J Korean Med Sci.
2023 Sep;38(35):e274. 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e274.
Predicted Impact of the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease 3.0 in a Region Suffering Severe Organ Shortage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, The Research Institute for Transplantation, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2545552
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e274
Abstract
- Background
The model for end-stage liver disease 3.0 (MELD3.0) is expected to address the flaws of the current allocation system for deceased donor liver transplantation (DDLT). We aimed to validate MELD3.0 in the Korean population where living donor liver transplantation is predominant due to organ shortages.
Methods
Korean large-volume single-centric waitlist data were merged with the Korean Network for Organ Sharing (KONOS) data. The 90-day mortality was compared between MELD and MELD3.0 using the C-index in 2,353 eligible patients registered for liver transplantation. Patient numbers and outcomes were compared based on changes in KONOS-MELD categorization using MELD3.0. Possible gains in MELD points and reduced waitlist mortality were analyzed.
Results
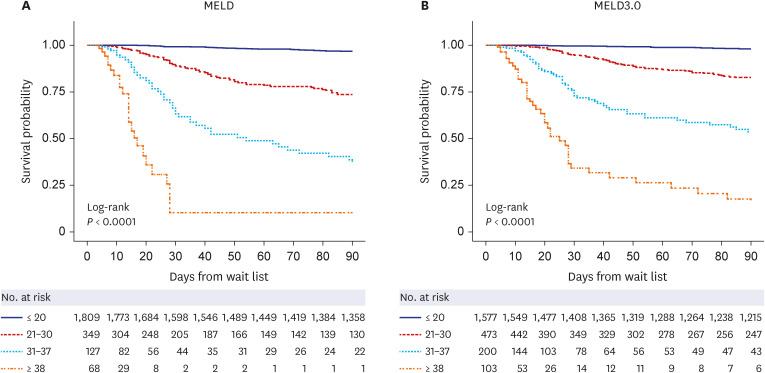
MELD3.0 performed better than MELD (C-index 0.893 for MELD3.0 vs. 0.889 for MELD). When stratified according to the KONOS-MELD categories, 15.9% of the total patients and 35.2% of the deceased patients were up-categorized using MELD3.0 versus MELD categories. The mean gain of MELD points was higher in women (2.6 ± 2.1) than men (2.1 ± 1.9, P < 0.001), and higher in patients with severe ascites (3.3 ± 1.8) than in controls (1.9 ± 1.8, P< 0.001); however, this trend was not significant when the MELD score was higher than 30. When the possible increase in DDLT chance was calculated via up-categorizing using MELD3.0, reducible waitlist mortality was 2.7%.
Conclusion
MELD3.0 could predict better waitlist mortality than MELD; however, the merit for women and patients with severe ascites is uncertain, and reduced waitlist mortality from implementing MELD3.0 is limited in regions suffering from organ shortage, as in Korea.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, Kremers W, Therneau TM, Kosberg CL, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology. 2001; 33(2):464–470. PMID: 11172350.
Article2. Kim WR, Biggins SW, Kremers WK, Wiesner RH, Kamath PS, Benson JT, et al. Hyponatremia and mortality among patients on the liver-transplant waiting list. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359(10):1018–1026. PMID: 18768945.
Article3. Nagai S, Chau LC, Schilke RE, Safwan M, Rizzari M, Collins K, et al. Effects of allocating livers for transplantation based on model for end-stage liver disease-sodium scores on patient outcomes. Gastroenterology. 2018; 155(5):1451–1462.e3. PMID: 30056096.
Article4. Godfrey EL, Malik TH, Lai JC, Mindikoglu AL, Galván NT, Cotton RT, et al. The decreasing predictive power of MELD in an era of changing etiology of liver disease. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19(12):3299–3307. PMID: 31394020.
Article5. Locke JE, Shelton BA, Olthoff KM, Pomfret EA, Forde KA, Sawinski D, et al. Quantifying sex-based disparities in liver allocation. JAMA Surg. 2020; 155(7):e201129. PMID: 32432699.
Article6. Kim WR, Mannalithara A, Heimbach JK, Kamath PS, Asrani SK, Biggins SW, et al. MELD 3.0: the model for end-stage liver disease updated for the modern era. Gastroenterology. 2021; 161(6):1887–1895.e4. PMID: 34481845.
Article7. Goudsmit BF, Putter H, Van Hoek B. The model for end-stage liver disease 3.0: an update without proven accuracy. Gastroenterology. 2022; 162(6):1781–1782. PMID: 34582897.
Article8. Lee J, Kim DG, Lee JY, Lee JG, Joo DJ, Kim SI, et al. Impact of model for end-stage liver disease score-based allocation system in Korea: a nationwide study. Transplantation. 2019; 103(12):2515–2522. PMID: 30985735.
Article9. iRODAT Database. Worldwide liver transplant from deceased donors 2021 (PMP). Accessed December 19, 2023. https://www.irodat.org/?p=database .10. 2020 Annual report of Korean Organ Transplantation Registry. Accessed December 19, 2023. https://www.kotry.org/ko/rang_board/list.html?code=old_report .11. 2020 Annual report of Korean Network for Organ Sharing (KONOS). Accessed December 19, 2023. https://www.konos.go.kr/board/boardListPage.do?page=sub4_2_1&boardId=30 .12. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, Korea National Institute of Health. Korean Society for Transplantation. Korean Organ Transplantation Registry. 2021 KOTRY Annual Data Report. Cheongwon, Korea: Korea National Institute of Health;2022. p. 59–60.13. Harrell FE Jr, Califf RM, Pryor DB, Lee KL, Rosati RA. Evaluating the yield of medical tests. JAMA. 1982; 247(18):2543–2546. PMID: 7069920.
Article14. Goudsmit BF, Putter H, Tushuizen ME, de Boer J, Vogelaar S, Alwayn IP, et al. Validation of the model for end-stage liver disease sodium (MELD-Na) score in the Eurotransplant region. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21(1):229–240. PMID: 32529758.
Article15. OPTN policies, 9.5 specific standardized MELD or PELD score exceptions. Updated 2023. Accessed December 19, 2023. https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/media/eavh5bf3/optn_policies.pdf .16. Vodkin I, Kuo A. Extended criteria donors in liver transplantation. Clin Liver Dis. 2017; 21(2):289–301. PMID: 28364814.
Article17. Park H, Jung ES, Oh JS, Lee YM, Lee JM. Organ donation after controlled circulatory death (Maastricht classification III) following the withdrawal of life-sustaining treatment in Korea: a suggested guideline. Korean J Transplant. 2021; 35(2):71–76. PMID: 35769520.
Article18. Moon DB, Lee SG, Kang WH, Song GW, Jung DH, Park GC, et al. Adult living donor liver transplantation for acute-on-chronic liver failure in high-model for end-stage liver disease score patients. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17(7):1833–1842. PMID: 28097804.
Article19. Wong TC, Fung JY, Pang HH, Leung CK, Li HF, Sin SL, et al. Analysis of survival benefits of living versus deceased donor liver transplant in high model for end-stage liver disease and hepatorenal syndrome. Hepatology. 2021; 73(6):2441–2454. PMID: 33006772.
Article20. Roll GR, Spiro M, Raptis DA, Jalal A, Yan CT, Olthoff KM, et al. Which recipient pretransplant factors, such as MELD, renal function, sarcopenia, and recent sepsis influence suitability for and outcome after living donor liver transplantation? A systematic review of the literature and expert panel recommendations. Clin Transplant. 2022; 36(10):e14656. PMID: 35340054.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Status of Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation for Alcoholic Liver Disease in Korea in MELD Era
- Mortality scoring systems for liver transplant recipients: before and after model for end-stage liver disease score
- Impact of the introduction of the model for end-stage liver disease system on the low volume liver transplant centers: a multicenter study
- Activation Policy for Brain-dead Organ Donation
- Decellularlized Matrix in Organ Transplantation