J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2023 Aug;49(4):233-238. 10.5125/jkaoms.2023.49.4.233.
A rare histopathological variant of Schwannoma with rosette-like arrangements and epithelioid cells: a case report from a histopathologist’s perspective
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, I.T.S Dental College, Hospital & Research Centre, Greater Noida, India
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, Sudha Rustagi College of Dental Sciences & Research, Faridabad, India
- KMID: 2545591
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2023.49.4.233
Abstract
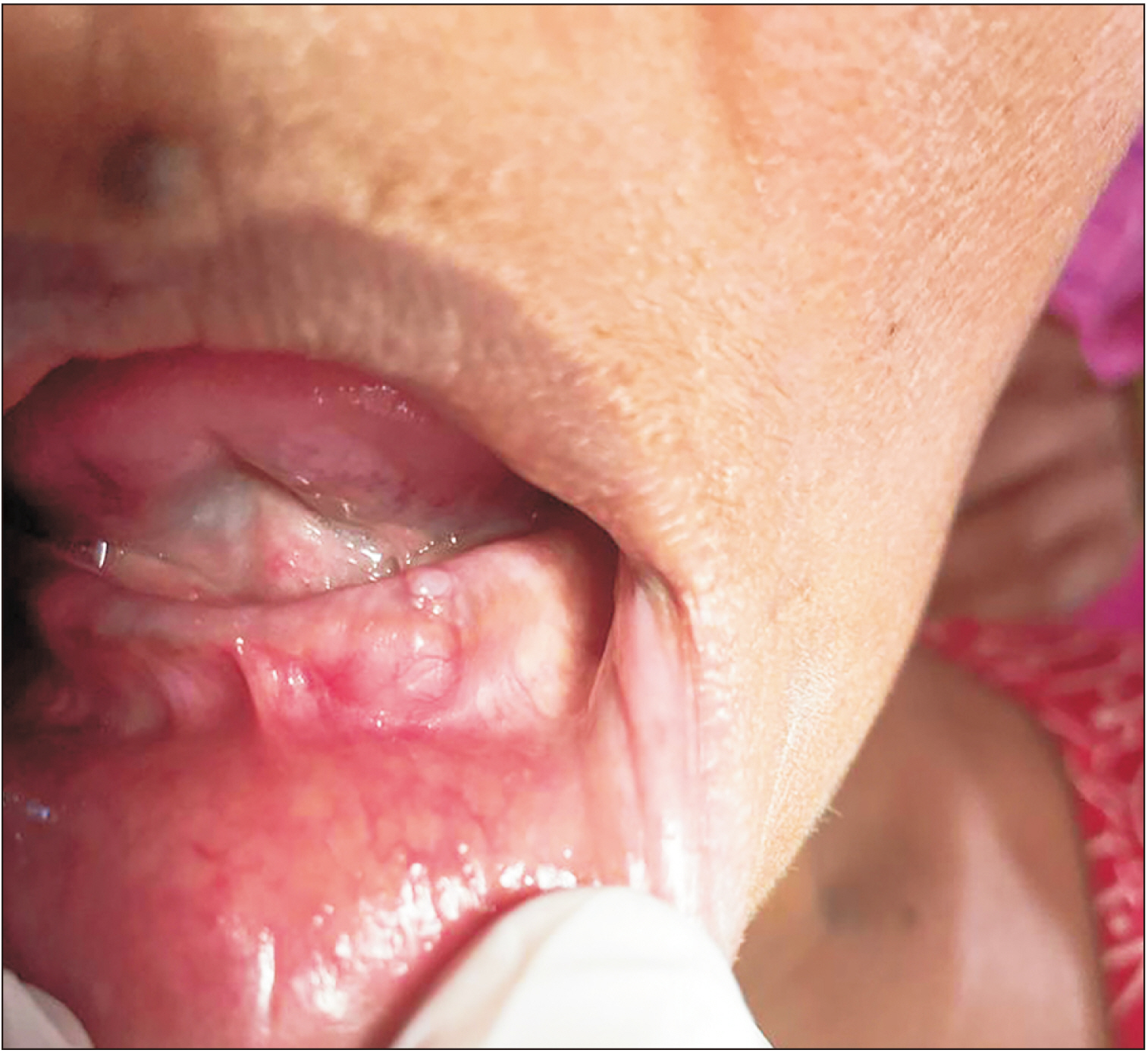
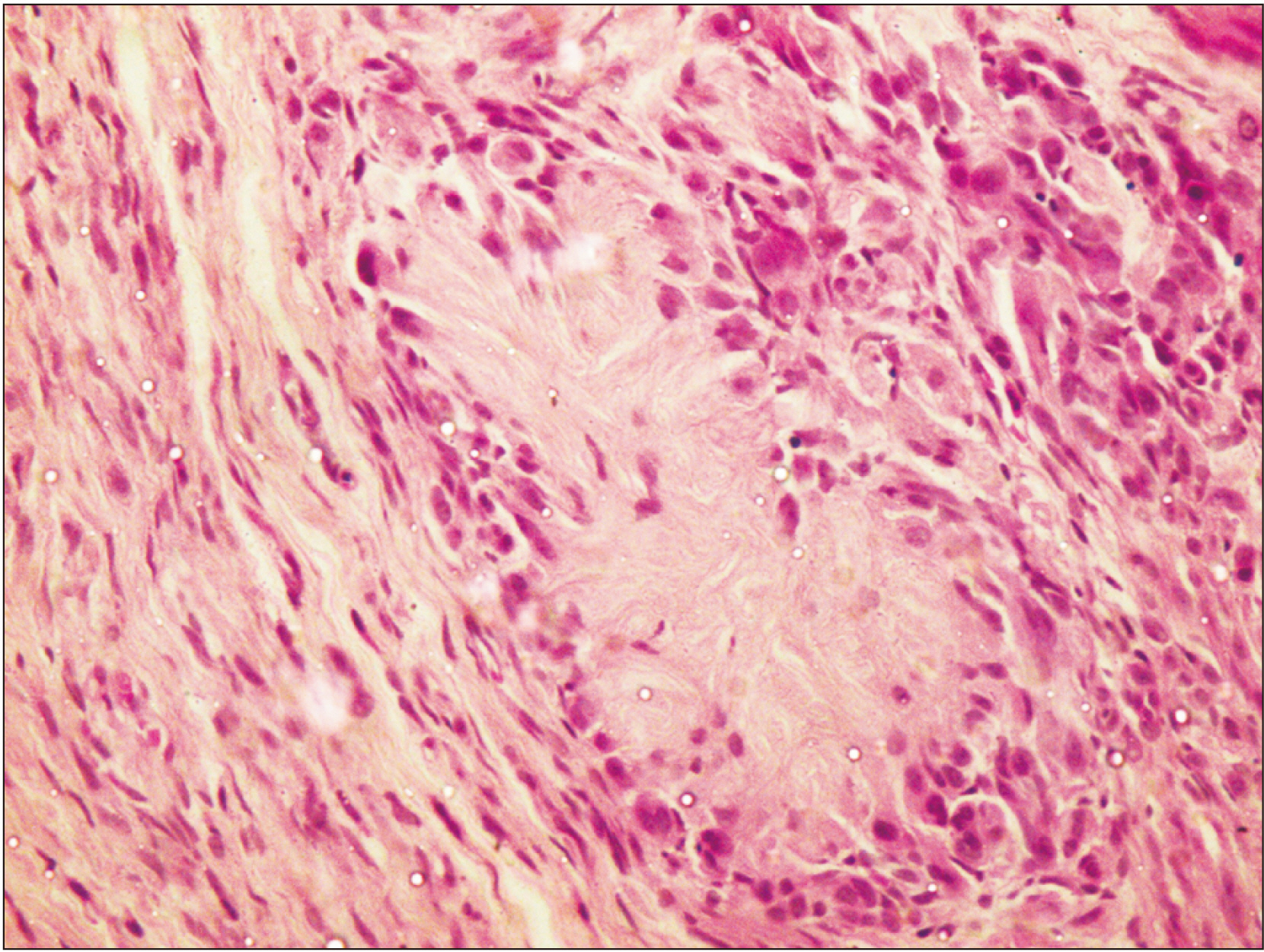
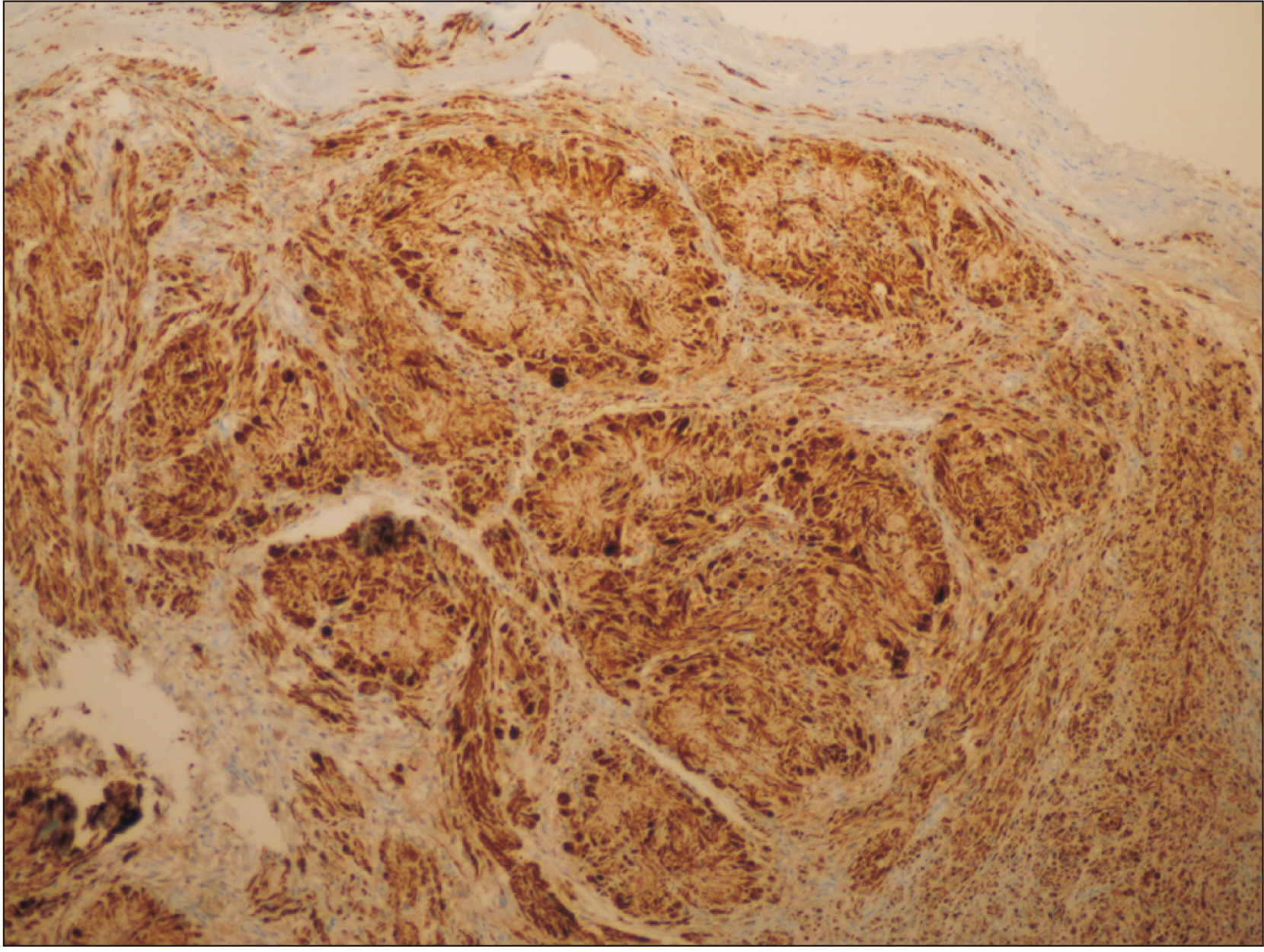
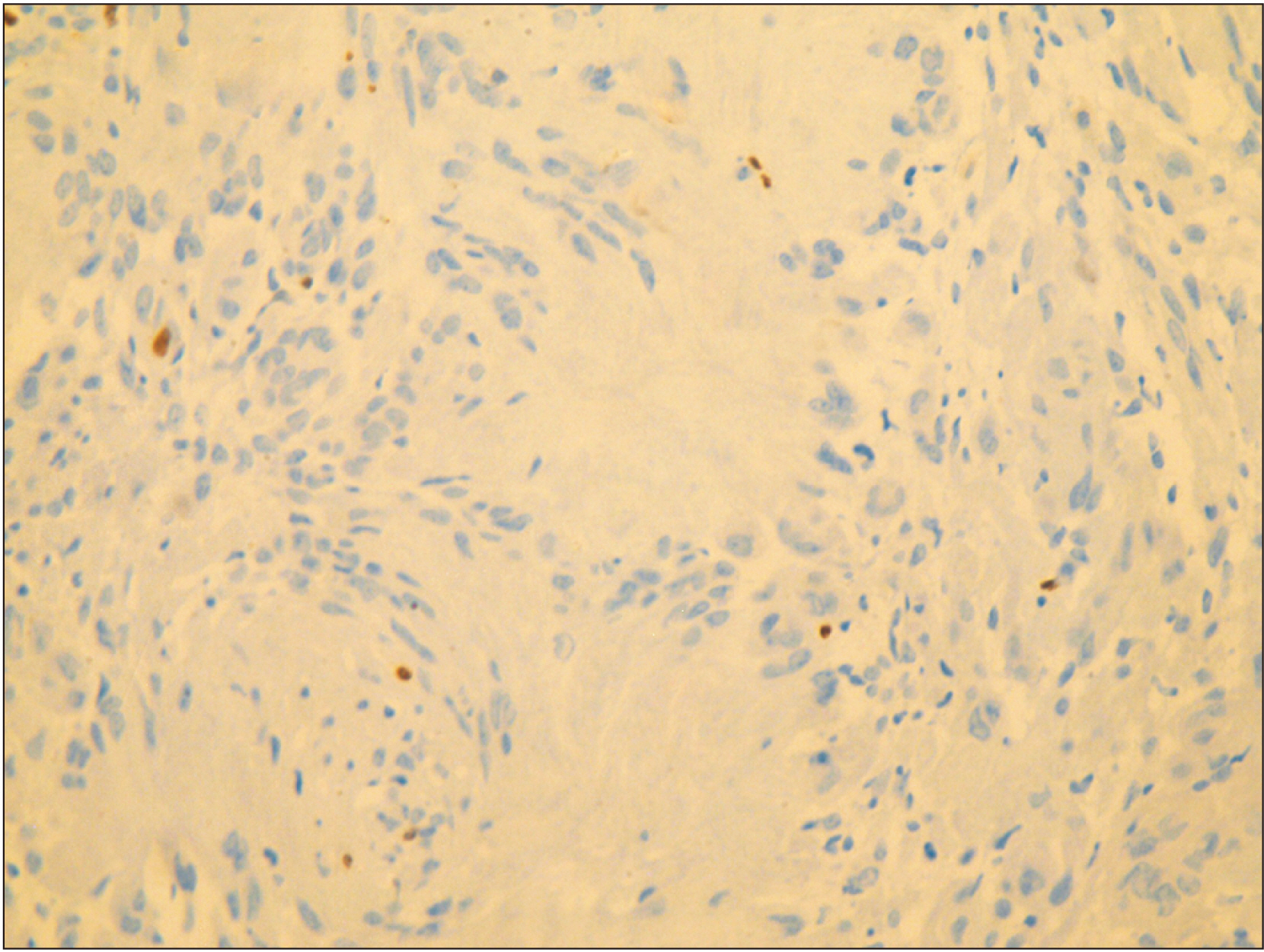
- Schwannomas exhibit histopathological variation that leads to diagnostic dilemmas, although less frequent in the oral cavity. We describe a case with unique histopathology and no relevant clinical history that adds to the breadth of literature on the diversity presented by Schwannoma. A 60-year-old female patient presented with a small dome-shaped, asymptomatic swelling on the alveolar ridge 6 years in duration. Histopathologically, it showed rich cellular pathology with a unique arrangement of tumor cells forming irregular rosettes. Each rosette presented with a central core of fibrincollagenous material and the tumor cells were arranged on the periphery, exhibiting epithelioid change with evidence of mild cellular and nuclear pleomorphism. On immunohistochemical evaluation, the cells were strongly and diffusely positive for S-100 and negative for Ki-67. A diagnosis of benign Schwannoma with a rosette-like arrangement with epithelioid change was made. The case report emphasizes the risk of misdiagnosis and the importance of awareness regarding rare histopathological variants of Schwannoma.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Heo SJ, Kim AY, Kim JS. 2022; Two cases of neurilemmoma in the nasal vestibule: a case report and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 101:e29006. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000029006. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029006. PMID: 35451397. PMCID: PMC8913084.
Article2. Urs AB, Kumar P, Augustine J, Malhotra R, Jot K. 2021; Pathological diversity in Schwannomas of the orofacial region. Asian J Neurosurg. 16:402–5. https://doi.org/10.4103/ajns.ajns_470_20. DOI: 10.4103/ajns.AJNS_470_20. PMID: 34268175. PMCID: PMC8244711.
Article3. Sitenga J, Aird G, Vaudreuil A, Huerter CJ. 2018; Clinical features and management of Schwannoma affecting the upper and lower lips. Int J Dermatol. 57:1047–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijd.13920. DOI: 10.1111/ijd.13920. PMID: 29377087.
Article4. Bakir M, Enabi J, Almeshal H. 2021; Unusual lower lip swelling: a rare case of lip Schwannoma. Cureus. 13:e19242. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.19242. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.19242. PMID: 34900449. PMCID: PMC8647776.
Article5. Lee JD, Kwon TJ, Kim UK, Lee WS. 2012; Genetic and epigenetic alterations of the NF2 gene in sporadic vestibular Schwannomas. PLoS One. 7:e30418. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030418. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030418. PMID: 22295085. PMCID: PMC3266248.
Article6. Cardoso VS, Quelemes PV, Amorin A, Primo FL, Gobo GG, Tedesco AC, et al. 2014; Collagen-based silver nanoparticles for biological applications: synthesis and characterization. J Nanobiotechnology. 12:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-014-0036-6. DOI: 10.1186/s12951-014-0036-6. PMID: 25223611. PMCID: PMC4428528.
Article7. Nishijima Sakanashi E, Sonobe J, Chin M, Bessho K. 2015; Schwannoma located in the upper gingival mucosa: case report and literature review. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 14(Suppl 1):222–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-012-0445-8. DOI: 10.1007/s12663-012-0445-8. PMID: 25838700. PMCID: PMC4379268.
Article8. Belakhoua SM, Rodriguez FJ. 2021; Diagnostic pathology of tumors of peripheral nerve. Neurosurgery. 88:443–56. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyab021. DOI: 10.1093/neuros/nyab021. PMID: 33588442. PMCID: PMC7884141.
Article9. Qi Z, Yang N, Pi M, Yu W. 2021; Current status of the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal Schwannoma. Oncol Lett. 21:384. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2021.12645. DOI: 10.3892/ol.2021.12645. PMID: 33777207. PMCID: PMC7988712.
Article10. Joshi R. 2012; Learning from eponyms: Jose Verocay and Verocay bodies, Antoni A and B areas, Nils Antoni and Schwannomas. Indian Dermatol Online J. 3:215–9. https://doi.org/10.4103/2229-5178.101826. DOI: 10.4103/2229-5178.101826. PMCID: PMC3505436. PMID: 23189261.
Article11. Weiner JA, Fukushima N, Contos JJ, Scherer SS, Chun J. 2001; Regulation of Schwann cell morphology and adhesion by receptor-mediated lysophosphatidic acid signaling. J Neurosci. 21:7069–78. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.21-18-07069.2001. DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-18-07069.2001. PMID: 11549717. PMCID: PMC6763011.
Article12. Weiss SW, Goldblum JR. 2008. Enzinger and Weiss's soft tissue tumors. 5th ed. Elsevier.13. Koubaa Mahjoub W, Jouini R, Khanchel F, Ben Brahim E, Llamas-Velasco M, Helel I, et al. 2019; Neuroblastoma-like Schwannoma with giant rosette: a potential diagnostic pitfall for hyalinizing spindle cell tumor. J Cutan Pathol. 46:234–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/cup.13405. DOI: 10.1111/cup.13405. PMID: 30582192.
Article14. Vélez D, Reina Duran T, Pérez-Gala S, Fernández JF. 2006; Rosetoid Schwannoma (neuroblastoma-like) in association with an anetoderma. J Cutan Pathol. 33:573–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00480.x. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00480.x. PMID: 16919032.
Article15. Suchak R, Luzar B, Bacchi CE, Maguire B, Calonje E. 2010; Cutaneous neuroblastoma-like schwannoma: a report of two cases, one with a plexiform pattern, and a review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 37:997–1001. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0560.2009.01455.x. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2009.01455.x. PMID: 19922484.
Article16. Goldblum JR, Beals TF, Weiss SW. 1994; Neuroblastoma-like neurilemoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 18:266–73. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000478-199403000-00006. DOI: 10.1097/00000478-199403000-00006. PMID: 8116794.
Article17. Sedassari BT, da Silva Lascane NA, Cury Gallottini MH, Orsini Machado de Sousa SC, Pinto Júnior Ddos S. 2014; Neuroblastoma-like Schwannoma of the lower labial mucosa: a rare morphologic variant of peripheral nerve sheath tumor. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 118:579–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oooo.2014.05.023. DOI: 10.1016/j.oooo.2014.05.023. PMID: 25174314.
Article18. Fisher C, Chappell ME, Weiss SW. 1995; Neuroblastoma-like epithelioid Schwannoma. Histopathology. 26:193–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2559.1995.tb00654.x. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1995.tb00654.x. PMID: 7737668.
Article19. Shim SK, Myoung H. 2016; Neurilemmoma in the floor of the mouth: a case report. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 42:60–4. https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.1.60. DOI: 10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.1.60. PMID: 26904498. PMCID: PMC4761576.
Article20. Hart J, Gardner JM, Edgar M, Weiss SW. 2016; Epithelioid Schwannomas: an analysis of 58 cases including atypical variants. Am J Surg Pathol. 40:704–13. https://doi.org/10.1097/pas.0000000000000589. DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000589. PMID: 26752543.
Article