Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2023 Sep;27(5):427-436. 10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.5.427.
Mad2B forms a complex with Cdc20, Cdc27, Rev3 and Rev1 in response to cisplatin-induced DNA damage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, Dankook University, Cheonan 31116, Korea
- 2Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of Leicester, Leicester LE1 7RH, UK
- KMID: 2545533
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.5.427
Abstract
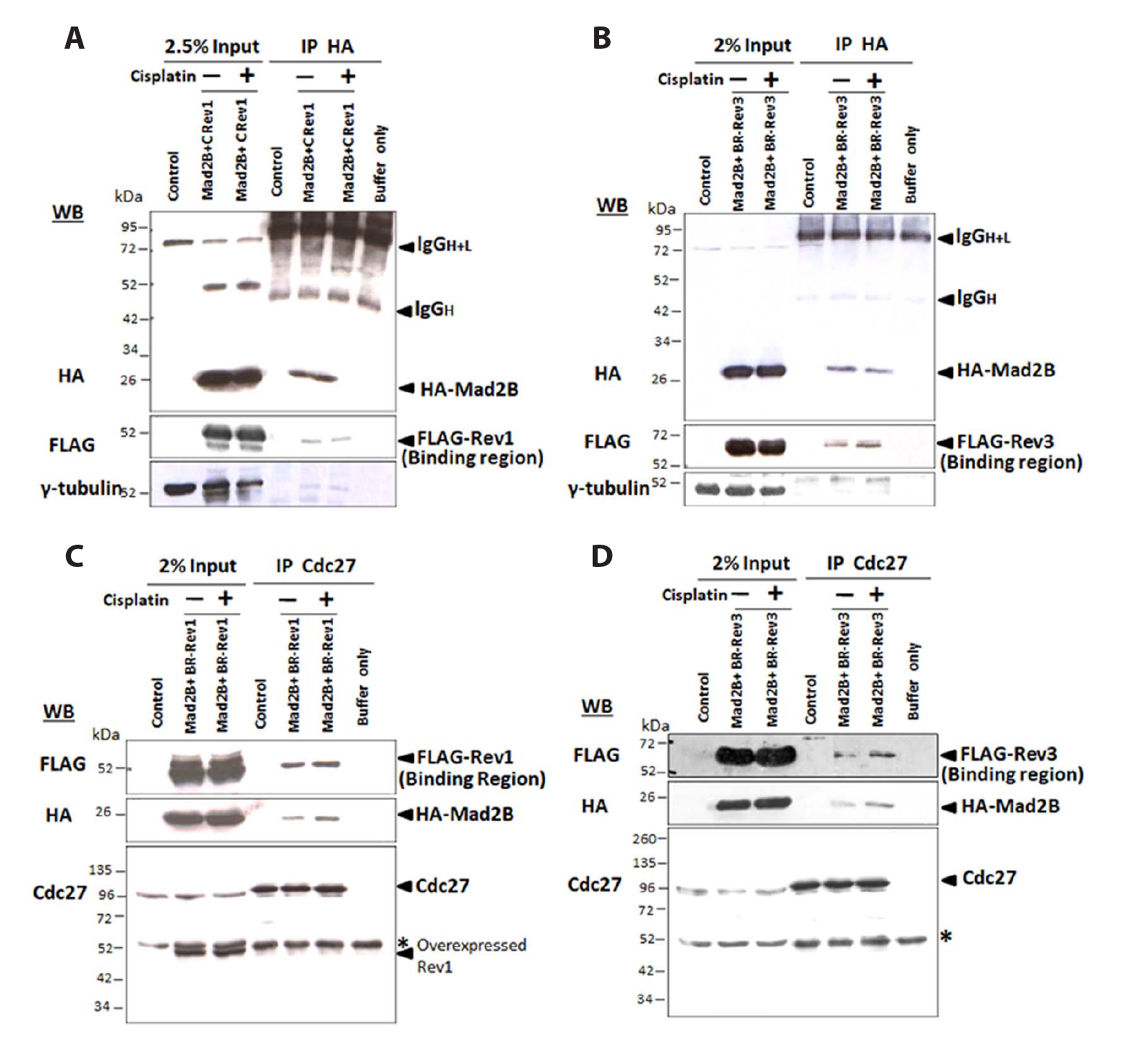
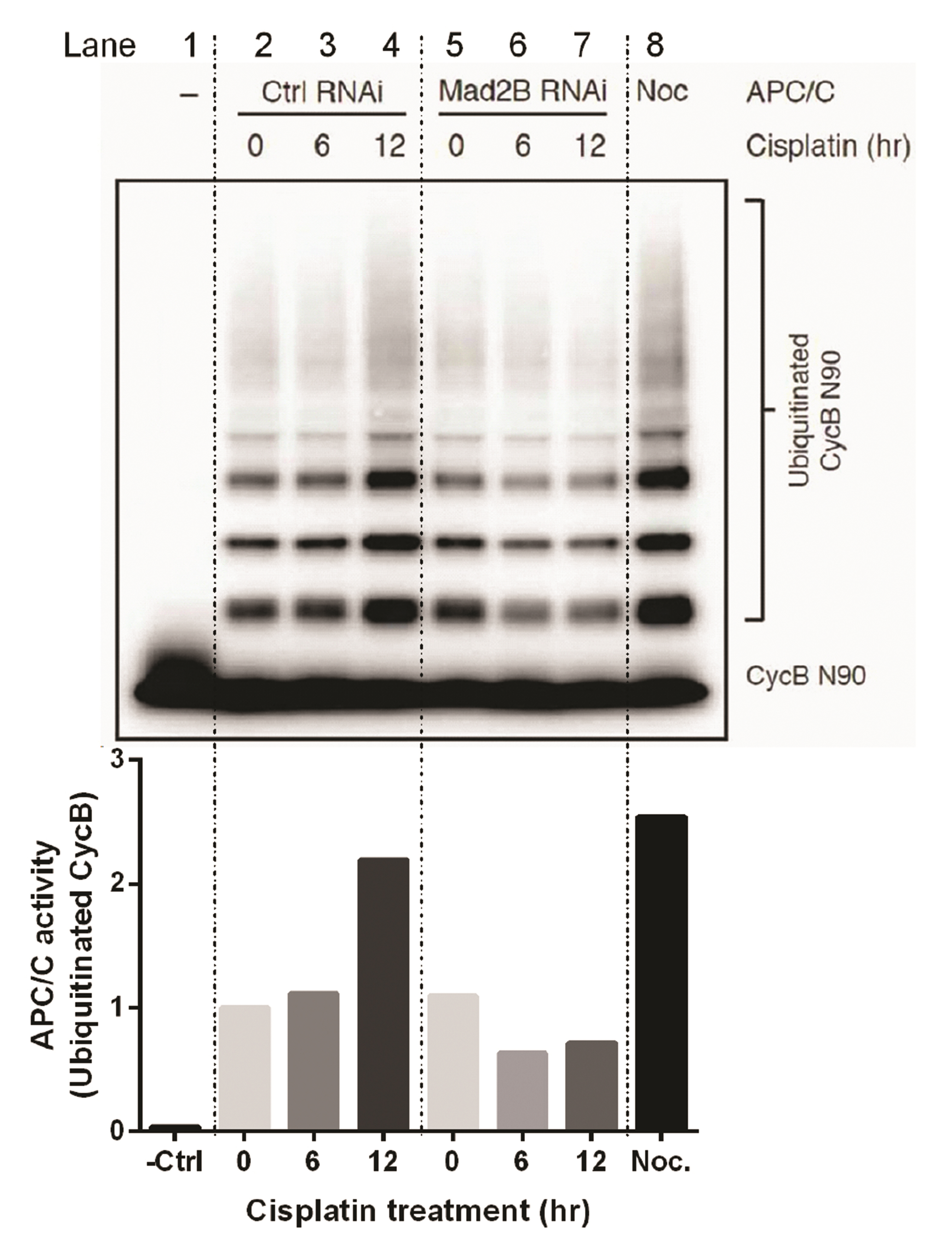
- Mitotic arrest deficient 2 like 2 (Mad2L2, also known as Mad2B), the human homologue of the yeast Rev7 protein, is a regulatory subunit of DNA polymerase ζ that shares high sequence homology with Mad2, the mitotic checkpoint protein. Previously, we demonstrated the involvement of Mad2B in the cisplatininduced DNA damage response. In this study, we extend our findings to show that Mad2B is recruited to sites of DNA damage in human cancer cells in response to cisplatin treatment. We found that in undamaged cells, Mad2B exists in a complex with Polζ-Rev1 and the APC/C subunit Cdc27. Following cisplatin-induced DNA damage, we observed an increase in the recruitment of Mad2B and Cdc20 (the activators of the APC/C), to the complex. The involvement of Mad2B-Cdc20-APC/C during DNA damage has not been reported before and suggests that the APC/C is activated following cisplatin-induced DNA damage. Using an in vitro ubiquitination assay, our data confirmed Mad2B-dependent activation of APC/C in cisplatin-treated cells. Mad2B may act as an accelerator for APC/C activation during DNA damage response. Our data strongly suggest a role for Mad2B-APC/C-Cdc20 in the ubiquitination of proteins involved in the DNA damage response.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Prakash S, Johnson RE, Prakash L. 2005; Eukaryotic translesion synthesis DNA polymerases: specificity of structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 74:317–353. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.74.082803.133250. PMID: 15952890.
Article2. Weaver TM, Click TH, Khoang TH, Todd Washington M, Agarwal PK, Freudenthal BD. 2022; Mechanism of nucleotide discrimination by the translesion synthesis polymerase Rev1. Nat Commun. 13:2876. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30577-0. PMID: 35610266. PMCID: PMC9130138. PMID: 910c77d8426543aaaf98c3556e2e1127.
Article3. Lawrence CW. 2002; Cellular roles of DNA polymerase zeta and Rev1 protein. DNA Repair (Amst). 1:425–435. DOI: 10.1016/S1568-7864(02)00038-1. PMID: 12509231.4. Sharma S, Canman CE. 2012; REV1 and DNA polymerase zeta in DNA interstrand crosslink repair. Environ Mol Mutagen. 53:725–740. DOI: 10.1002/em.21736. PMID: 23065650. PMCID: PMC5543726.
Article5. Hoege C, Pfander B, Moldovan GL, Pyrowolakis G, Jentsch S. 2002; RAD6-dependent DNA repair is linked to modification of PCNA by ubiquitin and SUMO. Nature. 419:135–141. DOI: 10.1038/nature00991. PMID: 12226657.
Article6. Murakumo Y, Roth T, Ishii H, Rasio D, Numata S, Croce CM, Fishel R. 2000; A human REV7 homolog that interacts with the polymerase zeta catalytic subunit hREV3 and the spindle assembly checkpoint protein hMAD2. J Biol Chem. 275:4391–4397. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.275.6.4391. PMID: 10660610.
Article7. Cahill DP, da Costa LT, Carson-Walter EB, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Lengauer C. 1999; Characterization of MAD2B and other mitotic spindle checkpoint genes. Genomics. 58:181–187. DOI: 10.1006/geno.1999.5831. PMID: 10366450.
Article8. Chen J, Fang G. 2001; MAD2B is an inhibitor of the anaphase-promoting complex. Genes Dev. 15:1765–1770. DOI: 10.1101/gad.898701. PMID: 11459826. PMCID: PMC312737.
Article9. Pfleger CM, Salic A, Lee E, Kirschner MW. 2001; Inhibition of Cdh1-APC by the MAD2-related protein MAD2L2: a novel mechanism for regulating Cdh1. Genes Dev. 15:1759–1764. DOI: 10.1101/gad.897901. PMID: 11459825. PMCID: PMC312740.
Article10. Yamano H. 2019; APC/C: current understanding and future perspectives. F1000Res. 8:F1000 Faculty Rev-1725. DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.18582.1. PMID: 31164978. PMCID: PMC6534075. PMID: 466802ec17f141048781677faebd9613.
Article11. Boersma V, Moatti N, Segura-Bayona S, Peuscher MH, van der Torre J, Wevers BA, Orthwein A, Durocher D, Jacobs JJL. 2015; MAD2L2 controls DNA repair at telomeres and DNA breaks by inhibiting 5' end resection. Nature. 521:537–540. DOI: 10.1038/nature14216. PMID: 25799990. PMCID: PMC4481296.
Article12. Okada T, Sonoda E, Yoshimura M, Kawano Y, Saya H, Kohzaki M, Takeda S. 2005; Multiple roles of vertebrate REV genes in DNA repair and recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 25:6103–6111. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.14.6103-6111.2005. PMID: 15988022. PMCID: PMC1168817.13. Xu G, Chapman JR, Brandsma I, Yuan J, Mistrik M, Bouwman P, Bartkova J, Gogola E, Warmerdam D, Barazas M, Jaspers JE, Watanabe K, Pieterse M, Kersbergen A, Sol W, Celie PHN, Schouten PC, van den Broek B, Salman A, Nieuwland M, et al. 2015; REV7 counteracts DNA double-strand break resection and affects PARP inhibition. Nature. 521:541–544. DOI: 10.1038/nature14328. PMID: 25799992. PMCID: PMC4671316.
Article14. Clairmont CS, D'Andrea AD. 2021; REV7 directs DNA repair pathway choice. Trends Cell Biol. 31:965–978. DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2021.05.009. PMID: 34147298. PMCID: PMC8608404.
Article15. Bennett EJ, Harper JW. 2008; DNA damage: ubiquitin marks the spot. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 15:20–22. DOI: 10.1038/nsmb0108-20. PMID: 18176551.
Article16. Lehmann AR. 2011; Ubiquitin-family modifications in the replication of DNA damage. FEBS Lett. 585:2772–2779. DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.06.005. PMID: 21704031.
Article17. Sharma S, Helchowski CM, Canman CE. 2013; The roles of DNA polymerase ζ and the Y family DNA polymerases in promoting or preventing genome instability. Mutat Res. 743-744:97–110. DOI: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2012.11.002. PMID: 23195997. PMCID: PMC3616148.
Article18. de Krijger I, Boersma V, Jacobs JJL. 2021; REV7: Jack of many trades. Trends Cell Biol. 31:686–701. DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2021.04.002. PMID: 33962851. PMCID: PMC7611290.
Article19. Kim JH, Kim HR, Patel R. 2023; Inactivation of Mad2B enhances apoptosis in human cervical cancer cell line upon cisplatin-induced DNA damage. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 31:340–349. DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2022.130. PMID: 36642928. PMCID: PMC10129849.
Article20. Iwai H, Kim M, Yoshikawa Y, Ashida H, Ogawa M, Fujita Y, Muller D, Kirikae T, Jackson PK, Kotani S, Sasakawa C. 2007; A bacterial effector targets Mad2L2, an APC inhibitor, to modulate host cell cycling. Cell. 130:611–623. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.043. PMID: 17719540.
Article21. Deacon K, Mistry P, Chernoff J, Blank JL, Patel R. 2003; p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates cell death and p21-activated kinase mediates cell survival during chemotherapeutic drug-induced mitotic arrest. Mol Biol Cell. 14:2071–2087. DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-10-0653. PMID: 12802076. PMCID: PMC165098.
Article22. Gillotin S. 2018; Isolation of chromatin-bound proteins from subcellular fractions for biochemical analysis. Bio Protoc. 8:e3035. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3035. PMID: 34532513. PMCID: PMC8342065.
Article23. Deacon K, Blank JL. 1999; MEK kinase 3 directly activates MKK6 and MKK7, specific activators of the p38 and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases. J Biol Chem. 274:16604–16610. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.274.23.16604. PMID: 10347227.
Article24. Lara-Gonzalez P, Scott MI, Diez M, Sen O, Taylor SS. 2011; BubR1 blocks substrate recruitment to the APC/C in a KEN-box-dependent manner. J Cell Sci. 124:4332–4345. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.094763. PMID: 22193957. PMCID: PMC3258114.
Article25. Murakumo Y, Ogura Y, Ishii H, Numata S, Ichihara M, Croce CM, Fishel R, Takahashi M. 2001; Interactions in the error-prone postreplication repair proteins hREV1, hREV3, and hREV7. J Biol Chem. 276:35644–35651. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M102051200. PMID: 11485998.
Article26. Hara K, Hashimoto H, Murakumo Y, Kobayashi S, Kogame T, Unzai S, Akashi S, Takeda S, Shimizu T, Sato M. 2010; Crystal structure of human REV7 in complex with a human REV3 fragment and structural implication of the interaction between DNA polymerase zeta and REV1. J Biol Chem. 285:12299–12307. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.092403. PMID: 20164194. PMCID: PMC2852969.
Article27. Bhat A, Wu Z, Maher VM, McCormick JJ, Xiao W. 2015; Rev7/Mad2B plays a critical role in the assembly of a functional mitotic spindle. Cell Cycle. 14:3929–3938. DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1120922. PMID: 26697843. PMCID: PMC4825701.
Article28. Cheung HW, Chun AC, Wang Q, Deng W, Hu L, Guan XY, Nicholls JM, Ling MT, Chuan Wong Y, Tsao SW, Jin DY, Wang X. 2006; Inactivation of human MAD2B in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells leads to chemosensitization to DNA-damaging agents. Cancer Res. 66:4357–4367. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3602. PMID: 16618761.29. Gibbs PE, McDonald J, Woodgate R, Lawrence CW. 2005; The relative roles in vivo of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pol eta, Pol zeta, Rev1 protein and Pol32 in the bypass and mutation induction of an abasic site, T-T (6-4) photoadduct and T-T cis-syn cyclobutane dimer. Genetics. 169:575–582. DOI: 10.1534/genetics.104.034611. PMID: 15520252. PMCID: PMC1449107.
Article30. da Fonseca PC, Kong EH, Zhang Z, Schreiber A, Williams MA, Morris EP, Barford D. 2011; Structures of APC/C(Cdh1) with substrates identify Cdh1 and Apc10 as the D-box co-receptor. Nature. 470:274–278. DOI: 10.1038/nature09625. PMID: 21107322. PMCID: PMC3037847.
Article31. Zur A, Brandeis M. 2002; Timing of APC/C substrate degradation is determined by fzy/fzr specificity of destruction boxes. EMBO J. 21:4500–4510. DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf452. PMID: 12198152. PMCID: PMC126191.
Article32. Hicks JK, Chute CL, Paulsen MT, Ragland RL, Howlett NG, Guéranger Q, Glover TW, Canman CE. 2010; Differential roles for DNA polymerases eta, zeta, and REV1 in lesion bypass of intrastrand versus interstrand DNA cross-links. Mol Cell Biol. 30:1217–1230. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00993-09. PMID: 20028736. PMCID: PMC2820889.
Article33. Collins PL, Purman C, Porter SI, Nganga V, Saini A, Hayer KE, Gurewitz GL, Sleckman BP, Bednarski JJ, Bassing CH, Oltz EM. 2020; DNA double-strand breaks induce H2Ax phosphorylation domains in a contact-dependent manner. Nat Commun. 11:3158. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16926-x. PMID: 32572033. PMCID: PMC7308414. PMID: 52e96531818443018246302cc0d348bc.
Article34. Fang G. 2002; Checkpoint protein BubR1 acts synergistically with Mad2 to inhibit anaphase-promoting complex. Mol Biol Cell. 13:755–766. DOI: 10.1091/mbc.01-09-0437. PMID: 11907259. PMCID: PMC99596.
Article35. Nezi L, Rancati G, De Antoni A, Pasqualato S, Piatti S, Musacchio A. 2006; Accumulation of Mad2-Cdc20 complex during spindle checkpoint activation requires binding of open and closed conformers of Mad2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 174:39–51. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200602109. PMID: 16818718. PMCID: PMC2064158.36. Izawa D, Pines J. 2011; How APC/C-Cdc20 changes its substrate specificity in mitosis. Nat Cell Biol. 13:223–233. Erratum in: Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13:633. DOI: 10.1038/ncb2165. PMID: 21336306. PMCID: PMC3059483.37. Chao WC, Kulkarni K, Zhang Z, Kong EH, Barford D. 2012; Structure of the mitotic checkpoint complex. Nature. 484:208–213. DOI: 10.1038/nature10896. PMID: 22437499.38. Coster G, Hayouka Z, Argaman L, Strauss C, Friedler A, Brandeis M, Goldberg M. 2007; The DNA damage response mediator MDC1 directly interacts with the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome. J Biol Chem. 282:32053–32064. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M705890200. PMID: 17827148.39. Zhang L, Park CH, Wu J, Kim H, Liu W, Fujita T, Balasubramani M, Schreiber EM, Wang XF, Wan Y. 2010; Proteolysis of Rad17 by Cdh1/APC regulates checkpoint termination and recovery from genotoxic stress. EMBO J. 29:1726–1737. DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.55. PMID: 20424596. PMCID: PMC2876963.40. Chun AC, Kok KH, Jin DY. 2013; REV7 is required for anaphase-promoting complex-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of translesion DNA polymerase REV1. Cell Cycle. 12:365–378. DOI: 10.4161/cc.23214. PMID: 23287467. PMCID: PMC3575465.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Inactivation of Mad2B Enhances Apoptosis in Human Cervical Cancer Cell Line upon Cisplatin-Induced DNA Damage
- Cisplatin-induced Kidney Dysfunction and Perspectives on Improving Treatment Strategies
- Exogenous spermidine ameliorates tubular necrosis during cisplatin nephrotoxicity
- Analysis of Ultraviolet Light Damage in Mammalian Cells by Flowcytometry
- Activation of NF-kappa B in the cisplatin-induced apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma