Endocrinol Metab.
2024 Apr;39(2):191-205. 10.3803/EnM.2023.1910.
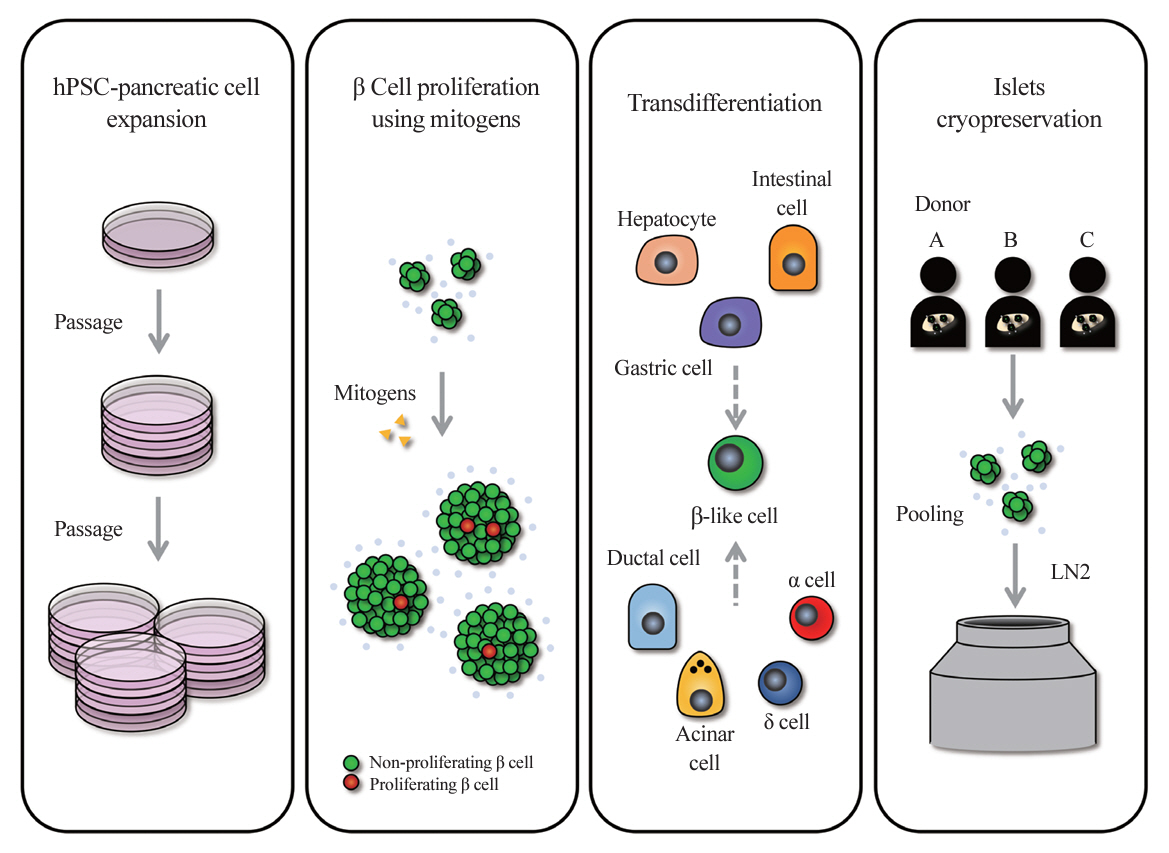
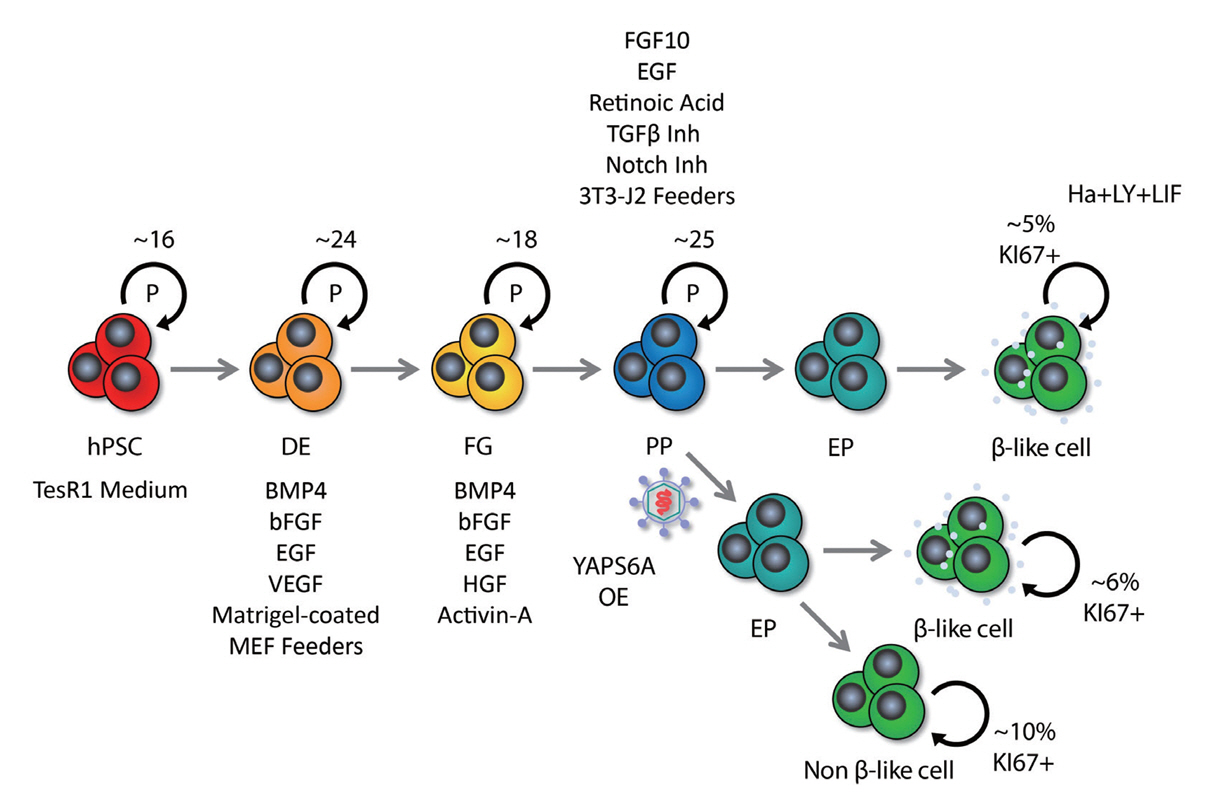
Scaling Insulin-Producing Cells by Multiple Strategies
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Lundquist Institute for Biomedical Innovation at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, Torrance, CA, USA
- 2David Geffen School of Medicine at University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, USA
- KMID: 2554625
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1910
Abstract
- In the quest to combat insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM), allogenic pancreatic islet cell therapy sourced from deceased donors represents a significant therapeutic advance. However, the applicability of this approach is hampered by donor scarcity and the demand for sustained immunosuppression. Human induced pluripotent stem cells are a game-changing resource for generating synthetic functional insulin-producing β cells. In addition, novel methodologies allow the direct expansion of pancreatic progenitors and mature β cells, thereby circumventing prolonged differentiation. Nevertheless, achieving practical reproducibility and scalability presents a substantial challenge for this technology. As these innovative approaches become more prominent, it is crucial to thoroughly evaluate existing expansion techniques with an emphasis on their optimization and scalability. This manuscript delineates these cutting-edge advancements, offers a critical analysis of the prevailing strategies, and underscores pivotal challenges, including cost-efficiency and logistical issues. Our insights provide a roadmap, elucidating both the promises and the imperatives in harnessing the potential of these cellular therapies for IDDM.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ashcroft FM, Rorsman P. Diabetes mellitus and the β cell: the last ten years. Cell. 2012; 148:1160–71.
Article2. Rutter GA, Georgiadou E, Martinez-Sanchez A, Pullen TJ. Metabolic and functional specialisations of the pancreatic beta cell: gene disallowance, mitochondrial metabolism and intercellular connectivity. Diabetologia. 2020; 63:1990–8.
Article3. Ikegami H, Babaya N, Noso S. β-Cell failure in diabetes: common susceptibility and mechanisms shared between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. 2021; 12:1526–39.4. Rezania A, Bruin JE, Arora P, Rubin A, Batushansky I, Asadi A, et al. Reversal of diabetes with insulin-producing cells derived in vitro from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2014; 32:1121–33.
Article5. Pagliuca FW, Millman JR, Gurtler M, Segel M, Van Dervort A, Ryu JH, et al. Generation of functional human pancreatic β cells in vitro. Cell. 2014; 159:428–39.
Article6. Russ HA, Parent AV, Ringler JJ, Hennings TG, Nair GG, Shveygert M, et al. Controlled induction of human pancreatic progenitors produces functional beta-like cells in vitro. EMBO J. 2015; 34:1759–72.7. Yoshihara E, Wei Z, Lin CS, Fang S, Ahmadian M, Kida Y, et al. ERRγ is required for the metabolic maturation of therapeutically functional glucose-responsive β cells. Cell Metab. 2016; 23:622–34.8. Vegas AJ, Veiseh O, Gurtler M, Millman JR, Pagliuca FW, Bader AR, et al. Long-term glycemic control using polymer-encapsulated human stem cell-derived beta cells in immune-competent mice. Nat Med. 2016; 22:306–11.
Article9. Hogrebe NJ, Augsornworawat P, Maxwell KG, Velazco-Cruz L, Millman JR. Targeting the cytoskeleton to direct pancreatic differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2020; 38:460–70.
Article10. Yoshihara E, O’Connor C, Gasser E, Wei Z, Oh TG, Tseng TW, et al. Immune-evasive human islet-like organoids ameliorate diabetes. Nature. 2020; 586:606–11.
Article11. Balboa D, Barsby T, Lithovius V, Saarimaki-Vire J, Omar-Hmeadi M, Dyachok O, et al. Functional, metabolic and transcriptional maturation of human pancreatic islets derived from stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2022; 40:1042–55.
Article12. Deng H, Zhang A, Pang DR, Xi Y, Yang Z, Matheson R, et al. Bioengineered omental transplant site promotes pancreatic islet allografts survival in non-human primates. Cell Rep Med. 2023; 4:100959.13. Ramzy A, Thompson DM, Ward-Hartstonge KA, Ivison S, Cook L, Garcia RV, et al. Implanted pluripotent stem-cell-derived pancreatic endoderm cells secrete glucose-responsive C-peptide in patients with type 1 diabetes. Cell Stem Cell. 2021; 28:2047–61.
Article14. Shapiro AM, Thompson D, Donner TW, Bellin MD, Hsueh W, Pettus J, et al. Insulin expression and C-peptide in type 1 diabetes subjects implanted with stem cell-derived pancreatic endoderm cells in an encapsulation device. Cell Rep Med. 2021; 2:100466.
Article15. Keymeulen B, De Groot K, Jacobs-Tulleneers-Thevissen D, Thompson DM, Bellin MD, Kroon EJ, et al. Encapsulated stem cell-derived β cells exert glucose control in patients with type 1 diabetes. Nat Biotechnol. 2023; Nov. 27. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-023-02055-5.
Article16. Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, Korbutt GS, Toth E, Warnock GL, et al. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343:230–8.
Article17. Salib A, Cayabyab F, Yoshihara E. Stem cell-derived islets for type 2 diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23:5099.
Article18. Yoshihara E. Adapting physiology in functional human islet organogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022; 10:854604.
Article19. Parsons JA, Brelje TC, Sorenson RL. Adaptation of islets of Langerhans to pregnancy: increased islet cell proliferation and insulin secretion correlates with the onset of placental lactogen secretion. Endocrinology. 1992; 130:1459–66.
Article20. Toselli C, Hyslop CM, Hughes M, Natale DR, Santamaria P, Huang CT. Contribution of a non-β-cell source to β-cell mass during pregnancy. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e100398.
Article21. Lam CJ, Cox AR, Jacobson DR, Rankin MM, Kushner JA. Highly proliferative α-cell-related islet endocrine cells in human pancreata. Diabetes. 2018; 67:674–86.
Article22. Dai C, Hang Y, Shostak A, Poffenberger G, Hart N, Prasad N, et al. Age-dependent human β cell proliferation induced by glucagon-like peptide 1 and calcineurin signaling. J Clin Invest. 2017; 127:3835–44.
Article23. Aamodt KI, Aramandla R, Brown JJ, Fiaschi-Taesch N, Wang P, Stewart AF, et al. Development of a reliable automated screening system to identify small molecules and biologics that promote human β-cell regeneration. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016; 311:E859–68.
Article24. Wang P, Alvarez-Perez JC, Felsenfeld DP, Liu H, Sivendran S, Bender A, et al. A high-throughput chemical screen reveals that harmine-mediated inhibition of DYRK1A increases human pancreatic beta cell replication. Nat Med. 2015; 21:383–8.
Article25. Wang P, Karakose E, Liu H, Swartz E, Ackeifi C, Zlatanic V, et al. Combined inhibition of DYRK1A, SMAD, and trithorax pathways synergizes to induce robust replication in adult human beta cells. Cell Metab. 2019; 29:638–52.
Article26. Rosado-Olivieri EA, Aigha II, Kenty JH, Melton DA. Identification of a LIF-responsive, replication-competent subpopulation of human β cells. Cell Metab. 2020; 31:327–38.
Article27. Ferber S, Halkin A, Cohen H, Ber I, Einav Y, Goldberg I, et al. Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox gene 1 induces expression of insulin genes in liver and ameliorates streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia. Nat Med. 2000; 6:568–72.
Article28. Shen CN, Slack JM, Tosh D. Molecular basis of transdifferentiation of pancreas to liver. Nat Cell Biol. 2000; 2:879–87.
Article29. Eicher AK, Kechele DO, Sundaram N, Berns HM, Poling HM, Haines LE, et al. Functional human gastrointestinal organoids can be engineered from three primary germ layers derived separately from pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2022; 29:36–51.
Article30. Lee J, Sugiyama T, Liu Y, Wang J, Gu X, Lei J, et al. Expansion and conversion of human pancreatic ductal cells into insulin-secreting endocrine cells. Elife. 2013; 2:e00940.
Article31. Rhee M, Lee SH, Kim JW, Ham DS, Park HS, Yang HK, et al. Preadipocyte factor 1 induces pancreatic ductal cell differentiation into insulin-producing cells. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:23960.
Article32. Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007; 131:861–72.
Article33. Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006; 126:663–76.
Article34. Kim K, Doi A, Wen B, Ng K, Zhao R, Cahan P, et al. Epigenetic memory in induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 2010; 467:285–90.
Article35. Bulic-Jakus F, Katusic Bojanac A, Juric-Lekic G, Vlahovic M, Sincic N. Teratoma: from spontaneous tumors to the pluripotency/malignancy assay. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2016; 5:186–209.
Article36. Li X, Yang KY, Chan VW, Leung KT, Zhang XB, Wong AS, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals that CD9 is a negative marker of glucose-responsive pancreatic β-like cells derived from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2020; 15:1111–26.
Article37. Veres A, Faust AL, Bushnell HL, Engquist EN, Kenty JH, Harb G, et al. Charting cellular identity during human in vitro β-cell differentiation. Nature. 2019; 569:368–73.
Article38. Davis JC, Alves TC, Helman A, Chen JC, Kenty JH, Cardone RL, et al. Glucose response by stem cell-derived β cells in vitro is inhibited by a bottleneck in glycolysis. Cell Rep. 2020; 31:107623.39. Augsornworawat P, Maxwell KG, Velazco-Cruz L, Millman JR. Single-cell transcriptome profiling reveals β cell maturation in stem cell-derived islets after transplantation. Cell Rep. 2020; 32:108067.
Article40. Velazco-Cruz L, Song J, Maxwell KG, Goedegebuure MM, Augsornworawat P, Hogrebe NJ, et al. Acquisition of dynamic function in human stem cell-derived β cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2019; 12:351–65.
Article41. Nair GG, Liu JS, Russ HA, Tran S, Saxton MS, Chen R, et al. Recapitulating endocrine cell clustering in culture promotes maturation of human stem-cell-derived β cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2019; 21:263–74.
Article42. Dorrell C, Schug J, Canaday PS, Russ HA, Tarlow BD, Grompe MT, et al. Human islets contain four distinct subtypes of β cells. Nat Commun. 2016; 7:11756.
Article43. Ameri J, Borup R, Prawiro C, Ramond C, Schachter KA, Scharfmann R, et al. Efficient generation of glucose-responsive beta cells from isolated GP2+ human pancreatic progenitors. Cell Rep. 2017; 19:36–49.
Article44. Cogger KF, Sinha A, Sarangi F, McGaugh EC, Saunders D, Dorrell C, et al. Glycoprotein 2 is a specific cell surface marker of human pancreatic progenitors. Nat Commun. 2017; 8:331.
Article45. Ramond C, Glaser N, Berthault C, Ameri J, Kirkegaard JS, Hansson M, et al. Reconstructing human pancreatic differentiation by mapping specific cell populations during development. Elife. 2017; 6:e27564.
Article46. Jiang W, Sui X, Zhang D, Liu M, Ding M, Shi Y, et al. CD24: a novel surface marker for PDX1-positive pancreatic progenitors derived from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2011; 29:609–17.
Article47. Rubio-Navarro A, Gomez-Banoy N, Stoll L, Dundar F, Mawla AM, Ma L, et al. A beta cell subset with enhanced insulin secretion and glucose metabolism is reduced in type 2 diabetes. Nat Cell Biol. 2023; 25:565–78.
Article48. Augsornworawat P, Hogrebe NJ, Ishahak M, Schmidt MD, Marquez E, Maestas MM, et al. Single-nucleus multi-omics of human stem cell-derived islets identifies deficiencies in lineage specification. Nat Cell Biol. 2023; 25:904–16.
Article49. Huang X, Gu W, Zhang J, Lan Y, Colarusso JL, Li S, et al. Stomach-derived human insulin-secreting organoids restore glucose homeostasis. Nat Cell Biol. 2023; 25:778–86.
Article50. Choi J, Cayabyab F, Yoshihara E. A guide from the stomach to β cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2023; 25:637–8.
Article51. Tahbaz M, Yoshihara E. Immune protection of stem cell-derived islet cell therapy for treating diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021; 12:716625.
Article52. Perez VL, Caicedo A, Berman DM, Arrieta E, Abdulreda MH, Rodriguez-Diaz R, et al. The anterior chamber of the eye as a clinical transplantation site for the treatment of diabetes: a study in a baboon model of diabetes. Diabetologia. 2011; 54:1121–6.
Article53. Bartholomeus K, Jacobs-Tulleneers-Thevissen D, Shouyue S, Suenens K, In’t Veld PA, Pipeleers-Marichal M, et al. Omentum is better site than kidney capsule for growth, differentiation, and vascularization of immature porcine β-cell implants in immunodeficient rats. Transplantation. 2013; 96:1026–33.
Article54. Mandal PK, Ferreira LM, Collins R, Meissner TB, Boutwell CL, Friesen M, et al. Efficient ablation of genes in human hematopoietic stem and effector cells using CRISPR/Cas9. Cell Stem Cell. 2014; 15:643–52.
Article55. Han X, Wang M, Duan S, Franco PJ, Kenty JH, Hedrick P, et al. Generation of hypoimmunogenic human pluripotent stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019; 116:10441–6.
Article56. Ye Q, Sung TC, Yang JM, Ling QD, He Y, Higuchi A. Generation of universal and hypoimmunogenic human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Prolif. 2020; 53:e12946.
Article57. Shi L, Li W, Liu Y, Chen Z, Hui Y, Hao P, et al. Generation of hypoimmunogenic human pluripotent stem cells via expression of membrane-bound and secreted β2m-HLA-G fusion proteins. Stem Cells. 2020; 38:1423–37.
Article58. Cefalu WT, Andersen DK, Arreaza-Rubin G, Pin CL, Sato S, Verchere CB, et al. Heterogeneity of diabetes: β-cells, phenotypes, and precision medicine: Proceedings of an International Symposium of the Canadian Institutes of Health Research’s Institute of Nutrition, Metabolism and Diabetes and the U.S. National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Diabetes. 2022; 71:1–22.
Article59. Desai T, Shea LD. Advances in islet encapsulation technologies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017; 16:338–50.
Article60. Cayabyab F, Nih LR, Yoshihara E. Advances in pancreatic islet transplantation sites for the treatment of diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021; 12:732431.
Article61. Khatri R, Hussmann B, Rawat D, Gurol AO, Linn T. Intraportal transplantation of pancreatic islets in mouse model. J Vis Exp. 2018; 135:57559.
Article62. Warnock GL, Rajotte RV. Critical mass of purified islets that induce normoglycemia after implantation into dogs. Diabetes. 1988; 37:467–70.
Article63. Lingwal N, Padmasekar M, Samikannu B, Bretzel RG, Preissner KT, Linn T. Inhibition of gelatinase B (matrix metalloprotease-9) activity reduces cellular inflammation and restores function of transplanted pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 2012; 61:2045–53.
Article64. Chen C, Moreno R, Samikannu B, Bretzel RG, Schmitz ML, Linn T. Improved intraportal islet transplantation outcome by systemic IKK-beta inhibition: NF-κB activity in pancreatic islets depends on oxygen availability. Am J Transplant. 2011; 11:215–24.
Article65. Cardona K, Korbutt GS, Milas Z, Lyon J, Cano J, Jiang W, et al. Long-term survival of neonatal porcine islets in nonhuman primates by targeting costimulation pathways. Nat Med. 2006; 12:304–6.
Article66. Hering BJ, Wijkstrom M, Graham ML, Hardstedt M, Aasheim TC, Jie T, et al. Prolonged diabetes reversal after intraportal xenotransplantation of wild-type porcine islets in immunosuppressed nonhuman primates. Nat Med. 2006; 12:301–3.
Article67. van der Windt DJ, Bottino R, Casu A, Campanile N, Smetanka C, He J, et al. Long-term controlled normoglycemia in diabetic non-human primates after transplantation with hCD46 transgenic porcine islets. Am J Transplant. 2009; 9:2716–26.
Article68. Kroon E, Martinson LA, Kadoya K, Bang AG, Kelly OG, Eliazer S, et al. Pancreatic endoderm derived from human embryonic stem cells generates glucose-responsive insulin-secreting cells in vivo. Nat Biotechnol. 2008; 26:443–52.
Article69. Scharp DW, Lacy PE, Santiago JV, McCullough CS, Weide LG, Falqui L, et al. Insulin independence after islet transplantation into type I diabetic patient. Diabetes. 1990; 39:515–8.
Article70. Miller CA, Brooks EF, DeFriese GH, Gilbert B, Jain SC, Kavaler F. A survey of local public health departments and their directors. Am J Public Health. 1977; 67:931–9.
Article71. Ryan EA, Lakey JR, Paty BW, Imes S, Korbutt GS, Kneteman NM, et al. Successful islet transplantation: continued insulin reserve provides long-term glycemic control. Diabetes. 2002; 51:2148–57.72. Liu H, Li R, Liao HK, Min Z, Wang C, Yu Y, et al. Chemical combinations potentiate human pluripotent stem cell-derived 3D pancreatic progenitor clusters toward functional β cells. Nat Commun. 2021; 12:3330.
Article73. Braam MJ, Zhao J, Liang S, Ida S, Kloostra NK, Iworima DG, et al. Protocol development to further differentiate and transition stem cell-derived pancreatic progenitors from a monolayer into endocrine cells in suspension culture. Sci Rep. 2023; 13:8877.
Article74. Ma Q, Xiao Y, Xu W, Wang M, Li S, Yang Z, et al. ZnT8 loss-of-function accelerates functional maturation of hESC-derived β cells and resists metabolic stress in diabetes. Nat Commun. 2022; 13:4142.
Article75. Du Y, Liang Z, Wang S, Sun D, Wang X, Liew SY, et al. Human pluripotent stem-cell-derived islets ameliorate diabetes in non-human primates. Nat Med. 2022; 28:272–82.
Article76. Yoshihara M, Hayashizaki Y, Murakawa Y. Genomic instability of iPSCs: challenges towards their clinical applications. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2017; 13:7–16.
Article77. Wang P, Fiaschi-Taesch NM, Vasavada RC, Scott DK, Garcia-Ocana A, Stewart AF. Diabetes mellitus: advances and challenges in human β-cell proliferation. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015; 11:201–12.
Article78. Cozar-Castellano I, Weinstock M, Haught M, VelazquezGarcia S, Sipula D, Stewart AF. Evaluation of beta-cell replication in mice transgenic for hepatocyte growth factor and placental lactogen: comprehensive characterization of the G1/S regulatory proteins reveals unique involvement of p21cip. Diabetes. 2006; 55:70–7.
Article79. Fiaschi-Taesch N, Bigatel TA, Sicari B, Takane KK, Salim F, Velazquez-Garcia S, et al. Survey of the human pancreatic beta-cell G1/S proteome reveals a potential therapeutic role for cdk-6 and cyclin D1 in enhancing human beta-cell replication and function in vivo. Diabetes. 2009; 58:882–93.80. Fiaschi-Taesch NM, Salim F, Kleinberger J, Troxell R, Cozar-Castellano I, Selk K, et al. Induction of human beta-cell proliferation and engraftment using a single G1/S regulatory molecule, cdk6. Diabetes. 2010; 59:1926–36.81. Georgia S, Hinault C, Kawamori D, Hu J, Meyer J, Kanji M, et al. Cyclin D2 is essential for the compensatory beta-cell hyperplastic response to insulin resistance in rodents. Diabetes. 2010; 59:987–96.82. Stamateris RE, Sharma RB, Kong Y, Ebrahimpour P, Panday D, Ranganath P, et al. Glucose induces mouse β-cell proliferation via IRS2, MTOR, and cyclin D2 but not the insulin receptor. Diabetes. 2016; 65:981–95.
Article83. Ackeifi C, Swartz E, Kumar K, Liu H, Chalada S, Karakose E, et al. Pharmacologic and genetic approaches define human pancreatic β cell mitogenic targets of DYRK1A inhibitors. JCI Insight. 2020; 5:e132594.
Article84. Dirice E, Walpita D, Vetere A, Meier BC, Kahraman S, Hu J, et al. Inhibition of DYRK1A stimulates human β-cell proliferation. Diabetes. 2016; 65:1660–71.
Article85. Wang P, Karakose E, Argmann C, Wang H, Balev M, Brody RI, et al. Disrupting the DREAM complex enables proliferation of adult human pancreatic β cells. J Clin Invest. 2022; 132:e157086.
Article86. Xiao X, Wiersch J, El-Gohary Y, Guo P, Prasadan K, Paredes J, et al. TGFβ receptor signaling is essential for inflammation-induced but not β-cell workload-induced β-cell proliferation. Diabetes. 2013; 62:1217–26.
Article87. Lin HM, Lee JH, Yadav H, Kamaraju AK, Liu E, Zhigang D, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta/Smad3 signaling regulates insulin gene transcription and pancreatic islet beta-cell function. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284:12246–57.88. Mussmann R, Geese M, Harder F, Kegel S, Andag U, Lomow A, et al. Inhibition of GSK3 promotes replication and survival of pancreatic beta cells. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282:12030–7.
Article89. Purwana I, Zheng J, Li X, Deurloo M, Son DO, Zhang Z, et al. GABA promotes human β-cell proliferation and modulates glucose homeostasis. Diabetes. 2014; 63:4197–205.
Article90. Untereiner A, Abdo S, Bhattacharjee A, Gohil H, Pourasgari F, Ibeh N, et al. GABA promotes β-cell proliferation, but does not overcome impaired glucose homeostasis associated with diet-induced obesity. FASEB J. 2019; 33:3968–84.
Article91. Abdolazimi Y, Zhao Z, Lee S, Xu H, Allegretti P, Horton TM, et al. CC-401 promotes β-cell replication via pleiotropic consequences of DYRK1A/B inhibition. Endocrinology. 2018; 159:3143–57.
Article92. Ackeifi C, Wang P, Karakose E, Manning Fox JE, Gonzalez BJ, Liu H, et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists synergize with DYRK1A inhibitors to potentiate functional human β cell regeneration. Sci Transl Med. 2020; 12:eaaw9996.
Article93. Trott J, Tan EK, Ong S, Titmarsh DM, Denil SL, Giam M, et al. Long-term culture of self-renewing pancreatic progenitors derived from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2017; 8:1675–88.
Article94. Kimura A, Toyoda T, Nishi Y, Nasu M, Ohta A, Osafune K. Small molecule AT7867 proliferates PDX1-expressing pancreatic progenitor cells derived from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2017; 24:61–8.
Article95. Ma X, Lu Y, Zhou Z, Li Q, Chen X, Wang W, et al. Human expandable pancreatic progenitor-derived β cells ameliorate diabetes. Sci Adv. 2022; 8:eabk1826.
Article96. Wang D, Wang J, Bai L, Pan H, Feng H, Clevers H, et al. Long-term expansion of pancreatic islet organoids from resident Procr+ progenitors. Cell. 2020; 180:1198–211.
Article97. Shen W, Taylor B, Jin Q, Nguyen-Tran V, Meeusen S, Zhang YQ, et al. Inhibition of DYRK1A and GSK3B induces human β-cell proliferation. Nat Commun. 2015; 6:8372.
Article98. Dhawan S, Dirice E, Kulkarni RN, Bhushan A. Inhibition of TGF-β signaling promotes human pancreatic β-cell replication. Diabetes. 2016; 65:1208–18.
Article99. Ludwig TE, Levenstein ME, Jones JM, Berggren WT, Mitchen ER, Frane JL, et al. Derivation of human embryonic stem cells in defined conditions. Nat Biotechnol. 2006; 24:185–7.
Article100. Cheng CW, Adams GB, Perin L, Wei M, Zhou X, Lam BS, et al. Prolonged fasting reduces IGF-1/PKA to promote hematopoietic-stem-cell-based regeneration and reverse immunosuppression. Cell Stem Cell. 2014; 14:810–23.
Article101. Hannan NR, Fordham RP, Syed YA, Moignard V, Berry A, Bautista R, et al. Generation of multipotent foregut stem cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2013; 1:293–306.
Article102. Rosado-Olivieri EA, Anderson K, Kenty JH, Melton DA. YAP inhibition enhances the differentiation of functional stem cell-derived insulin-producing β cells. Nat Commun. 2019; 10:1464.
Article103. Mazur P. Freezing of living cells: mechanisms and implications. Am J Physiol. 1984; 247(3 Pt 1):C125–42.
Article104. Polge C, Smith AU, Parkes AS. Revival of spermatozoa after vitrification and dehydration at low temperatures. Nature. 1949; 164:666.
Article105. Fahy GM, MacFarlane DR, Angell CA, Meryman HT. Vitrification as an approach to cryopreservation. Cryobiology. 1984; 21:407–26.
Article106. Best BP. Cryoprotectant toxicity: facts, issues, and questions. Rejuvenation Res. 2015; 18:422–36.
Article107. Rajotte RV, Stewart HL, Voss WA, Shnitka TK. Viability studies on frozen: thawed rat islets of Langerhans. Cryobiology. 1977; 14:116–20.
Article108. Bank HL. Cryobiology of isolated islets of Langerhans circa 1982. Cryobiology. 1983; 20:119–28.
Article109. Wise MH, Gordon C, Johnson RW. Intraportal autotransplantation of cryopreserved porcine islets of Langerhans. Cryobiology. 1985; 22:359–66.
Article110. Lakey JR, Rajotte RV, Fedorow CA, Taylor MJ. Islet cryopreservation using intracellular preservation solutions. Cell Transplant. 2001; 10:583–9.
Article111. Modak MA, Parab PB, Ghaskadbi SS. Pancreatic islets are very poor in rectifying oxidative DNA damage. Pancreas. 2009; 38:23–9.
Article112. Hardikar AA, Risbud MV, Remacle C, Reusens B, Hoet JJ, Bhonde RR. Islet cryopreservation: improved recovery following taurine pretreatment. Cell Transplant. 2001; 10:247–53.
Article113. Chandravanshi B, Dhanushkodi A, Bhonde R. High recovery of functional islets stored at low and ultralow temperatures. Rev Diabet Stud. 2014; 11:267–78.
Article114. Pisania A, Weir GC, O’Neil JJ, Omer A, Tchipashvili V, Lei J, et al. Quantitative analysis of cell composition and purity of human pancreatic islet preparations. Lab Invest. 2010; 90:1661–75.
Article115. Dolezalova N, Gruszczyk A, Barkan K, Gamble JA, Galvin S, Moreth T, et al. Accelerating cryoprotectant diffusion kinetics improves cryopreservation of pancreatic islets. Sci Rep. 2021; 11:10418.
Article116. Rawal S, Harrington S, Williams SJ, Ramachandran K, Stehno-Bittel L. Long-term cryopreservation of reaggregated pancreatic islets resulting in successful transplantation in rats. Cryobiology. 2017; 76:41–50.
Article117. Nagaya M, Matsunari H, Kanai T, Maehara M, Nakano K, Umeki I, et al. An effective new cryopreservation procedure for pancreatic islets using hollow fiber vitrification. Horm Metab Res. 2016; 48:540–9.
Article118. Kojayan GG, Flores A, Li S, Alexander M, Lakey JR. Cryopreserved alginate-encapsulated islets can restore euglycemia in a diabetic animal model better than cryopreserved non-encapsulated islets. Cell Med. 2019; 11:2155179019876641.
Article119. Zhan L, Rao JS, Sethia N, Slama MQ, Han Z, Tobolt D, et al. Pancreatic islet cryopreservation by vitrification achieves high viability, function, recovery and clinical scalability for transplantation. Nat Med. 2022; 28:798–808.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Induction of Nestin Early Expression as a Hallmark for Mesenchymal Stem Cells Expression of PDX-1 as a Pre-disposing Factor for Their Conversion into Insulin Producing Cells
- Generation of Insulin-Producing Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus
- Effects of Periodontal Disease Knowledge and Awareness of Scaling on Scaling Fear in Adults
- Generation of Insulin-Expressing Cells in Mouse Small Intestine by Pdx1, MafA, and BETA2/NeuroD
- Cell Replacement and Regeneration Therapy for Diabetes