Diabetes Metab J.
2023 Nov;47(6):808-817. 10.4093/dmj.2022.0387.
Efficacy and Safety of Evogliptin Add-on Therapy to Dapagliflozin/Metformin Combinations in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week Multicenter Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel-Design Phase-3 Trial with a 28-Week Extension
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 2Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Nowon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University College of Medicine, Jeju, Korea
- 9Department of Internal Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- 10Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 11Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hwaseong, Korea
- 12Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea
- 13Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2548157
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0387
Abstract
- Background
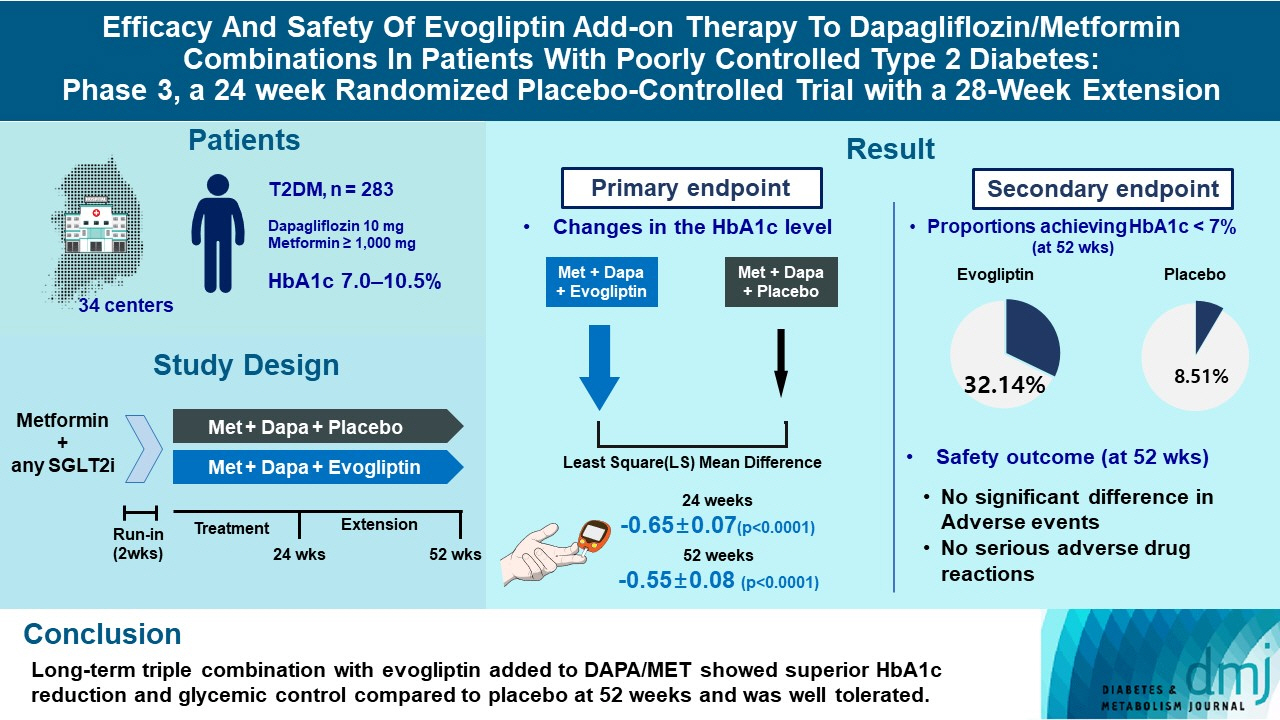
This study investigates the long-term efficacy and safety of evogliptin add-on therapy in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) previously received dapagliflozin and metformin (DAPA/MET) combination.
Methods
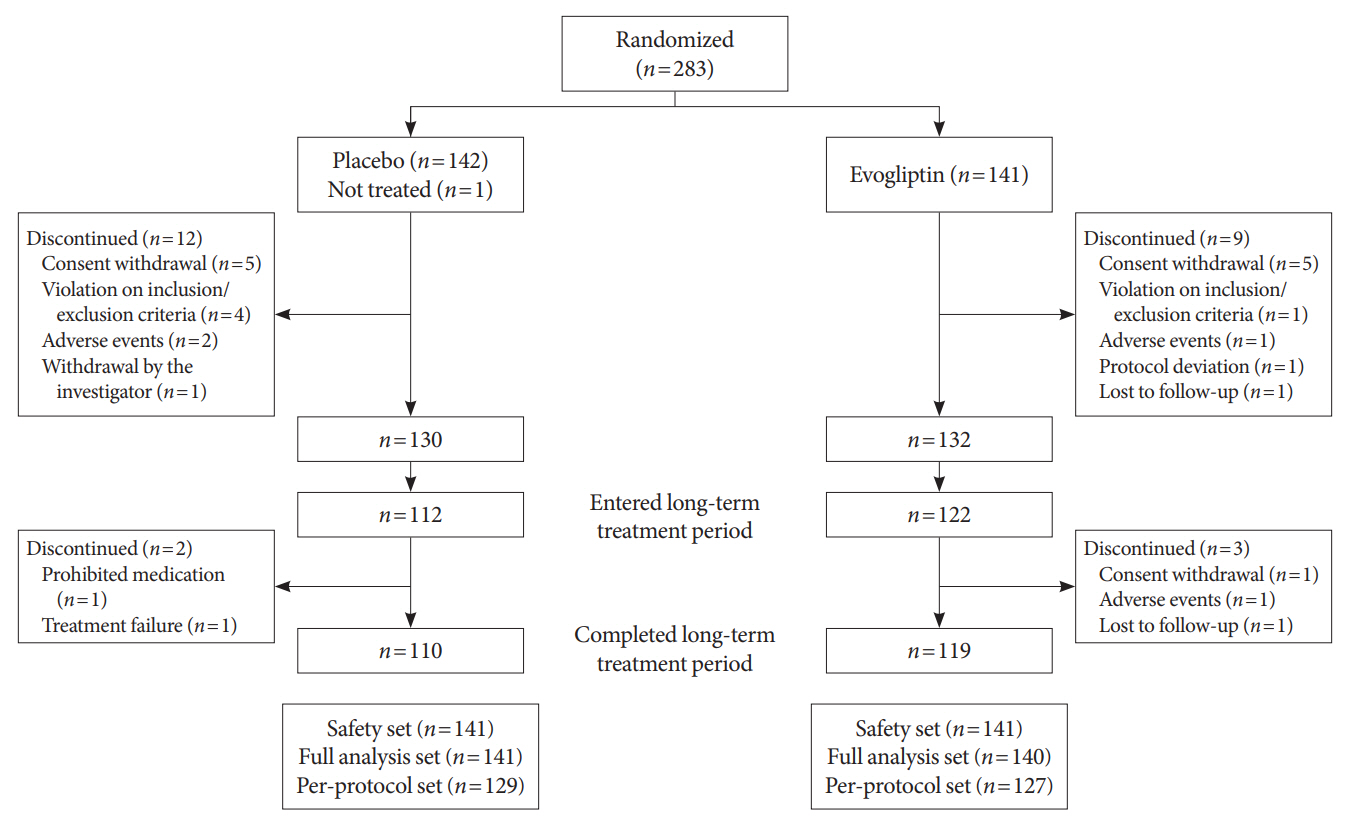
In this multicenter randomized placebo-controlled phase 3 trial, patients with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels 7.0% to 10.5% (n=283) previously used DAPA 10 mg plus MET (≥1,000 mg) were randomly assigned to the evogliptin 5 mg once daily or placebo group (1:1). The primary endpoint was the difference in the HbA1c level from baseline at week 24, and exploratory endpoints included the efficacy and safety of evogliptin over 52 weeks (trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04170998).
Results
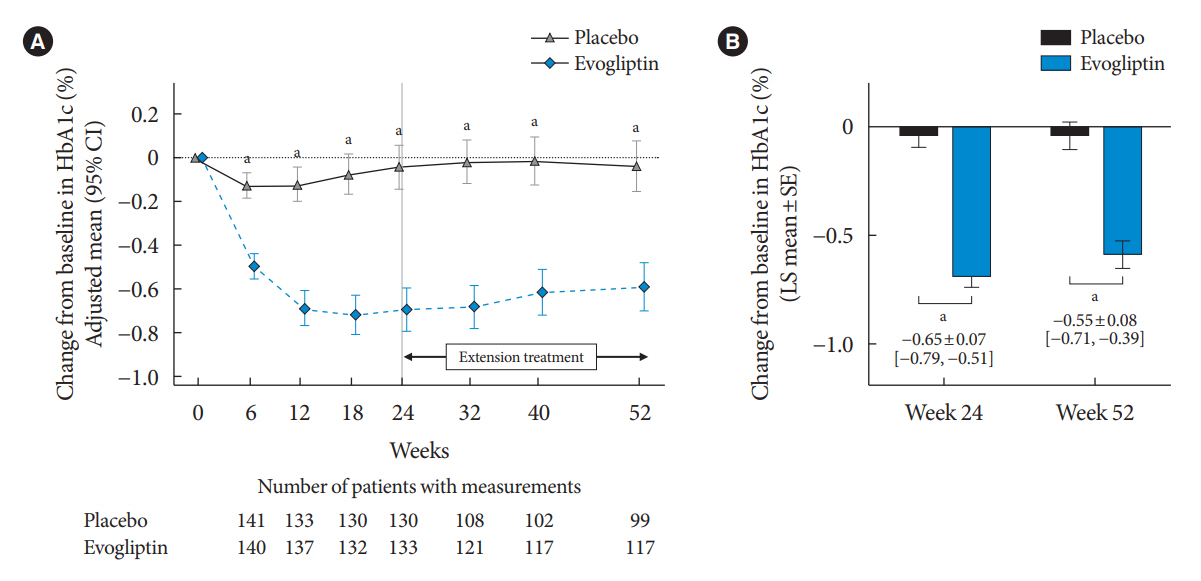
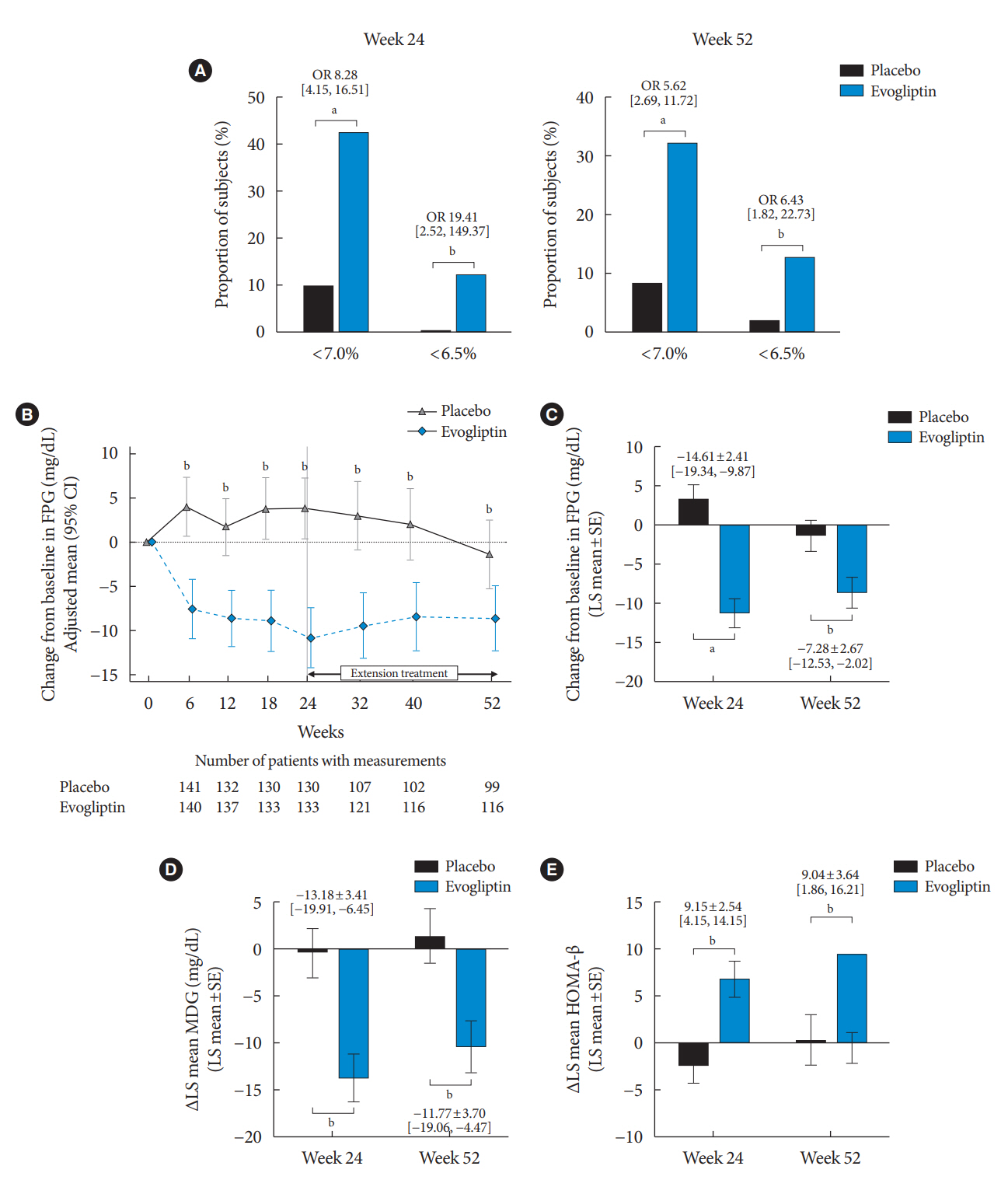
Evogliptin add-on to DAPA/MET therapy was superior in HbA1c reduction compared to placebo at weeks 24 and 52 (least square [LS] mean difference, –0.65% and –0.55%; 95% confidence interval [CI], –0.79 to –0.51 and –0.71 to –0.39; P<0.0001). The proportion of patients achieving HbA1c <7% was higher in the triple combination group at week 52 (32.14% vs. 8.51% in placebo; odds ratio, 5.62; P<0.0001). Evogliptin significantly reduced the fasting glucose levels and mean daily glucose levels with improvement in homeostatic model assessment of β-cell function (LS mean difference, 9.04; 95% CI, 1.86 to 16.21; P=0.0138). Adverse events were similar between the groups, and no serious adverse drug reactions were reported in the evogliptin group.
Conclusion
Long-term triple combination with evogliptin added to DAPA/MET showed superior HbA1c reduction and glycemic control compared to placebo at 52 weeks and was well tolerated.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ogle GD, James S, Dabelea D, Pihoker C, Svennson J, Maniam J, et al. Global estimates of incidence of type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents: results from the international diabetes federation atlas, 10th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022; 183:109083.
Article2. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998; 352:837–53.3. Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10- Year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1577–89.
Article4. Bae JH, Han KD, Ko SH, Yang YS, Choi JH, Choi KM, et al. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea 2021. Diabetes Metab J. 2022; 46:417–26.
Article5. Phung OJ, Sobieraj DM, Engel SS, Rajpathak SN. Early combination therapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014; 16:410–7.
Article6. Zaccardi F, Dhalwani NN, Dales J, Mani H, Khunti K, Davies MJ, et al. Comparison of glucose-lowering agents after dual therapy failure in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018; 20:985–97.
Article7. Ko SH, Hur KY, Rhee SY, Kim NH, Moon MK, Park SO, et al. Antihyperglycemic agent therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus 2017: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J. 2017; 41:337–48.
Article8. Hong AR, Koo BK, Kim SW, Yi KH, Moon MK. Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in real-world clinical practice. Diabetes Metab J. 2019; 43:590–606.
Article9. Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:347–57.
Article10. Jung CH, Jang JE, Park JY. A novel therapeutic agent for type 2 diabetes mellitus: SGLT2 inhibitor. Diabetes Metab J. 2014; 38:261–73.
Article11. Alatrach M, Laichuthai N, Martinez R, Agyin C, Ali AM, AlJobori H, et al. Evidence against an important role of plasma insulin and glucagon concentrations in the increase in EGP caused by SGLT2 inhibitors. Diabetes. 2020; 69:681–8.
Article12. Ferrannini E, Muscelli E, Frascerra S, Baldi S, Mari A, Heise T, et al. Metabolic response to sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Invest. 2014; 124:499–508.
Article13. Kim G, Lim S, Kwon HS, Park IB, Ahn KJ, Park CY, et al. Efficacy and safety of evogliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: a multicentre, active-controlled, randomized, doubleblind study with open-label extension (the EVERGREEN study). Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020; 22:1527–36.14. Lewin A, DeFronzo RA, Patel S, Liu D, Kaste R, Woerle HJ, et al. Initial combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:394–402.
Article15. Li D, Shi W, Wang T, Tang H. SGLT2 inhibitor plus DPP-4 inhibitor as combination therapy for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018; 20:1972–6.
Article16. Scheen AJ. DPP-4 inhibitor plus SGLT-2 inhibitor as combination therapy for type 2 diabetes: from rationale to clinical aspects. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016; 12:1407–17.
Article17. Lee CM, Woodward M, Colagiuri S. Triple therapy combinations for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a network meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016; 116:149–58.18. Lee JY, Cho Y, Lee M, Kim YJ, Lee YH, Lee BW, et al. Predictors of the therapeutic efficacy and consideration of the best combination therapy of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors. Diabetes Metab J. 2019; 43:158–73.
Article19. Olansky L, Reasner C, Seck TL, Williams-Herman DE, Chen M, Terranella L, et al. A treatment strategy implementing combination therapy with sitagliptin and metformin results in superior glycaemic control versus metformin monotherapy due to a low rate of addition of antihyperglycaemic agents. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011; 13:841–9.
Article20. van Baar MJ, van Ruiten CC, Muskiet MH, van Bloemendaal L, IJzerman RG, van Raalte DH. SGLT2 inhibitors in combination therapy: from mechanisms to clinical considerations in type 2 diabetes management. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:1543–56.
Article21. Dicembrini I, Montereggi C, Nreu B, Mannucci E, Monami M. Pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer in patients treated with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: an extensive and updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020; 159:107981.22. Ferrannini E, Seman L, Seewaldt-Becker E, Hantel S, Pinnetti S, Woerle HJ. A phase IIb, randomized, placebo-controlled study of the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013; 15:721–8.23. Petrykiv S, Laverman GD, de Zeeuw D, Heerspink HJ. Does SGLT2 inhibition with dapagliflozin overcome individual therapy resistance to RAAS inhibition? Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018; 20:224–7.24. Merovci A, Solis-Herrera C, Daniele G, Eldor R, Fiorentino TV, Tripathy D, et al. Dapagliflozin improves muscle insulin sensitivity but enhances endogenous glucose production. J Clin Invest. 2014; 124:509–14.
Article25. Kim YG, Hahn S, Oh TJ, Kwak SH, Park KS, Cho YM. Differences in the glucose-lowering efficacy of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors between Asians and non-Asians: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2013; 56:696–708.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pioglitazone as Add-on Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Inadequately Controlled with Dapagliflozin and Metformin: Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
- Efficacy of Gemigliptin Add-on to Dapagliflozin and Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study (SOLUTION)
- Efficacy and Safety of Enavogliflozin versus Dapagliflozin as Add-on to Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week, Double-Blind, Randomized Trial
- The Efficacy of Fixed Dose Rosiglitazone and Metformin Combination Therapy in Poorly Controlled Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Addition of Ipragliflozin to Metformin Treatment in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Subgroup Analysis of a Phase 3 Trial