Korean J Gastroenterol.
2024 Jul;84(1):9-16. 10.4166/kjg.2024.038.
Etiology and Outcomes of Patients with Extreme Hyperbilirubinemia in Korea: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine and Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea
- 2Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine and Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea
- KMID: 2558284
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2024.038
Abstract
- Background
/Aim: Extreme hyperbilirubinemia is occasionally observed in intensive care unit (ICU) and non-ICU settings. This study examined the etiologies of extreme hyperbilirubinemia (bilirubin level ≥12 mg/dL) and the factors associated with the 30-day mortality.
Methods
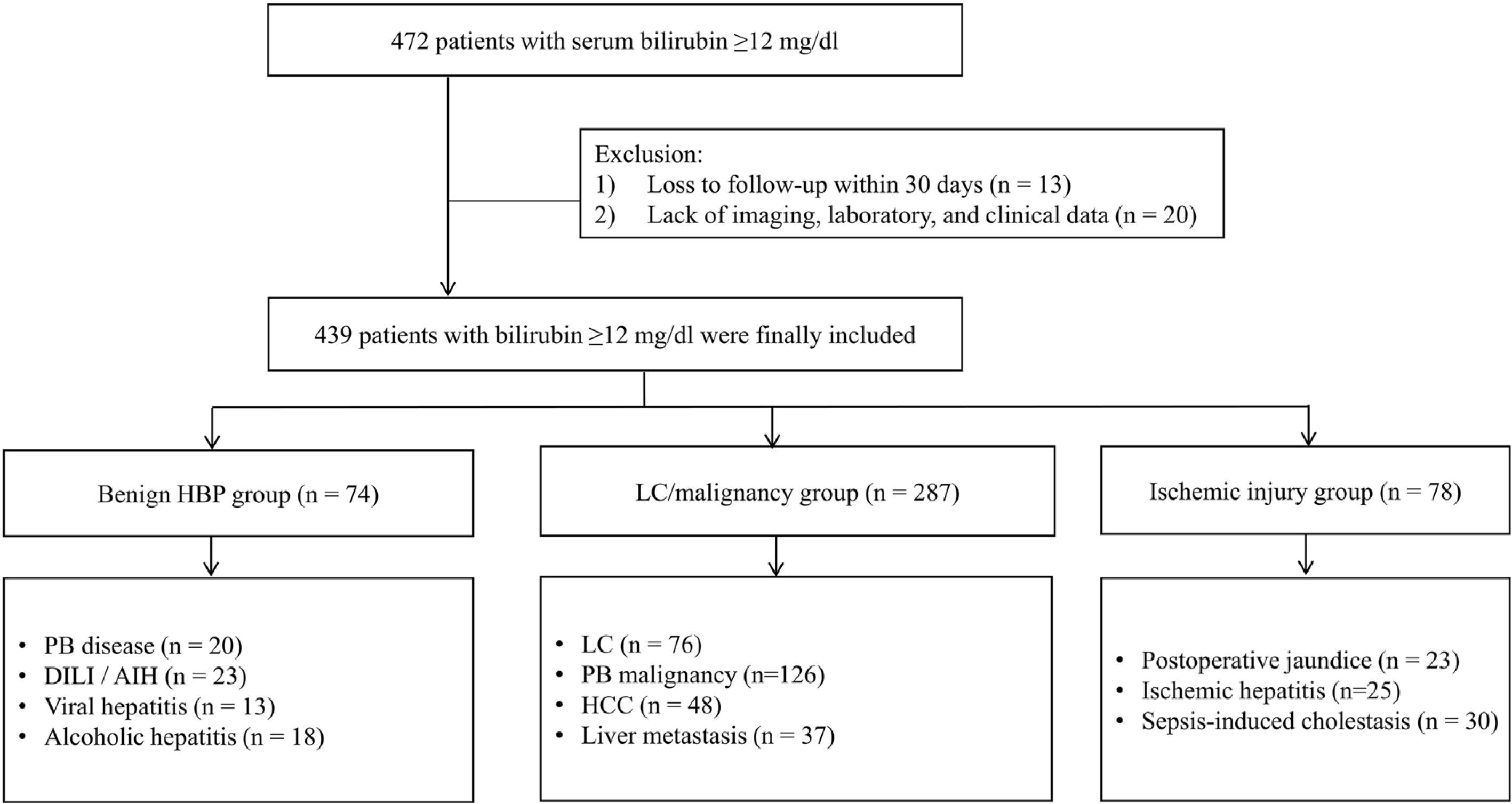
This retrospective observational cohort study identified 439 patients with extreme hyperbilirubinemia at the Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital between 2016 and 2020. The patients were classified into three groups and 11 diseases according to their etiology. The risk factors associated with 30-day mortality at the baseline were investigated using the Cox proportional hazards model.
Results
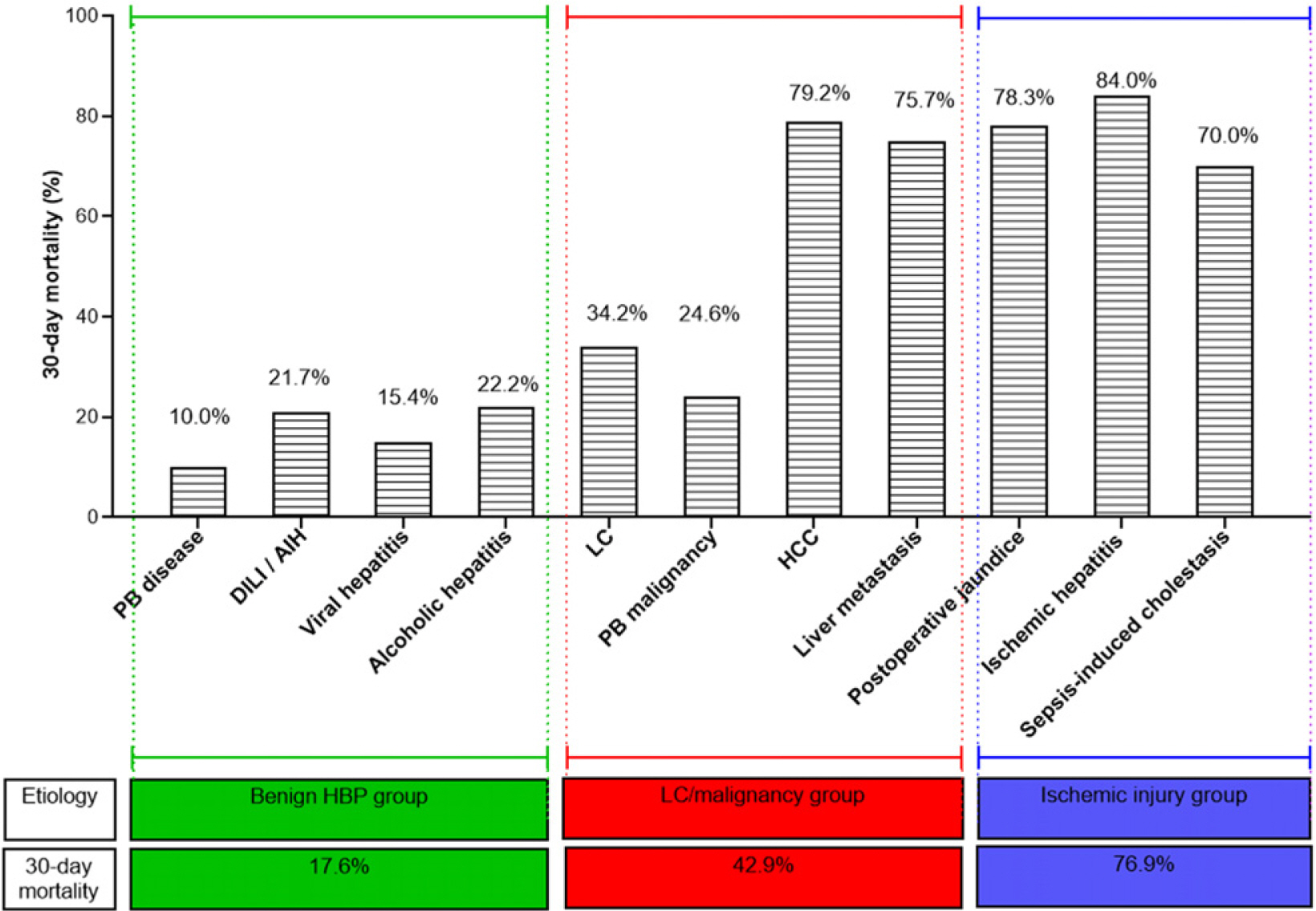
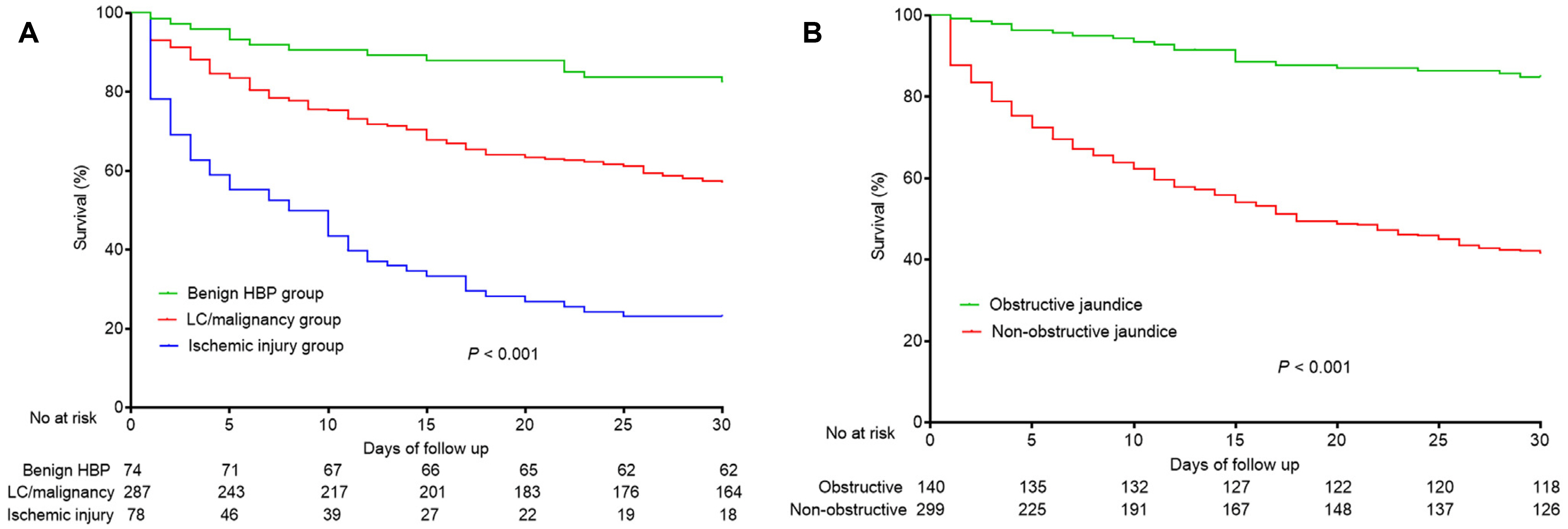
Of 439 patients with extreme hyperbilirubinemia, 287, 78, and 74 were in the liver cirrhosis/malignancy group, the ischemic injury group, and the benign hepatobiliary-pancreatic etiological group, respectively, with corresponding 30-day mortality rates of 42.9%, 76.9%, and 17.6%. The most common disease leading to hyperbilirubinemia was a pancreatobiliary malignancy (28.7%), followed by liver cirrhosis (17.3%), hepatocellular carcinoma (10.9%), and liver metastases (8.4%). The etiologies of hyperbilirubinemia, obstructive jaundice, infection, albumin level, creatinine level, and prothrombin time-international normalized ratio were independently associated with the 30-day mortality.
Conclusions
This study suggests three etiologies of extreme hyperbilirubinemia in the ICU and non-ICU settings. The prognosis of patients with extreme hyperbilirubinemia depends largely on the etiology and the presence of obstructive jaundice.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vuppalanchi R, Liangpunsakul S, Chalasani N. 2007; Etiology of new-onset jaundice: how often is it caused by idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury in the United States? Am J Gastroenterol. 102:558–562. quiz 693DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.01019.x. PMID: 17156142.
Article2. Whitehead MW, Hainsworth I, Kingham JG. 2001; The causes of obvious jaundice in South West Wales: perceptions versus reality. Gut. 48:409–413. DOI: 10.1136/gut.48.3.409. PMID: 11171834. PMCID: PMC1760136.
Article3. Björnsson E, Ismael S, Nejdet S, Kilander A. 2003; Severe jaundice in Sweden in the new millennium: causes, investigations, treatment and prognosis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 38:86–94. DOI: 10.1080/00365520310000492. PMID: 12608470.
Article4. Han HS, Park CM, Lee DS, Sinn DH, Gil E. 2021; Evaluating mortality and recovery of extreme hyperbilirubinemia in critically ill patients by phasing the peak bilirubin level: A retrospective cohort study. PLoS One. 16:e0255230. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255230. PMID: 34351969. PMCID: PMC8341602.
Article5. Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, et al. 1996; The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 22:707–710. DOI: 10.1007/BF01709751. PMID: 8844239.
Article6. Moreau R, Jalan R, Gines P, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a distinct syndrome that develops in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2013; 144:1426–1437. 1437.e1-9. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.02.042. PMID: 23474284.7. Kwo PY, Cohen SM, Lim JK. 2017; ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of abnormal liver chemistries. Am J Gastroenterol. 112:18–35. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2016.517. PMID: 27995906.
Article8. Kwak JY, Kim HG, Han JH, Jeon H, Cha RR, Lee SS. 2023; Association of the etiology and peak level of markedly elevated aminotransferases with mortality: a multicenter study. Hepatol Commun. 7:e0149. DOI: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000149. PMID: 37102763. PMCID: PMC10146537.
Article9. Whitehead MW, Hawkes ND, Hainsworth I, Kingham JG. 1999; A prospective study of the causes of notably raised aspartate aminotransferase of liver origin. Gut. 45:129–133. DOI: 10.1136/gut.45.1.129. PMID: 10369716. PMCID: PMC1727583.10. Galvin Z, McDonough A, Ryan J, Stewart S. 2015; Blood alanine aminotransferase levels >1,000 IU/l - causes and outcomes. Clin Med (Lond). 15:244–247. DOI: 10.7861/clinmedicine.15-3-244. PMID: 26031973. PMCID: PMC4953107.
Article11. Björnsson HK, Olafsson S, Bergmann OM, Björnsson ES. 2016; A prospective study on the causes of notably raised alanine aminotransferase (ALT). Scand J Gastroenterol. 51:594–600. DOI: 10.3109/00365521.2015.1121516. PMID: 26653080.
Article12. Van den Broecke A, Van Coile L, Decruyenaere A, et al. 2018; Epidemiology, causes, evolution and outcome in a single-center cohort of 1116 critically ill patients with hypoxic hepatitis. Ann Intensive Care. 8:15. DOI: 10.1186/s13613-018-0356-z. PMID: 29383510. PMCID: PMC5790763.13. Aboelsoud MM, Javaid AI, Al-Qadi MO, Lewis JH. 2017; Hypoxic hepatitis- its biochemical profile, causes and risk factors of mortality in critically-ill patients: A cohort study of 565 patients. J Crit Care. 41:9–15. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2017.04.040. PMID: 28460210.
Article14. Tapper EB, Sengupta N, Bonder A. 2015; The incidence and outcomes of ischemic hepatitis: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Am J Med. 128:1314–1321. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.07.033. PMID: 26299319.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epidemiology of Hyperbilirubinemia in a Quaternary Pediatric Emergency Department over a Three-Year Period
- Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia
- Etiology, Management, and Prognosis of Severe Hyperbilirubinemia (Serum Bilirubin Level=25 mg/dL) in Newborn
- Comparison of Bilirubin Levels in Neonates with Hyperbilirubinemia according to Delivery Methods
- Coexistence of Gilbert Syndrome and Hereditary Spherocytosis in a Child Presenting with Extreme Jaundice