Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2023 Nov;16(4):407-412. 10.21053/ceo.2023.01130.
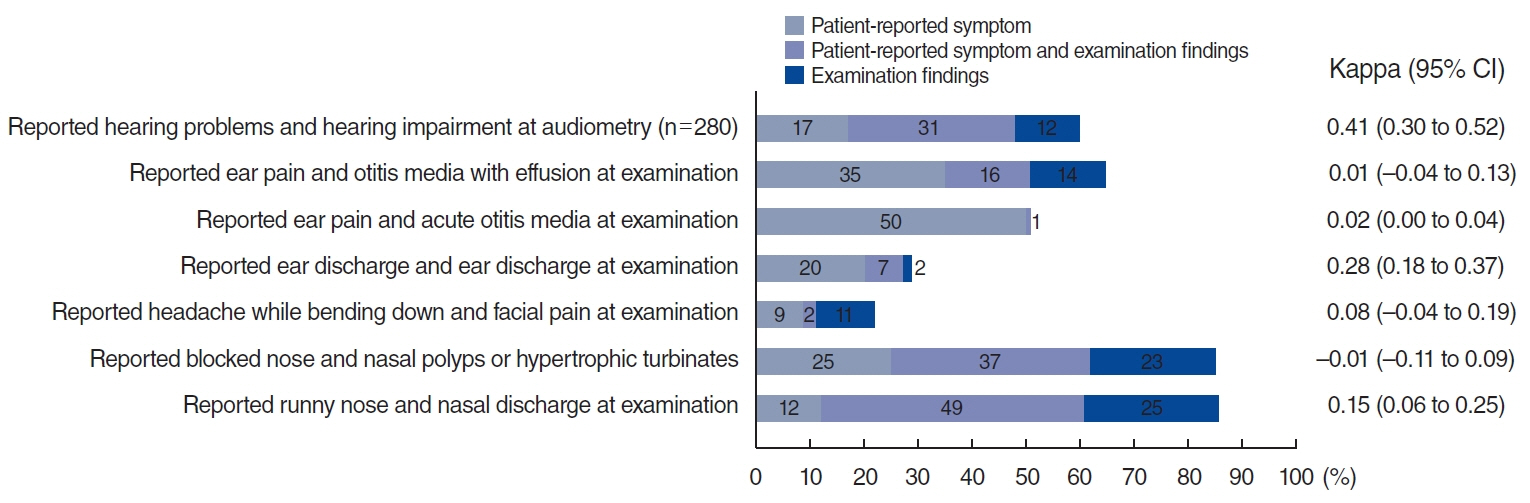
Lack of Correlation of Sinonasal and Otologic Reported Symptoms With Objective Measurements Among Patients With Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: An International Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Social and Preventive Medicine, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
- 2Graduate School for Cellular and Biomedical Sciences, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
- 3Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris (AP-HP), Université Paris-Saclay, Service d’ORL, Hôpital Bicêtre, Le Kremlin-Bicêtre, France
- 4Faculté de Médecine, Université Paris-Saclay, Le Kremlin-Bicêtre, France
- 5Département de Génétique Médicale, Sorbonne Université, Inserm UMR_S933, Maladies Génétiques D’expression Pédiatrique, Hôpital Armand Trousseau, Paris, France
- 6Department of Otolaryngology, Nicosia General Hospital, Nicosia, Cyprus
- 7Department of Otorhinolaryngology, and Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Unit, La Fe University and Polytechnic Hospital, Valencia, Spain
- 8Medical School, Valencia University, Valencia, Spain
- 9Molecular, Cellular and Genomic Biomedicine Group, IIS La Fe, Valencia, Spain
- 10Department of Paediatrics, University Hospitals Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
- 11Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Centre, Southampton Children’s Hospital, Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, Southampton, UK
- 12Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, University Hospital of Bern, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
- 13Paediatric Department of Allergy and Lung Diseases, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway
- 14Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway
- 15Faculty of Medicine, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway
- 16Department of Pediatric Pulmonology, Hacettepe University, School of Medicine, Ankara, Turkey
- 17Department of Pediatric Pulmonology, Marmara University, School of Medicine, Istanbul, Turkey
- 18Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Amsterdam UMC, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
- 19Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Hacettepe University School of Medicine, Ankara, Turkey
- 20Department of Pediatric Pulmonology, Emma Children’s Hospital, Amsterdam UMC, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
- 21Southampton Children’s Hospital, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK
- 22Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Centre, NIHR Respiratory Biomedical Research Centre, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK
- 23Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- 24Division of Respirology, Department of Pediatrics, University Hospital Liège, Liège, Belgium
- 25Department of Respiratory Diseases, University Hospitals Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
- 26Department of Pediatric Pulmonology, Immunology and Critical Care Medicine, Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- 27Department of Otorhinolaryngology, University Hospital of Liège, Liège, Belgium
- 28Biomedical Sciences Department, CEU-Cardenal Herrera University, Castellón, Spain
- 29Medical School, University of Cyprus, Nicosia, Cyprus
- 30Pediatric Pulmonology Unit, Hospital ‘Archbishop Makarios III’, Nicosia, Cyprus
- 31Paediatric Respiratory Medicine, Children’s University Hospital of Bern, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
- KMID: 2548370
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2023.01130
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lam YT, Papon JF, Alexandru M, Anagiotos A, Armengot M, Boon M, et al. Sinonasal disease among patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia: an international study. ERJ Open Res. 2023; May. 9(3):00701–2022.2. Goutaki M, Lam YT, Alexandru M, Anagiotos A, Armengot M, Boon M, et al. Characteristics of otologic disease among patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023; Jul. 149(7):587–96.3. Goutaki M, Meier AB, Halbeisen FS, Lucas JS, Dell SD, Maurer E, et al. Clinical manifestations in primary ciliary dyskinesia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J. 2016; Oct. 48(4):1081–95.4. Goutaki M, Lam YT, Alexandru M, Anagiotos A, Armengot M, Bequignon E, et al. Study protocol: the ear-nose-throat (ENT) prospective international cohort of patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia (EPIC-PCD). BMJ Open. 2021; Oct. 11(10):e051433.5. Lucas JS, Barbato A, Collins SA, Goutaki M, Behan L, Caudri D, et al. European Respiratory Society guidelines for the diagnosis of primary ciliary dyskinesia. Eur Respir J. 2017; Jan. 49(1):1601090.6. Goutaki M, Papon JF, Boon M, Casaulta C, Eber E, Escudier E, et al. Standardised clinical data from patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia: FOLLOW-PCD. ERJ Open Res. 2020; Feb. 6(1):00237–2019.7. Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research electronic data capture (REDCap): a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009; Apr. 42(2):377–81.8. McHugh ML. Interrater reliability: the kappa statistic. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2012; 22(3):276–82.9. Reichenheim ME. Confidence intervals for the kappa statistic. Stata J. 2004; Dec. 4(4):421–8.10. Cohen J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ Psychol Meas. 1960; Apr. 20(1):37–46.11. Campbell R. Managing upper respiratory tract complications of primary ciliary dyskinesia in children. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; Feb. 12(1):32–8.12. Majithia A, Fong J, Hariri M, Harcourt J. Hearing outcomes in children with primary ciliary dyskinesia: a longitudinal study. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2005; Aug. 69(8):1061–4.13. Racette SD, Wijewickrama RC, Jayaprakash V, Sherris DA, Santos C, Kita H, et al. Correlation of symptoms, clinical signs, and biomarkers of inflammation in postsurgical chronic rhinosinusitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2017; Jun. 126(6):455–62.14. Park DY, Lee EJ, Kim JH, Kim YS, Jung CM, Kim KS. Correlation between symptoms and objective findings may improve the symptom-based diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis for primary care and epidemiological studies. BMJ Open. 2015; Dec. 5(12):e009541.15. Cornford CS. Why patients consult when they cough: a comparison of consulting and non-consulting patients. Br J Gen Pract. 1998; Nov. 48(436):1751–4.16. Muramatsu K, Miyaoka H, Muramatsu Y, Fuse K, Yoshimine F, Kamijima K, et al. The amplification of somatic symptoms in upper respiratory tract infections. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2002; May-Jun. 24(3):172–5.17. Mozun R, Ardura-Garcia C, Pedersen ES, Goutaki M, Usemann J, Singer F, et al. Agreement of parent- and child-reported wheeze and its association with measurable asthma traits. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2021; Dec. 56(12):3813–21.18. Swierniak W, Gos E, Skarzynski PH, Czajka N, Skarzynski H. The accuracy of parental suspicion of hearing loss in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2021; Feb. 141:110552.