Nutr Res Pract.
2023 Aug;17(4):682-697. 10.4162/nrp.2023.17.4.682.
In-silico annotation of the chemical composition of Tibetan tea and its mechanism on antioxidant and lipidlowering in mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Bioengineering, Sichuan University of Science and Engineering, Zigong 643000, China
- 2Luzhou LaoJiao Group Co. Ltd., Luzhou 646000, China
- 3College of Horticulture, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha 410128, China
- 4Department of Bioinformatics and Biotechnology, Government College University Faisalabad, Faisalabad, 38000, Pakistan
- 5Ya’an Youyi Tea Co., Ltd, Ya’an 625000, China
- 6Comprehensive Agricultural Service Center of Dachuan, Lushan, Ya’an 625000, China
- 7School of Food and Biological Engineering, Xihua University, Chengdu 610039, China
- KMID: 2545185
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2023.17.4.682
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
Tibetan tea is a kind of dark tea, due to the inherent complexity of natural products, the chemical composition and beneficial effects of Tibetan tea are not fully understood. The objective of this study was to unravel the composition of Tibetan tea using knowledge-guided multilayer network (KGMN) techniques and explore its potential antioxidant and hypolipidemic mechanisms in mice.
MATERIALS/METHODS
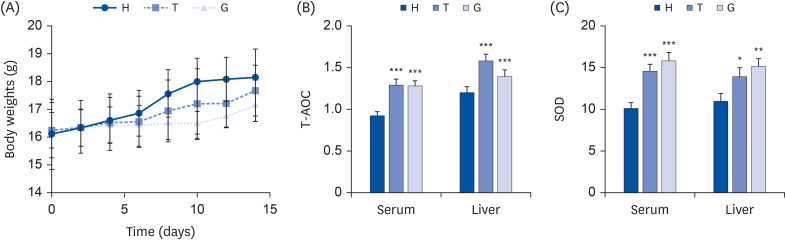
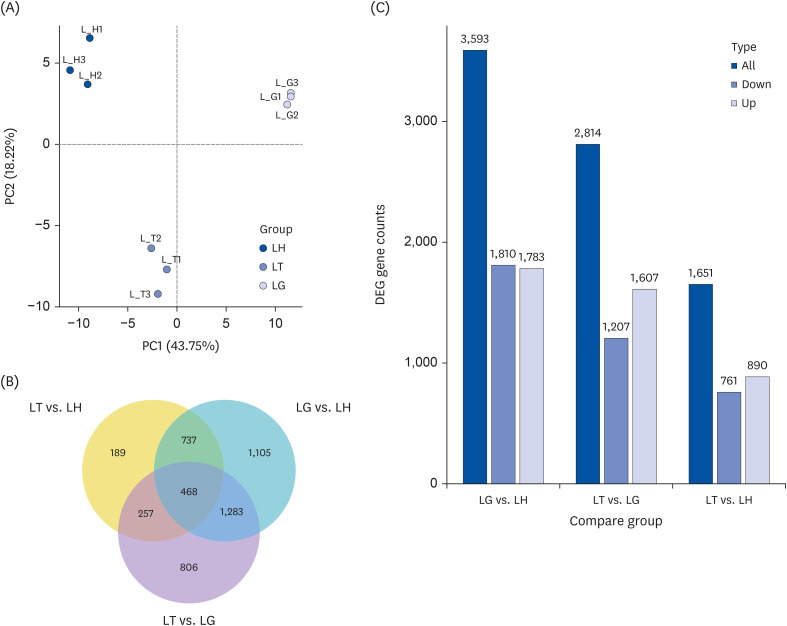
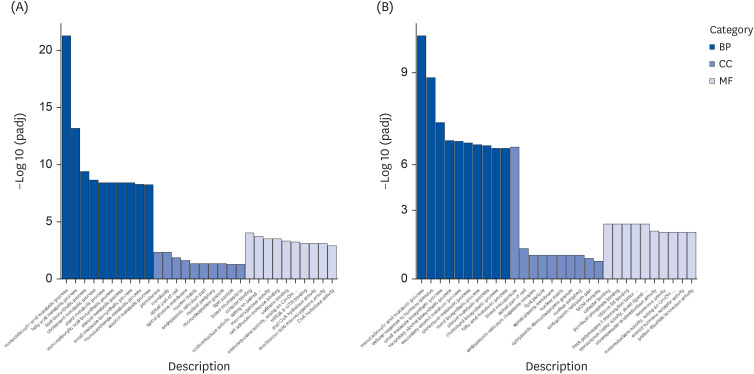
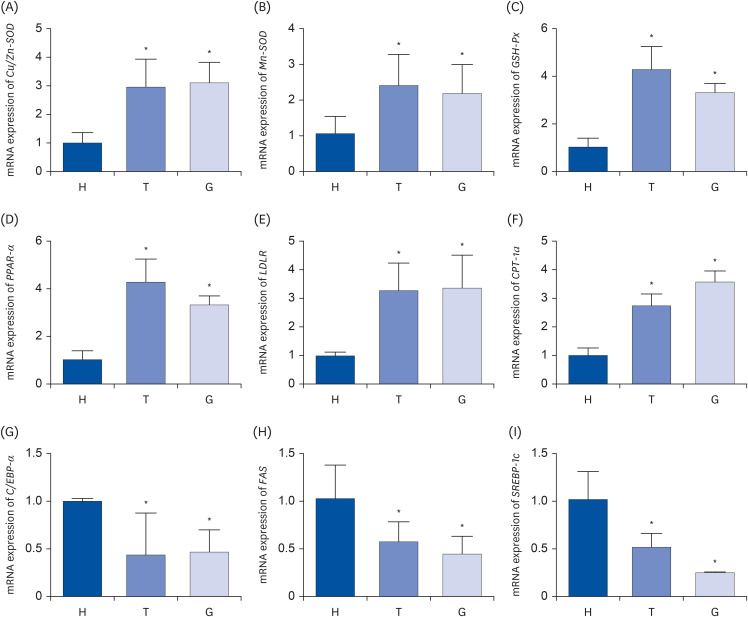
The C57BL/6J mice were continuously gavaged with Tibetan tea extract (T group), green tea extract (G group) and ddH 2 O (H group) for 15 days. The activity of total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in mice was detected. Transcriptome sequencing technology was used to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying the antioxidant and lipid-lowering effects of Tibetan tea in mice. Furthermore, the expression levels of liver antioxidant and lipid metabolism related genes in various groups were detected by the real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) method.
RESULTS
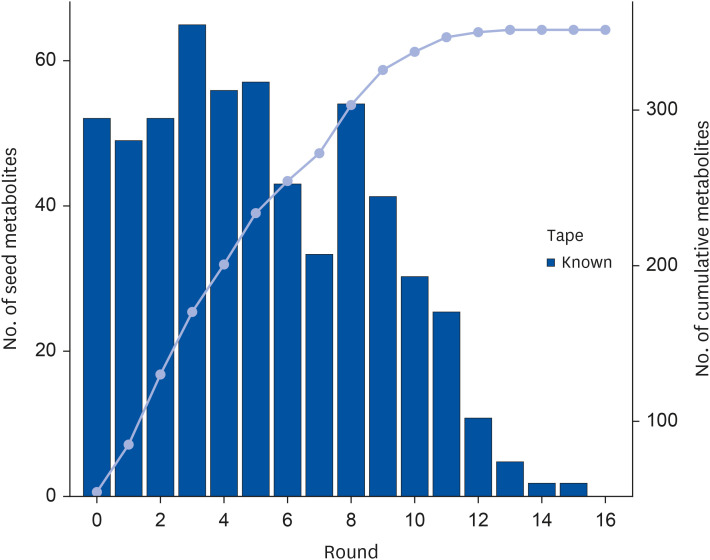
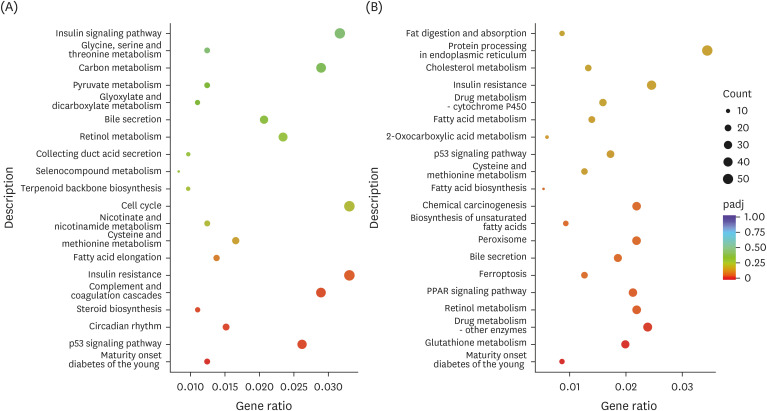
The results showed that a total of 42 flavonoids are provisionally annotated in Tibetan tea using KGMN strategies. Tibetan tea significantly reduced body weight gain and increased T-AOC and SOD activities in mice compared with the H group. Based on the results of transcriptome and qPCR, it was confirmed that Tibetan tea could play a key role in antioxidant and lipid lowering by regulating oxidative stress and lipid metabolism related pathways such as insulin resistance, P53 signaling pathway, insulin signaling pathway, fatty acid elongation and fatty acid metabolism.
CONCLUSIONS
This study was the first to use computational tools to deeply explore the composition of Tibetan tea and revealed its potential antioxidant and hypolipidemic mechanisms, and it provides new insights into the composition and bioactivity of Tibetan tea.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Xiao Y, He C, Chen Y, Ho CT, Wu X, Huang Y, Gao Y, Hou A, Li Z, Wang Y, et al. UPLC-QQQ-MS/MS-based widely targeted metabolomic analysis reveals the effect of solid-state fermentation with Eurotium cristatum on the dynamic changes in the metabolite profile of dark tea. Food Chem. 2022; 378:131999. PMID: 35081481.2. Xie H, Li X, Ren Z, Qiu W, Chen J, Jiang Q, Chen B, Chen D. Antioxidant and cytoprotective effects of Tibetan tea and its phenolic components. Molecules. 2018; 23:179. PMID: 29364183.
Article3. Liu Y, Huang W, Zhang C, Li C, Fang Z, Zeng Z, Hu B, Chen H, Wu W, Wang T, et al. Targeted and untargeted metabolomic analyses and biological activity of Tibetan tea. Food Chem. 2022; 384:132517. PMID: 35228002.
Article4. Wang S, Qiu Y, Gan RY, Zhu F. Chemical constituents and biological properties of Pu-erh tea. Food Res Int. 2022; 154:110899. PMID: 35337597.
Article5. Zhu J, Yu C, Zhou H, Wei X, Wang Y. Comparative evaluation for phytochemical composition and regulation of blood glucose, hepatic oxidative stress and insulin resistance in mice and HepG2 models of four typical Chinese dark teas. J Sci Food Agric. 2021; 101:6563–6577. PMID: 34018615.
Article6. Long P, Wen M, Granato D, Zhou J, Wu Y, Hou Y, Zhang L. Untargeted and targeted metabolomics reveal the chemical characteristic of pu-erh tea (Camellia assamica) during pile-fermentation. Food Chem. 2020; 311:125895. PMID: 31780220.7. DesRochers N, Walsh JP, Renaud JB, Seifert KA, Yeung KK, Sumarah MW. Metabolomic profiling of fungal pathogens responsible for root rot in American ginseng. Metabolites. 2020; 10:35. PMID: 31947697.
Article8. Reveglia P, Raimondo ML, Masi M, Cimmino A, Nuzzo G, Corso G, Fontana A, Carlucci A, Evidente A. Untargeted and targeted LC-MS/MS based metabolomics study on in vitro culture of Phaeoacremonium species. J Fungi (Basel). 2022; 8:55. PMID: 35049995.
Article9. Xu J, Liang X, Wang W, Chen S, Tang Q. Study on anti-radiation effect of Ya’an Tibetan tea. J Phys Conf Ser. 2020; 1549:032049.
Article10. Blaženović I, Kind T, Ji J, Fiehn O. Software tools and approaches for compound identification of LC-MS/MS data in metabolomics. Metabolites. 2018; 8:31. PMID: 29748461.
Article11. Zhou Z, Luo M, Zhang H, Yin Y, Cai Y, Zhu ZJ. Metabolite annotation from knowns to unknowns through knowledge-guided multi-layer metabolic network. bioRxiv. 2022; 6:494523.
Article12. Zheng Q, Li W, Zhang H, Gao X, Tan S. Optimizing synchronous extraction and antioxidant activity evaluation of polyphenols and polysaccharides from Ya’an Tibetan tea (Camellia sinensis). Food Sci Nutr. 2019; 8:489–499. PMID: 31993173.
Article13. Li L, Shi M, Salerno S, Tang M, Guo F, Liu J, Feng Y, Fu M, Huang Q, Ma L, et al. Microbial and metabolomic remodeling by a formula of Sichuan dark tea improves hyperlipidemia in apoE-deficient mice. PLoS One. 2019; 14:e0219010. PMID: 31269076.
Article14. Xu J, Sun R, Wang J. Human trial of health effects of Tibetan tea. Food Res Dev. 2017; 38:168–171.15. Tsugawa H, Ikeda K, Takahashi M, Satoh A, Mori Y, Uchino H, Okahashi N, Yamada Y, Tada I, Bonini P, et al. A lipidome atlas in MS-DIAL 4. Nat Biotechnol. 2020; 38:1159–1163. PMID: 32541957.
Article16. Pandurangan AK, Ismail S, Saadatdoust Z, Esa NM. Allicin alleviates dextran sodium sulfate- (DSS-) induced ulcerative colitis in BALB/c mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015; 2015:605208. PMID: 26075036.
Article17. Shi J, Ma W, Wang C, Wu W, Tian J, Zhang Y, Shi Y, Wang J, Peng Q, Lin Z, et al. Impact of various microbial-fermented methods on the chemical profile of dark tea using a single raw tea material. J Agric Food Chem. 2021; 69:4210–4222. PMID: 33792297.
Article18. Zhu MZ, Li N, Zhou F, Ouyang J, Lu DM, Xu W, Li J, Lin HY, Zhang Z, Xiao JB, et al. Microbial bioconversion of the chemical components in dark tea. Food Chem. 2020; 312:126043. PMID: 31896450.
Article19. Wang Y, Kan Z, Thompson HJ, Ling T, Ho CT, Li D, Wan X. Impact of six typical processing methods on the chemical composition of tea leaves using a single Camellia sinensis cultivar, Longjing 43. J Agric Food Chem. 2019; 67:5423–5436. PMID: 30403138.
Article20. Al-Ishaq RK, Abotaleb M, Kubatka P, Kajo K, Büsselberg D. Flavonoids and their anti-diabetic effects: cellular mechanisms and effects to improve blood sugar levels. Biomolecules. 2019; 9:430. PMID: 31480505.
Article21. Zuo L, Prather ER, Stetskiv M, Garrison DE, Meade JR, Peace TI, Zhou T. Inflammaging and oxidative stress in human diseases: from molecular mechanisms to novel treatments. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20:4472. PMID: 31510091.
Article22. Phaniendra A, Jestadi DB, Periyasamy L. Free radicals: properties, sources, targets, and their implication in various diseases. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2015; 30:11–26. PMID: 25646037.
Article23. Nobari H, Saedmocheshi S, Chung LH, Suzuki K, Maynar-Mariño M, Pérez-Gómez J. An overview on how exercise with green tea consumption can prevent the production of reactive oxygen species and improve sports performance. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021; 19:218. PMID: 35010479.
Article24. Mu S, Yang W, Huang G. Antioxidant activities and mechanisms of polysaccharides. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021; 97:628–632. PMID: 32946177.
Article25. Song Y, Hui J, Kou W, Xin R, Jia F, Wang N, Hu F, Zhang H, Liu H. Identification of Inonotus obliquus and analysis of antioxidation and antitumor activities of polysaccharides. Curr Microbiol. 2008; 57:454–462. PMID: 18795365.
Article26. Hernández Borrero LJ, El-Deiry WS. Tumor suppressor p53: biology, signaling pathways, and therapeutic targeting. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021; 1876:188556. PMID: 33932560.
Article27. Tu Y, Chen D, Pan T, Chen Z, Xu J, Jin L, Sheng L, Jin X, Wang X, Lan X, et al. Inhibition of miR-431-5p attenuated liver apoptosis through KLF15/p53 signal pathway in S100 induced autoimmune hepatitis mice. Life Sci. 2021; 280:119698. PMID: 34111466.
Article28. Jazvinšćak Jembrek M, Oršolić N, Mandić L, Sadžak A, Šegota S. Anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of flavonols: targeting Nrf2, NF-κB and p53 pathways in neurodegeneration. Antioxidants. 2021; 10:1628. PMID: 34679762.
Article29. Seo DB, Jeong HW, Cho D, Lee BJ, Lee JH, Choi JY, Bae IH, Lee SJ. Fermented green tea extract alleviates obesity and related complications and alters gut microbiota composition in diet-induced obese mice. J Med Food. 2015; 18:549–556. PMID: 25764354.
Article30. Wang C, Liu J, Sang S, Ao X, Su M, Hu B, Li H. Effects of tea treatments against high-fat diet-induced disorder by regulating lipid metabolism and the gut microbiota. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022; 2022:9336080. PMID: 35677179.
Article31. Liu C, Guo Y, Sun L, Lai X, Li Q, Zhang W, Xiang L, Sun S, Cao F. Six types of tea reduce high-fat-diet-induced fat accumulation in mice by increasing lipid metabolism and suppressing inflammation. Food Funct. 2019; 10:2061–2074. PMID: 30907897.
Article32. Li N, Zhou X, Wang J, Chen J, Lu Y, Sun Y, Song Y, Tan X, Xie G, Chen Y, et al. White tea alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating energy expenditure and lipid metabolism. Gene. 2022; 833:146553. PMID: 35569768.
Article33. Hussain K, Yang Y, Wang J, Bian H, Lei X, Chen J, Li Q, Wang L, Zhong Q, Fang X, et al. Comparative study on the weight loss and lipid metabolism by tea polyphenols in diet induced obese C57BL/6J pseudo germ free and conventionalized mice. Food Sci Hum Well. 2022; 11:697–710.
Article34. Cho D, Jeong HW, Kim JK, Kim AY, Hong YD, Lee JH, Choi JK, Seo DB. Gallocatechin gallate-containing fermented green tea extract ameliorates obesity and hypertriglyceridemia through the modulation of lipid metabolism in adipocytes and myocytes. J Med Food. 2019; 22:779–788. PMID: 31210578.
Article35. Rains TM, Agarwal S, Maki KC. Antiobesity effects of green tea catechins: a mechanistic review. J Nutr Biochem. 2011; 22:1–7. PMID: 21115335.
Article36. Sirichaiwetchakoon K, Lowe GM, Kupittayanant S, Churproong S, Eumkeb G. Pluchea indica (L.) Less. tea ameliorates hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and obesity in high fat diet-fed mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020; 2020:8746137. PMID: 32595747.37. Wang J, Zheng D, Huang F, Zhao A, Kuang J, Ren Z, Chen T, Lei J, Lin J, Wang X, et al. Theabrownin and Poria cocos polysaccharide improve lipid metabolism via modulation of bile acid and fatty acid metabolism. Front Pharmacol. 2022; 13:875549. PMID: 35833020.
Article38. Xu J, Wang W, Liang X, Li P, Zou Y, Du X. Inhibitory effect of the theabrownin and tea polysaccharide extracts of dark tea on lipase. J Phys Conf Ser. 2020; 1549:032048.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Essential Oil of Marrubium vulgare: Chemical Composition and Biological Activities. A Review
- Effect of Extraction Conditions of Green Tea on Antioxidant Activity and EGCG Content: Optimization using Response Surface Methodology
- In-silico characterization and structure-based functional annotation of a hypothetical protein from Campylobacter jejuni involved in propionate catabolism
- Repellent effect of Mate tea and Jasmine tea against house dust mites (Dermatophagoides farinae and D. pteronyssinus)
- Anti-atherosclerotic Effect of Green Tea in Poluynsaturated Fatty Acids-treated Apo E KO Mice