: 10.1038/nri3495. PMID: 23954936.15. Chien LH, Deng JS, Jiang WP, Chou YN, Lin JG, Huang GJ. 2023; Evaluation of lung protection of Sanghuangporus sanghuang through TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK, keap1/Nrf2/HO-1, CaMKK/AMPK/Sirt1, and TGF-β/SMAD3 signaling pathways mediating apoptosis and autophagy. Biomed Pharmacother. 165:115080–115092. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115080. PMID: 37392658.16. Wang D, Yan Z, Bu L, An C, Deng B, Zhang J, Rao J, Cheng L, Zhang J, Zhang B, Xie J. 2019; Protective effect of peptide DR8 on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by regulating the TGF-β/MAPK signaling pathway and oxidative stress. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 382:114703–114734. DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2019.114703. PMID: 31398421.17. Rangarajan S, Bone NB, Zmijewska AA, Jiang S, Park DW, Bernard K, Locy ML, Ravi S, Deshane J, Mannon RB, Abraham E, Darley-Usmar V, Thannickal VJ, Zmijewski JW. 2018; Metformin reverses established lung fibrosis in a bleomycin model. Nat Med. 24:1121–1127. Erratum in: Nat Med. 2018;24:1627-1644. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0087-6. PMID: 29967351. PMCID: PMC6081262.18. Xuan LL, Hou Q.19. Cheng X, Yin M, Sun X, Zhang Z, Yao X, Liu H, Xia H. 2023; Hemin attenuated LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice via protecting pulmonary epithelial barrier and regulating HO-1/NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. Shock. 59:744–753. DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002101. PMID: 36821407.20. Shimzu K, Takahashi T, Iwasaki T, Shimizu H, Inoue K, Morimatsu H, Omori E, Matsumi M, Akagi R, Morita K. 2008; Hemin treatment abrogates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension. Med Chem. 4:572–576. DOI: 10.2174/157340608786241972. PMID: 18991742.21. Even B, Fayad-Kobeissi S, Gagliolo JM, Motterlini R, Boczkowski J, Foresti R, Dagouassat M. 2018; Heme oxygenase-1 induction attenuates senescence in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease lung fibroblasts by protecting against mitochondria dysfunction. Aging Cell. 17:e12837–e12848. DOI: 10.1111/acel.12837. PMID: 30341816. PMCID: PMC6260925.22. Tian S, Ge X, Wu K, Yang H, Liu Y. 2014; Ramipril protects the endothelium from high glucose-induced dysfunction through CaMKKβ/AMPK and heme oxygenase-1 activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 350:5–13. DOI: 10.1124/jpet.114.212928. PMID: 24741076.23. Kosuru R, Kandula V, Rai U, Prakash S, Xia Z, Singh S. 2018; Pterostilbene decreases cardiac oxidative stress and inflammation via activation of AMPK/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in fructose-fed diabetic rats. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 32:147–163. DOI: 10.1007/s10557-018-6780-3. PMID: 29556862.24. Yang H, Zhao LF, Zhao ZF, Wang Y, Zhao JJ, Zhang L. 2012; Heme oxygenase-1 prevents liver fibrosis in rats by regulating the expression of PPARγ and NF-κB. World J Gastroenterol. 18:1680–1688. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i14.1680. PMID: 22529699. PMCID: PMC3325536.25. Cho RL, Lin WN, Wang CY, Yang CC, Hsiao LD, Lin CC, Yang CM. 2018; Heme oxygenase-1 induction by rosiglitazone via PKCα/AMPKα/p38 MAPKα/SIRT1/PPARγ pathway suppresses lipopolysaccharide-mediated pulmonary inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol. 148:222–237. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.12.024. PMID: 29309760.26. Ma WH, Li M, Ma HF, Li W, Liu L, Yin Y, Zhou XM, Hou G. 2020; Protective effects of GHK-Cu in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via anti-oxidative stress and anti-inflammation pathways. Life Sci. 241:117139–117151. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117139. PMID: 31809714.27. Canesin G, Di Ruscio A, Li M, Ummarino S, Hedblom A, Choudhury R, Krzyzanowska A, Csizmadia E, Palominos M, Stiehm A, Ebralidze A, Chen SY, Bassal MA, Zhao P, Tolosano E, Hurley L, Bjartell A, Tenen DG, Wegiel B. 2020; Scavenging of labile heme by hemopexin is a key checkpoint in cancer growth and metastases. Cell Rep. 32:108181–108123. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108181. PMID: 32966797. PMCID: PMC7551404.28. Collino M, Pini A, Mugelli N, Mastroianni R, Bani D, Fantozzi R, Papucci L, Fazi M, Masini E. 2013; Beneficial effect of prolonged heme oxygenase 1 activation in a rat model of chronic heart failure. Dis Model Mech. 6:1012–1020. DOI: 10.1242/dmm.011528. PMID: 23592614. PMCID: PMC3701220.29. Huang C, Gong H, Mu B, Lan X, Yang C, Tan J, Liu W, Zou Y, Li L, Feng B, He X, Luo Q, Chen Z. 2022; BAF-L modulates histone-to-protamine transition during spermiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 23:1985–2001. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23041985. PMID: 35216101. PMCID: PMC8877947.30. Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, Brown KK, Colby TV, Cordier JF, Flaherty KR, Lasky JA, Lynch DA, Ryu JH, Swigris JJ, Wells AU, Ancochea J, Bouros D, Carvalho C, Costabel U, Ebina M, Hansell DM, et al. ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Committee on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. 2011; An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 183:788–824. DOI: 10.1164/rccm.2009-040GL. PMID: 21471066. PMCID: PMC5450933.31. Yue YL, Zhang MY, Liu JY, Fang LJ, Qu YQ. 2022; The role of autophagy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: from mechanisms to therapies. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 16:1–21. DOI: 10.1177/17534666221140972. PMID: 36468453. PMCID: PMC9726854.32. Dove EP, Olson AL, Glassberg MK. 2019; Trends in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis-related mortality in the United States: 2000-2017. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 200:929–931. DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201905-0958LE. PMID: 31225965.33. Richeldi L, Collard HR, Jones MG. 2017; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 389:1941–1952. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30866-8. PMID: 28365056.34. Moore BB, Hogaboam CM. 2008; Murine models of pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 294:L152–L160. DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00313.2007. PMID: 17993587.35. Lown JW, Sim SK. 1977; The mechanism of the bleomycin-induced cleavage of DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 77:1150–1157. DOI: 10.1016/S0006-291X(77)80099-5. PMID: 71149.36. Sausville EA, Peisach J, Horwitz SB. 1976; A role for ferrous ion and oxygen in the degradation of DNA by bleomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 73:814–822. DOI: 10.1016/0006-291X(76)90882-2. PMID: 64249.37. Yang JY, Tao LJ, Liu B, You XY, Zhang CF, Xie HF, Li RS. 2019; Wedelolactone attenuates pulmonary fibrosis partly through activating AMPK and regulating Raf-MAPKs signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 10:151–162. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00151. PMID: 30890932. PMCID: PMC6411994.38. Johnson GL, Lapadat R. 2002; Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. DOI: 10.1126/science.1072682. PMID: 12471242.39. Hashimoto S, Gon Y, Takeshita I, Matsumoto K, Maruoka S, Horie T. 2001; Transforming growth factor-beta1 induces phenotypic modulation of human lung fibroblasts to myofibroblast through a c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase-dependent pathway. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 163:152–157. DOI: 10.1164/ajrccm.163.1.2005069. PMID: 11208641.40. Guo H, Jian Z, Liu H, Cui H, Deng H, Fang J, Zuo Z, Wang X, Zhao L, Geng Y, Ouyang P, Tang H. 2021; TGF-β1-induced EMT activation via both Smad-dependent and MAPK signaling pathways in Cu-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 418:115500–115510. DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2021.115500. PMID: 33744278.41. Sakon S, Xue X, Takekawa M, Sasazuki T, Okazaki T, Kojima Y, Piao JH, Yagita H, Okumura K, Doi T, Nakano H. 2003; NF-kappaB inhibits TNF-induced accumulation of ROS that mediate prolonged MAPK activation and necrotic cell death. EMBO J. 22:3898–3909. DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg379. PMID: 12881424. PMCID: PMC169052.42. Kamata H, Honda S, Maeda S, Chang L, Hirata H, Karin M. 2005; Reactive oxygen species promote TNFalpha-induced death and sustained JNK activation by inhibiting MAP kinase phosphatases. Cell. 120:649–661. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.041. PMID: 15766528.43. Dong H, Yang J, Wang Y, Jiang Y, Chen J, Zhang W, Lu Y, Chen L, Chen Y. 2020; Polysaccharide SAFP from Sarcodon aspratus attenuates oxidative stress-induced cell damage and bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Biol Macromol. 164:1215–1236. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.120. PMID: 32693133.44. Yang Z, Bian M, Ma J, Dong Y, Yang D, Qiu M, Gao Z. 2023; Berberine regulates pulmonary inflammatory microenvironment and decreases collagen deposition in response to bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 132:154–170. DOI: 10.1111/bcpt.13818. PMID: 36433932.45. Jiang S, Li T, Yang Z, Yi W, Di S, Sun Y, Wang D, Yang Y. 2017; AMPK orchestrates an elaborate cascade protecting tissue from fibrosis and aging. Ageing Res Rev. 38:18–27. DOI: 10.1016/j.arr.2017.07.001. PMID: 28709692.46. Gao R, Ma Z, Hu Y, Chen J, Shetty S, Fu J. 2015; Sirt1 restrains lung inflammasome activation in a murine model of sepsis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 308:L847–L853. DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00274.2014. PMID: 25659903. PMCID: PMC4398874.47. Ruderman NB, Xu XJ, Nelson L, Cacicedo JM, Saha AK, Lan F, Ido Y. 2010; AMPK and SIRT1: a long-standing partnership? Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 298:E751–E760. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00745.2009. PMID: 20103737. PMCID: PMC2853213.48. Rius-Pérez S, Torres-Cuevas I, Millán I, Ortega ÁL, Pérez S. 2020; PGC-1α, inflammation, and oxidative stress: an integrative view in metabolism. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020:1452696–1452715. DOI: 10.1155/2020/1452696. PMID: 32215168. PMCID: PMC7085407.49. Yoshida T, Biro P, Cohen T, Müller RM, Shibahara S. 1988; Human heme oxygenase cDNA and induction of its mRNA by hemin. Eur J Biochem. 171:457–461. DOI: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13811.x. PMID: 3345742.50. Keyse SM, Tyrrell RM. 1989; Heme oxygenase is the major 32-kDa stress protein induced in human skin fibroblasts by UVA radiation, hydrogen peroxide, and sodium arsenite. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 86:99–103. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.99. PMID: 2911585. PMCID: PMC286411.51. Tyrrell RM, Applegate LA, Tromvoukis Y. 1993; The proximal promoter region of the human heme oxygenase gene contains elements involved in stimulation of transcriptional activity by a variety of agents including oxidants. Carcinogenesis. 14:761–765. DOI: 10.1093/carcin/14.4.761. PMID: 8472344.52. Janssen YM, Marsh JP, Absher MP, Gabrielson E, Borm PJ, Driscoll K, Mossman BT. 1994; Oxidant stress responses in human pleural mesothelial cells exposed to asbestos. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 149:795–802. DOI: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.3.8118652. PMID: 8118652.53. Motterlini R, Foresti R, Bassi R, Calabrese V, Clark JE, Green CJ. 2000; Endothelial heme oxygenase-1 induction by hypoxia. Modulation by inducible nitric-oxide synthase and S-nitrosothiols. J Biol Chem. 275:13613–13620. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.275.18.13613. PMID: 10788478.54. Fredenburgh LE, Perrella MA, Mitsialis SA. 2007; The role of heme oxygenase-1 in pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 36:158–165. DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0331TR. PMID: 16980551. PMCID: PMC2176110.55. Ameeramja J, Perumal E. 2017; Protocatechuic acid methyl ester ameliorates fluoride toxicity in A549 cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 109:941–950. DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2016.12.024. PMID: 28012895.56. Park EJ, Kim YM, Chang KC. 2017; Hemin reduces HMGB1 release by UVB in an AMPK/HO-1-dependent pathway in human keratinocytes HaCaT cells. Arch Med Res. 48:423–431. DOI: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2017.10.007. PMID: 29089150.57. Ali FF, Mokhemer SA, Elroby Ali DM. 2022; Administration of hemin ameliorates ovarian ischemia reperfusion injury via modulation of heme oxygenase-1 and p-JNK/p-NF-κBp65/iNOS signaling pathway. Life Sci. 296:120431–120440. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120431. PMID: 35218766.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Deficiency of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 2 (S1Pâ‚‚) Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
- PGC1-alpha plays a role in hypothermic renal protection of renal fibrosis after acute kidney injury
- The Effects of Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia in Bleomycin-Induced Lung Injury on Pulmonary Fibrosis via Regulating the NF-κB/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway
- Effect of FTY-720 on Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice via the TGF-β1 Signaling Pathway and Autophagy
- Increased Cellular NAD⺠Level through NQO1 Enzymatic Action Has Protective Effects on Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis in Mice