Ann Lab Med.
2024 Jul;44(4):354-358. 10.3343/alm.2023.0412.
Comparison of Measurable Residual Disease in Pediatric B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia Using Multiparametric Flow Cytometry and Next-Generation Sequencing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2557934
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.0412
Abstract
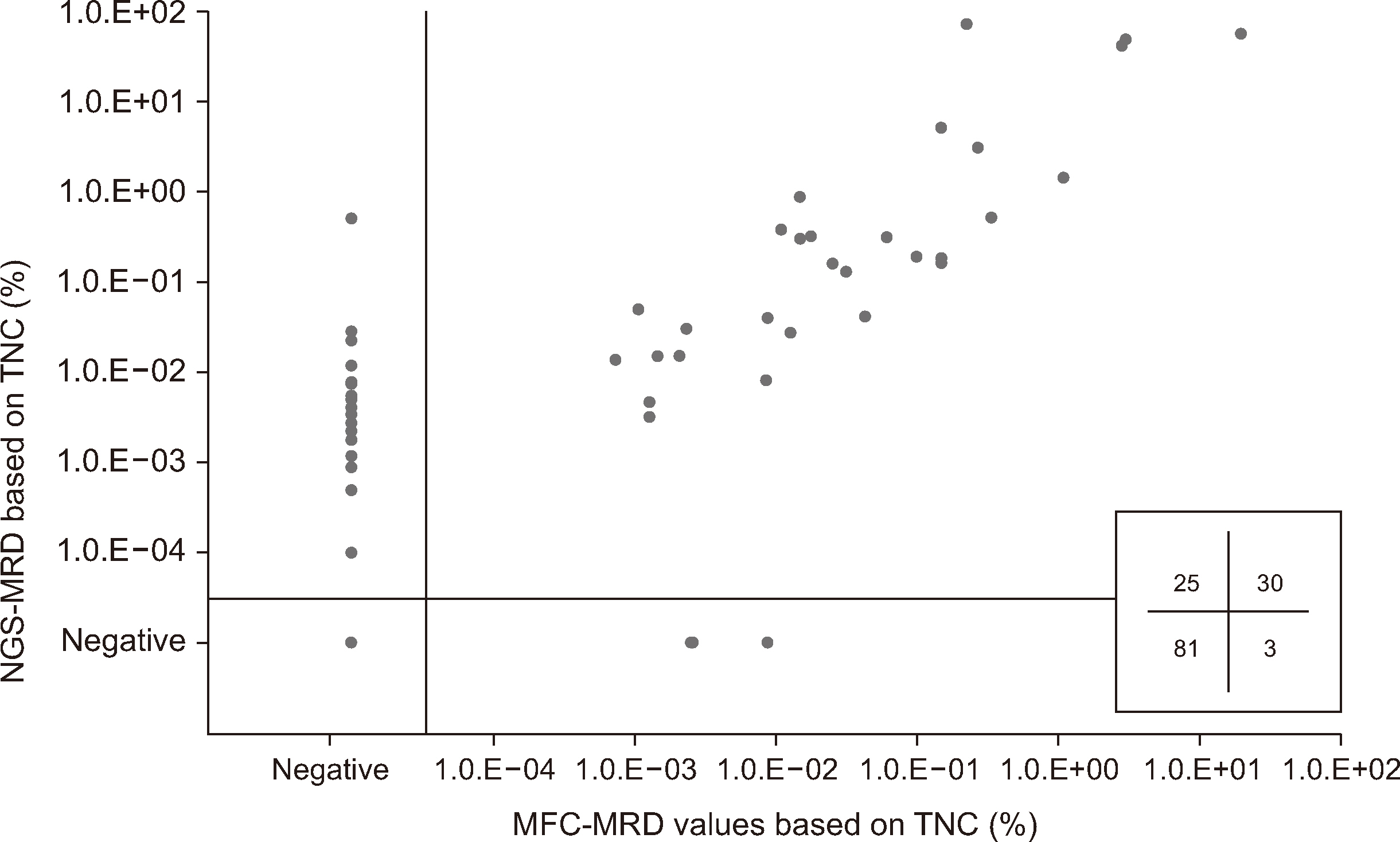
- Measurable residual disease (MRD) testing, a standard procedure in B-lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) diagnostics, is assessed using multiparametric flow cytometry (MFC) and next-generation sequencing (NGS) analysis of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. We evaluated the concordance between eight-color, two-tube MFC-MRD the LymphoTrack NGS-MRD assays using 139 follow-up samples from 54 pediatric patients with B-ALL. We also assessed the effect of hemodilution in MFC-MRD assays. The MRD-concordance rate was 79.9% (N = 111), with 25 (18.0%) and 3 (2.2%) samples testing positive only by NGSMRD (MFC − NGS + MRD) and MFC-MRD (MFC + NGS − MRD), respectively. We found a significant correlation in MRD values from total nucleated cells between the two methods (r = 0.736 [0.647–0.806], P < 0.001). The median MRD value of MFC − NGS + MRD samples was estimated to be 0.0012% (0.0001%–0.0263%) using the NGS-MRD assays. Notably, 14.3% of MFC − NGS + MRD samples showed NGS-MRD values below the limit of detection in the MFC-MRD assays. The percentages of hematogones detected in MFC-MRD assays significantly differed between the discordant and concordant cases (P < 0.001). MFC and NGS-MRD assays showed relatively high concordance and correlation in MRD assessment, whereas the NGS-MRD assay detected MRD more frequently than the MFC-MRD assay in pediatric B-ALL. Evaluating the hematogone percentages can aid in assessing the impact of sample hemodilution.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Brown P, Inaba H, Annesley C, Beck J, Colace S, Dallas M, et al. 2020; Pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia, version 2.2020, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 18:81–112. DOI: 10.6004/jnccn.2020.0001. PMID: 31910389.
Article2. Berry DA, Zhou S, Higley H, Mukundan L, Fu S, Reaman GH, et al. 2017; Association of minimal residual disease with clinical outcome in pediatric and adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 3:e170580. DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0580. PMID: 28494052. PMCID: PMC5824235.3. Cherian S, Soma LA. 2021; How I diagnose minimal/measurable residual disease in B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma by flow cytometry. Am J Clin Pathol. 155:38–54. DOI: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa242. PMID: 33236071.
Article4. Kim HY, Yoo IY, Lim DJ, Kim HJ, Kim SH, Yoon SE, et al. 2022; Clinical utility of next-generation flow-based minimal residual disease assessment in patients with multiple myeloma. Ann Lab Med. 42:558–65. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.5.558. PMID: 35470273. PMCID: PMC9057816.
Article5. Theunissen P, Mejstrikova E, Sedek L, van der Sluijs-Gelling AJ, Gaipa G, Bartels M, et al. 2017; Standardized flow cytometry for highly sensitive MRD measurements in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 129:347–57. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-07-726307. PMID: 27903527. PMCID: PMC5291958.
Article6. Wood B, Wu D, Crossley B, Dai Y, Williamson D, Gawad C, et al. 2018; Measurable residual disease detection by high-throughput sequencing improves risk stratification for pediatric B-ALL. Blood. 131:1350–9. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2017-09-806521. PMID: 29284596. PMCID: PMC5865233.
Article7. Paulsen K, Marincevic M, Cavelier L, Hollander P, Amini RM. 2022; LymphoTrack is equally sensitive as PCR GeneScan and Sanger sequencing for detection of clonal rearrangements in ALL patients. Diagnostics (Basel). 12:1389. DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12061389. PMID: 35741199. PMCID: PMC9222020. PMID: 59daed8511b247a0a966a0b0a83c5d19.
Article8. Wu D, Emerson RO, Sherwood A, Loh ML, Angiolillo A, Howie B, et al. 2014; Detection of minimal residual disease in B lymphoblastic leukemia by high-throughput sequencing of IGH. Clin Cancer Res. 20:4540–8. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3231. PMID: 24970842. PMCID: PMC5142743.9. Short NJ, Kantarjian H, Ravandi F, Konopleva M, Jain N, Kanagal-Shamanna R, et al. 2022; High-sensitivity next-generation sequencing MRD assessment in ALL identifies patients at very low risk of relapse. Blood Adv. 6:4006–14. DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022007378. PMID: 35533262. PMCID: PMC9278301.
Article10. Cheng S, Inghirami G, Cheng S, Tam W. 2018; Simple deep sequencing-based post-remission MRD surveillance predicts clinical relapse in B-ALL. J Hematol Oncol. 11:105. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-018-0652-y. PMID: 30134947. PMCID: PMC6103872. PMID: d7da29e8787e4610b0cda54e76957a87.
Article11. Cherian S, Miller V, McCullouch V, Dougherty K, Fromm JR, Wood BL. 2018; A novel flow cytometric assay for detection of residual disease in patients with B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma post anti-CD19 therapy. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 94:112–20. DOI: 10.1002/cyto.b.21482. PMID: 27598971.
Article12. Flores-Montero J, Sanoja-Flores L, Paiva B, Puig N, García-Sánchez O, Böttcher S, et al. 2017; Next generation flow for highly sensitive and standardized detection of minimal residual disease in multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 31:2094–103. DOI: 10.1038/leu.2017.29. PMID: 28104919. PMCID: PMC5629369.
Article13. Momen N, Tario J, Fu K, Qian YW. 2023; Multiparameter flow cytometry and ClonoSEQ correlation to evaluate precursor B-lymphoblastic leukemia measurable residual disease. J Hematopathol. 16:85–94. DOI: 10.1007/s12308-023-00544-9. PMID: 38175444.
Article14. Chen W, Karandikar NJ, McKenna RW, Kroft SH. 2007; Stability of leukemia-associated immunophenotypes in precursor B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma: a single institution experience. Am J Clin Pathol. 127:39–46. DOI: 10.1309/7R6MU7R9YWJBY5V4. PMID: 17145625.
Article15. Lee JW, Kim Y, Ahn A, Lee JM, Yoo JW, Kim S, et al. 2022; Clinical implication of minimal residual disease assessment by next-generation sequencing-based immunoglobulin clonality assay in pediatric B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Front Oncol. 12:957743. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.957743. PMID: 36185293. PMCID: PMC9521036. PMID: 980933830448449e973d16bb75c2529b.
Article16. Dworzak MN, Gaipa G, Ratei R, Veltroni M, Schumich A, Maglia O, et al. 2008; Standardization of flow cytometric minimal residual disease evaluation in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: multicentric assessment is feasible. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 74:331–40. DOI: 10.1002/cyto.b.20430. PMID: 18548617.
Article17. Kriegsmann K, Hundemer M, Hofmeister-Mielke N, Reichert P, Manta CP, Awwad MHS, et al. 2020; Comparison of NGS and MFC methods: Key metrics in multiple myeloma MRD assessment. Cancers (Basel). 12:2322. DOI: 10.3390/cancers12082322. PMID: 32824635. PMCID: PMC7464347. PMID: 11561f474ce44996ac5ae432665b4577.
Article18. Hoffmann J, Thrun MC, Röhnert MA, von Bonin M, Oelschlägel U, Neubauer A, et al. 2023; Identification of critical hemodilution by artificial intelligence in bone marrow assessed for minimal residual disease analysis in acute myeloid leukemia: the Cinderella method. Cytometry A. 103:304–12. DOI: 10.1002/cyto.a.24686. PMID: 36030398.
Article19. Mai H, Li Q, Wang G, Wang Y, Liu S, Tang X, et al. 2023; Clinical application of next-generation sequencing-based monitoring of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 149:3259–66. DOI: 10.1007/s00432-022-04151-6. PMID: 35918464.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relevance of flow cytometric categorization and end-of-induction measurable residual disease assessment in pediatric and adult T-lymphoblastic leukemia patients
- Immunophenotyping of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia by flow cytometry
- Measurements of treatment response in childhood acute leukemia
- Minimal Residual Disease Detection in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- Minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: technical aspects and implications for clinical interpretation