Clin Endosc.
2024 Jul;57(4):527-533. 10.5946/ce.2023.129.
Safety and efficacy of novel oblique-viewing scope for B2-endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Aichi Cancer Center Hospital, Nagoya, Japan
- 2Post Graduate Medical Education Center, Ehime University Hospital, Toon, Japan
- 3Department of Gastroenterology and Metabology, Ehime University Graduate School of Medicine, Toon, Japan
- KMID: 2558110
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2023.129
Abstract
- Background/Aims
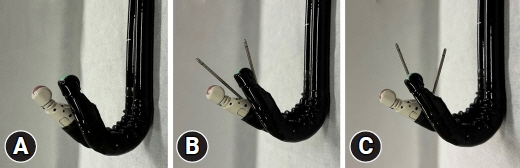
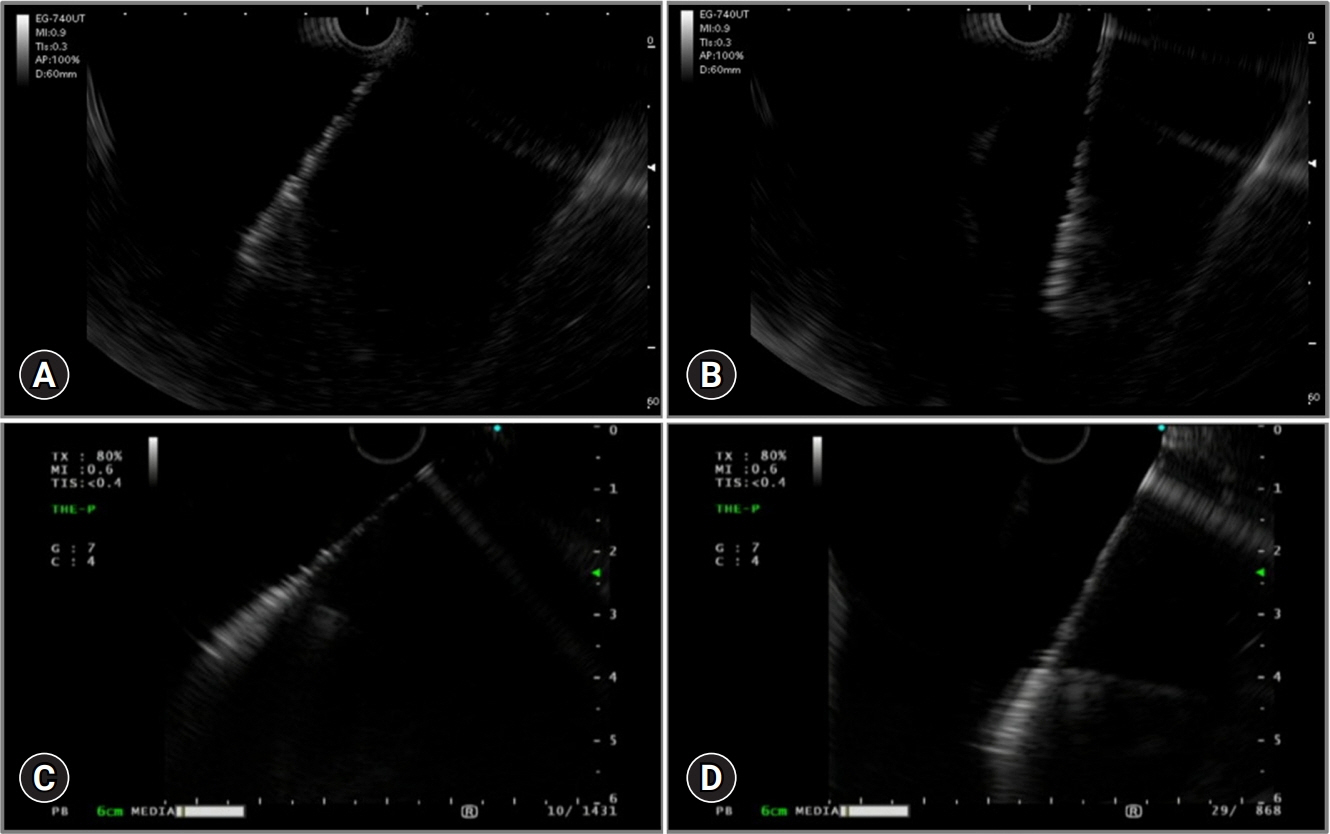
Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided hepaticogastrostomy (EUS-HGS) performed at the intrahepatic bile duct segment 3 (B3) is widely used for biliary drainage. Although performing post-puncture procedures is easier in the intrahepatic bile duct segment 2 (B2) when using a conventional oblique-viewing (OV) EUS scope, this method may cause transesophageal puncture and severe adverse events. We evaluated the safety and efficacy of B2 puncture using a novel OV-EUS scope.
Methods
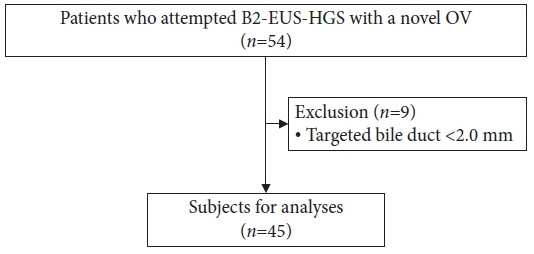
In this single-center retrospective study, we prospectively enrolled and collected data from 45 patients who consecutively underwent EUS-HGS procedures with a novel OV-EUS scope between September 2021 and December 2022 at our cancer center.
Results
The technical success rates of B2-EUS-HGS and EUS-HGS were 93.3% (42/45) and 97.8% (44/45), respectively. The early adverse event rate was 8.9% (4/45) with no cases of scope changes or transesophageal punctures. The median procedure time was 13 minutes (range, 5–30).
Conclusions
B2-EUS-HGS can be performed safely with the novel EG-740UT (Fujifilm) OV-scope without transesophageal puncture and with a high success rate. B2-EUS-HGS using this novel OV scope may be the preferred strategy for EUS-HGS.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hara K, Yamao K, Mizuno N, et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided biliary drainage: who, when, which, and how? World J Gastroenterol. 2016; 22:1297–1303.
Article2. Okuno N, Hara K, Mizuno N, et al. Efficacy of the 6-mm fully covered self-expandable metal stent during endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy as a primary biliary drainage for the cases estimated difficult endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: a prospective clinical study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018; 33:1413–1421.
Article3. Matsubara S, Nakagawa K, Suda K, et al. Practical tips for safe and successful endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy: a state-of-the-art technical review. J Clin Med. 2022; 11:1591.
Article4. Pawa R, Pleasant T, Tom C, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage: are we there yet? World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2021; 13:302–318.
Article5. Vila JJ, Pérez-Miranda M, Vazquez-Sequeiros E, et al. Initial experience with EUS-guided cholangiopancreatography for biliary and pancreatic duct drainage: a Spanish national survey. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:1133–1141.
Article6. Oh D, Park DH, Song TJ, et al. Optimal biliary access point and learning curve for endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy with transmural stenting. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2017; 10:42–53.
Article7. Isayama H, Nakai Y, Itoi T, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for safe performance of endoscopic ultrasound/ultrasonography-guided biliary drainage: 2018. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2019; 26:249–269.
Article8. Matsumoto S, Hara K, Mizuno N, et al. Risk factor analysis for adverse events and stent dysfunction of endoscopic ultrasound-guided choledochoduodenostomy. Dig Endosc. 2020; 32:957–966.
Article9. Hara K, Okuno N, Haba S, et al. How to perform EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy easier and safer. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2020; 27:563–564.
Article10. Sekine M, Hashimoto Y, Shibuki T, et al. A retrospective multicenter study comparing the punctures to B2 and B3 in endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy. DEN Open. 2023; 3:e201.
Article11. Okuno N, Hara K, Mizuno N, et al. B2 puncture with forward-viewing EUS simplifies EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy (with video). Endosc Ultrasound. 2022; 11:319–324.
Article12. Tsuchiya T, Itoi T, Sofuni A, et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided rendezvous technique. Dig Endosc. 2016; 28 Suppl 1:96–101.
Article13. Okuno N, Hara K, Mizuno N, et al. Risks of transesophageal endoscopic ultrasonography-guided biliary drainage. Gastrointest Interv. 2017; 6:82–84.
Article14. Ogura T, Itoi T. Technical tips and recent development of endoscopic ultrasound-guided choledochoduodenostomy. DEN Open. 2021; 1:e8.
Article15. Samanta J, Sundaram S, Dhar J, et al. EUS-guided biliary drainage in patients with moderate-severe cholangitis is safe and effective: a multi-center experience. Surg Endosc. 2023; 37:298–308.
Article16. Okuno N, Hara K, Mizuno N, et al. Infectious peritonitis after endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage in a patient with ascites. Gastrointest Interv. 2018; 7:40–43.
Article17. Okuno N, Hara K, Mizuno N, et al. Stent migration into the peritoneal cavity following endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy. Endoscopy. 2015; 47 Suppl 1 UCTN:E311.
Article18. Cotton PB, Eisen GM, Aabakken L, et al. A lexicon for endoscopic adverse events: report of an ASGE workshop. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:446–454.
Article19. Dell’Anna G, Ogura T, Vanella G, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound guided biliary interventions. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2022; 60-61:101810.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy by puncturing both B2 and B3: a single center experience
- Recent development of endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage
- Follow-up computed tomography can prevent stent migration after endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy
- Technical Review of Developments in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Hepaticogastrostomy
- Safety of endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy in patients with malignant biliary obstruction and ascites