Child Kidney Dis.
2023 Dec;27(2):76-81. 10.3339/ckd.23.021.
Tolvaptan: a possible preemptive treatment option in children with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2549737
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3339/ckd.23.021
Abstract
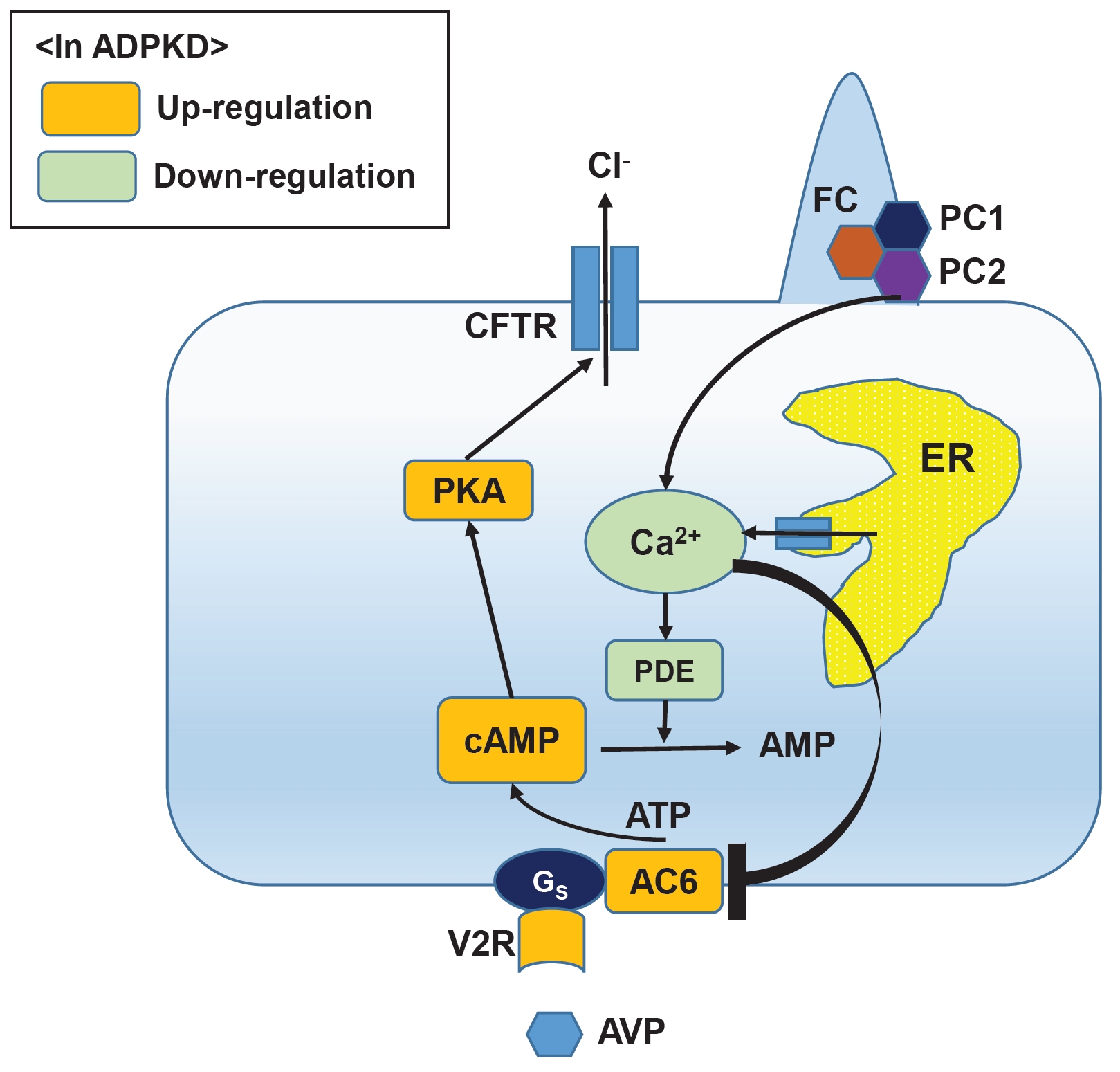
- Tolvaptan is a highly selective vasopressin receptor 2 antagonist that regulates cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels to inhibit both epithelial cell proliferation and chloride ion excretion, two mechanisms known to induce cyst expansion in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). Tolvaptan is currently the preferred treatment of rapidly progressive disease ADPKD in adult patients; however, since cyst formation in ADPKD begins early in life, (frequently in utero), and significant disease progression with cyst expansion occurs in the first decade, tolvaptan may be advantageous as a preemptive treatment in children with ADPKD. Tolvaptan has already been used to successfully treat refractory edema or hyponatremia in children; this literature review provides insight into the biochemical basis of its action to contextualize its use in the pediatric population.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Olesen ET, Fenton RA. Aquaporin 2 regulation: implications for water balance and polycystic kidney diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021; 17:765–81.
Article2. Torres VE. Role of vasopressin antagonists. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008; 3:1212–8.
Article3. Torres VE, Chapman AB, Desvuyst O, Gansevoort RT, Grantham JJ, Higashihara E, et al. Tolvaptan in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2012; 367:2407–18.
Article4. Torres VE, Chapman AB, Devuyst O, Gansevoort RT, Perrone RD, Koch G, et al. Tolvaptan in later-stage autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:1930–42.
Article5. Torres VE, Chapman AB, Devuyst O, Gansevoort RT, Perrone RD, Lee J, et al. Multicenter study of long-term safety of tolvaptan in later-stage autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020; 16:48–58.
Article6. Torres VE, Gansevoort RT, Perrone RD, Chapman AB, Ouyang J, Lee J, et al. Tolvaptan in ADPKD patients with very low kidney function. Kidney Int Rep. 2021; 6:2171–8.
Article7. Zhou X, Davenport E, Ouyang J, Hoke ME, Garbinsky D, Agarwal I, et al. Pooled data analysis of the long-term treatment effects of tolvaptan in ADPKD. Kidney Int Rep. 2022; 7:1037–48.
Article8. Chebib FT, Perrone RD, Chapman AB, Dahl NK, Harris PC, Mrug M, et al. A practical guide for treatment of rapidly progressive ADPKD with tolvaptan. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018; 29:2458–70.
Article9. Muller RU, Messchendorp AL, Birn H, Capasso G, Cornec-Le Gall E, Devuyst O, et al. An update on the use of tolvaptan for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: consensus statement on behalf of the ERA Working Group on Inherited Kidney Disorders, the European Rare Kidney Disease Reference Network and Polycystic Kidney Disease International. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022; 37:825–39.
Article10. Gkekas E, Tang TY, Green A, Davidson H, Fraser R, Sayer JA, et al. Outcomes from the Northeast England cohort of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) patients on tolvaptan. Front Nephrol. 2022; 2:984165.
Article11. Kataoka H, Shimada Y, Kimura T, Nishio S, Nakatani S, Mochizuki T, et al. Public support for patients with intractable diseases in Japan: impact on clinical indicators from nationwide registries in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2023; 27:809–18.
Article12. Gkika V, Louka M, Tsagkatakis M, Tsirpanlis G. The efficacy, the treatment response and the aquaretic effects of a three-year tolvaptan regimen in polycystic kidney disease patients. Clin Pract. 2023; 13:1035–42.
Article13. Shimizu M, Ishikawa S, Yachi Y, Muraoka M, Tasaki Y, Iwasaki H, et al. Tolvaptan therapy for massive edema in a patient with nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2014; 29:915–7.
Article14. Marx-Berger D, Milford DV, Bandhakavi M, Van't Hoff W, Kleta R, Dattani M, et al. Tolvaptan is successful in treating inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion in infants. Acta Paediatr. 2016; 105:e334–7.15. Higashi K, Murakami T, Ishikawa Y, Itoi T, Ohuchi H, Kodama Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of tolvaptan for pediatric patients with congestive heart failure. Multicenter survey in the working group of the Japanese Society of PEdiatric Circulation and Hemodynamics (J-SPECH). Int J Cardiol. 2016; 205:37–42.
Article16. Katayama Y, Ozawa T, Shiono N, Masuhara H, Fujii T, Watanabe Y. Safety and effectiveness of tolvaptan for fluid management after pediatric cardiovascular surgery. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017; 65:622–6.
Article17. Tuli G, Tessaris D, Einaudi S, De Sanctis L, Matarazzo P. Tolvaptan treatment in children with chronic hyponatremia due to inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion: a report of three cases. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2017; 9:288–92.
Article18. Koksoy AY, Kurtul M, Ozsahin AK, Cayci FS, Tayfun M, Bayrakci US. Tolvaptan use to treat SIADH in a child. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2018; 23:494–8.
Article19. Kerling A, Toka O, Ruffer A, Muller H, Habash S, Weiss C, et al. First experience with tolvaptan for the treatment of neonates and infants with capillary leak syndrome after cardiac surgery. BMC Pediatr. 2019; 19:57.
Article20. Delbet JD, Parmentier C, Ulinski T. Tolvaptan therapy to treat severe hyponatremia in pediatric nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2020; 35:1347–50.
Article21. Meena J, Hari P, Sinha A, Bagga A. Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with tolvaptan and furosemide in children with nephrotic syndrome and refractory edema: a prospective interventional study. Indian J Pediatr. 2022; 89:699–705.
Article22. Piffer A, Bianchetti MG, Leoni-Foglia C, Simonetti GD, Milani GP, Lava SA. Vaptans for oedematous and hyponatraemic disorders in childhood: a systematic literature review. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022; 88:4474–80.
Article23. Hartung EA. Tolvaptan for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in children: why, who, and when? Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023; 18:11–3.
Article24. Gimpel C, Bergmann C, Mekahli D. The wind of change in the management of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in childhood. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022; 37:473–87.
Article25. De Rechter S, Breysem L, Mekahli D. Is autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease becoming a pediatric disorder? Front Pediatr. 2017; 5:272.
Article26. Alpers DH, Lewis JH, Hunt CM, Freston JW, Torres VE, Li H, et al. Clinical pattern of tolvaptan-associated liver injury in trial participants with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD): an analysis of pivotal clinical trials. Am J Kidney Dis. 2023; 81:281–93.
Article27. Janssens P, Weydert C, De Rechter S, Wissing KM, Liebau MC, Mekahli D. Expanding the role of vasopressin antagonism in polycystic kidney diseases: from adults to children? Pediatr Nephrol. 2018; 33:395–408.
Article28. Gilbert RD, Evans H, Olalekan K, Nagra A, Haq MR, Griffiths M. Tolvaptan treatment for severe neonatal autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol. 2017; 32:893–6.
Article29. Raina R, Chakraborty R, DeCoy ME, Kline T. Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease: tolvaptan use in adolescents and young adults with rapid progression. Pediatr Res. 2021; 89:894–9.
Article30. Schaefer F, Mekahli D, Emma F, Gilbert RD, Bockenhauer D, Cadnapaphornchai MA, et al. Tolvaptan use in children and adolescents with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: rationale and design of a two-part, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Pediatr. 2019; 178:1013–21.
Article31. Mekahli D, Guay-Woodford LM, Cadnapaphornchai MA, Greenbaum LA, Litwin M, Seeman T, et al. Tolvaptan for children and adolescents with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: randomized controlled trial. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023; 18:36–46.
Article32. Gimpel C, Bergmann C, Bockenhauer D, Breysem L, Cadnapaphornchai MA, Cetiner M, et al. International consensus statement on the diagnosis and management of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in children and young people. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2019; 15:713–26.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Management of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in the era of disease-modifying treatment options
- Recent updates in therapeutic approach using tolvaptan for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
- Are you ready to accompany autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease patients in their treatment journey? Real practice for selecting rapid progressors and treatment with tolvaptan
- Long-term Tolvaptan Treatment of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease in Korea
- A Case of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Hemodialyzed