Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2023 Jul;27(4):383-398. 10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.4.383.
Dihydroaustrasulfone alcohol induces apoptosis in nasopharyngeal cancer cells by inducing reactive oxygen speciesdependent inactivation of the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Tungs’ Taichung Metro Harbor Hospital, Taichung 435, Taiwan
- 2College of Medicine, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung 402, Taiwan
- 3General Education Center, Jenteh Junior College of Medicine, Nursing and Management, Miaoli 356, Taiwan
- 4Hemato-Oncology Division, Department of Internal Medicine, Changhua Christian Hospital, Changhua 500, Taiwan
- 5Institute of Biomedical Science, The iEGG and Animal Biotechnology Center, National ChungHsing University, Taichung 402, Taiwan
- 6Department of Molecular Medicine and Surgery, Karolinska Institute, SE-17177 Stockholm, Sweden
- 7Department of Marine Biotechnology and Resources, National Sun Yat-sen University, Kaohsiung 804, Taiwan
- 8National Museum of Marine Biology and Aquarium, Pingtung 944, Taiwan
- 9Department of Medical Research, China Medical University Hospital, Taichung 404, Taiwan
- 10Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung 807, Taiwan
- KMID: 2544140
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.4.383
Abstract
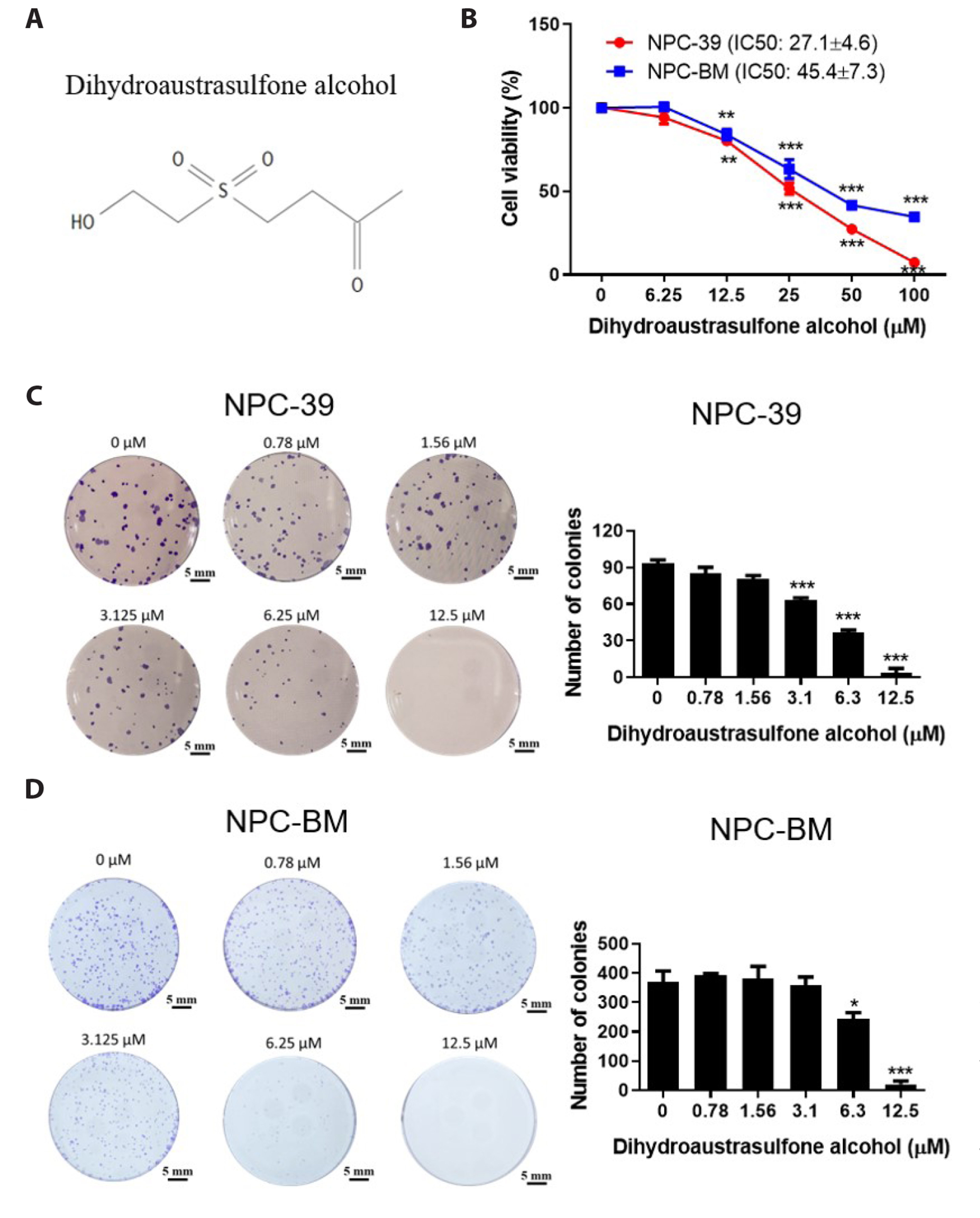
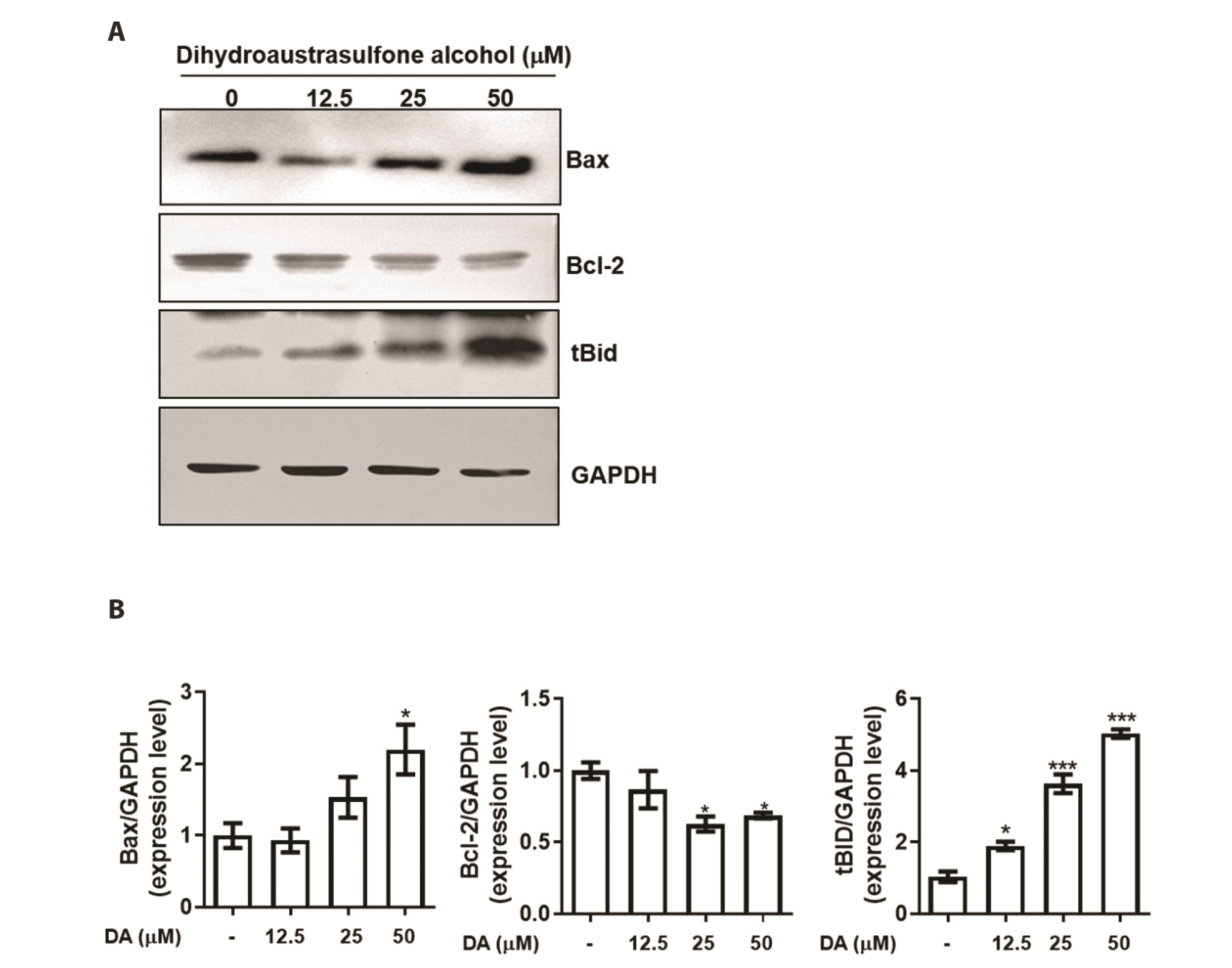
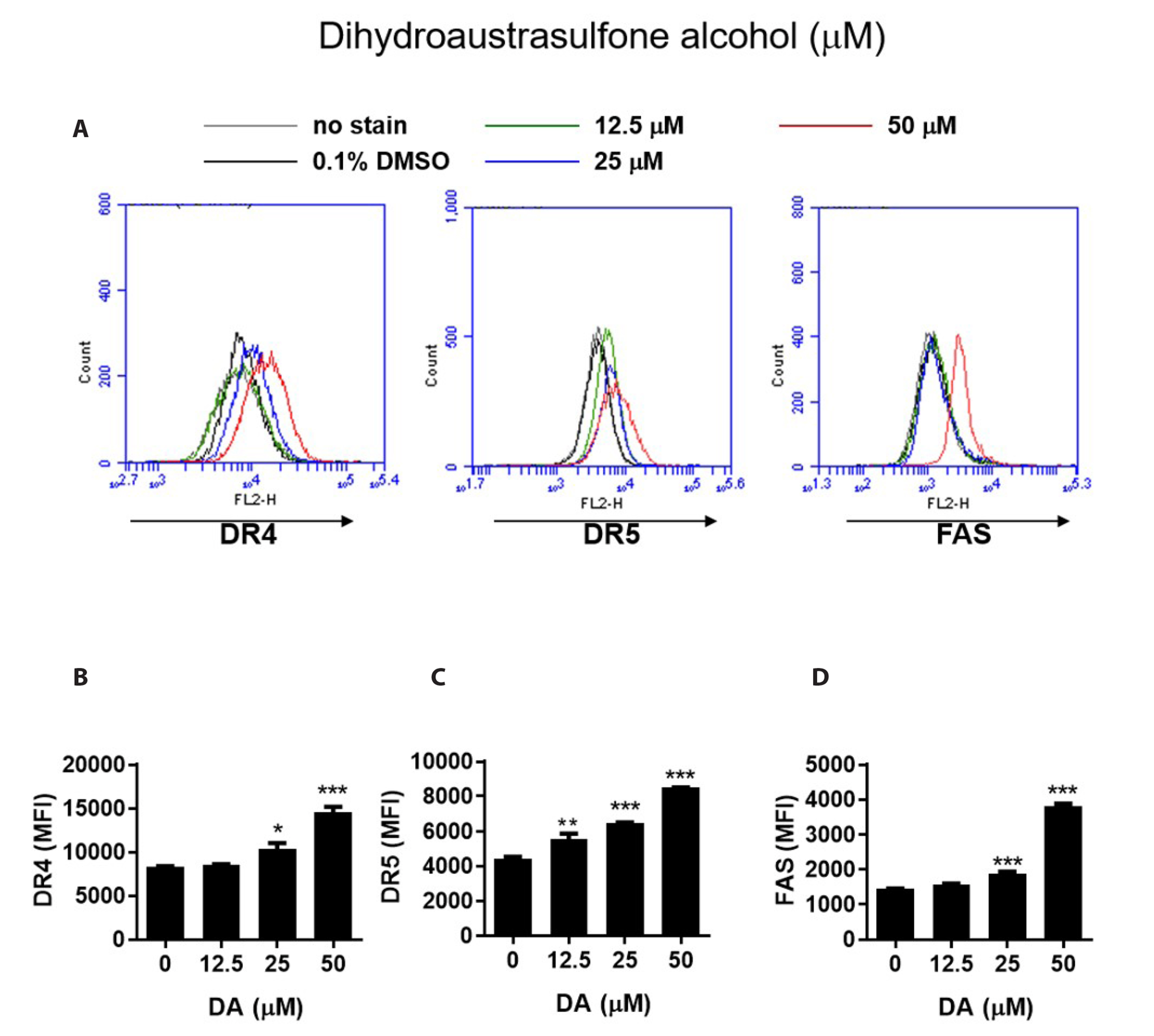
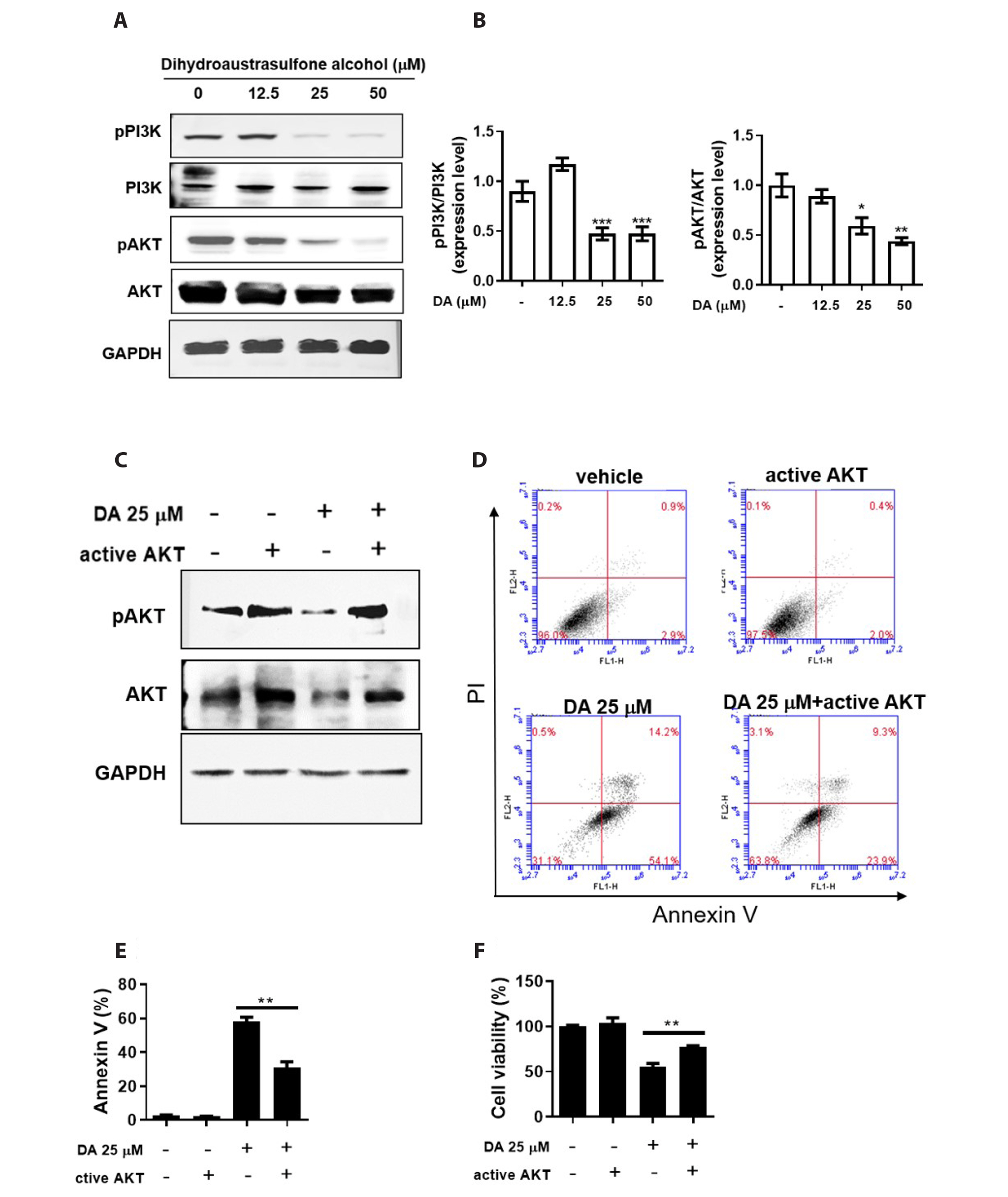
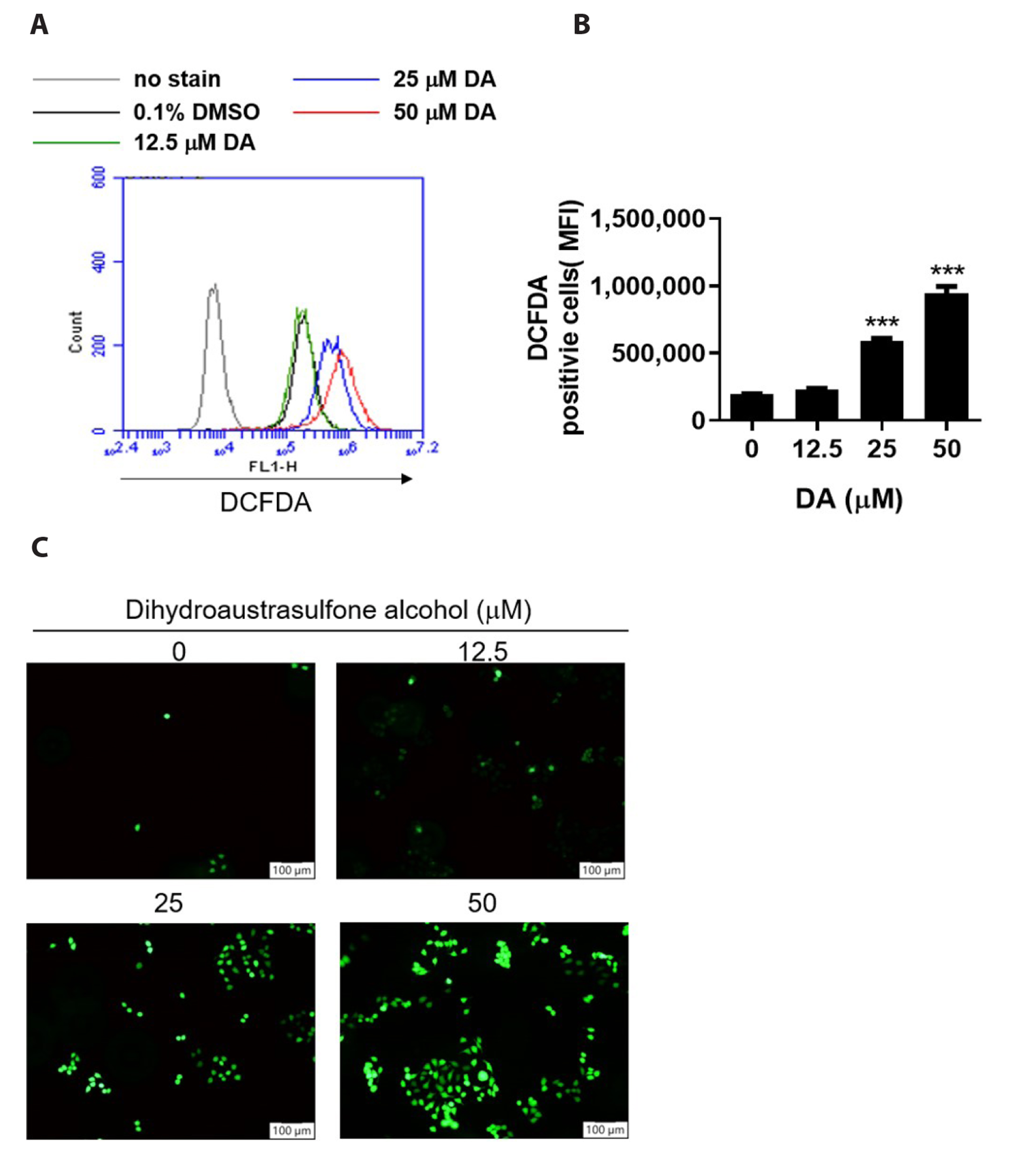
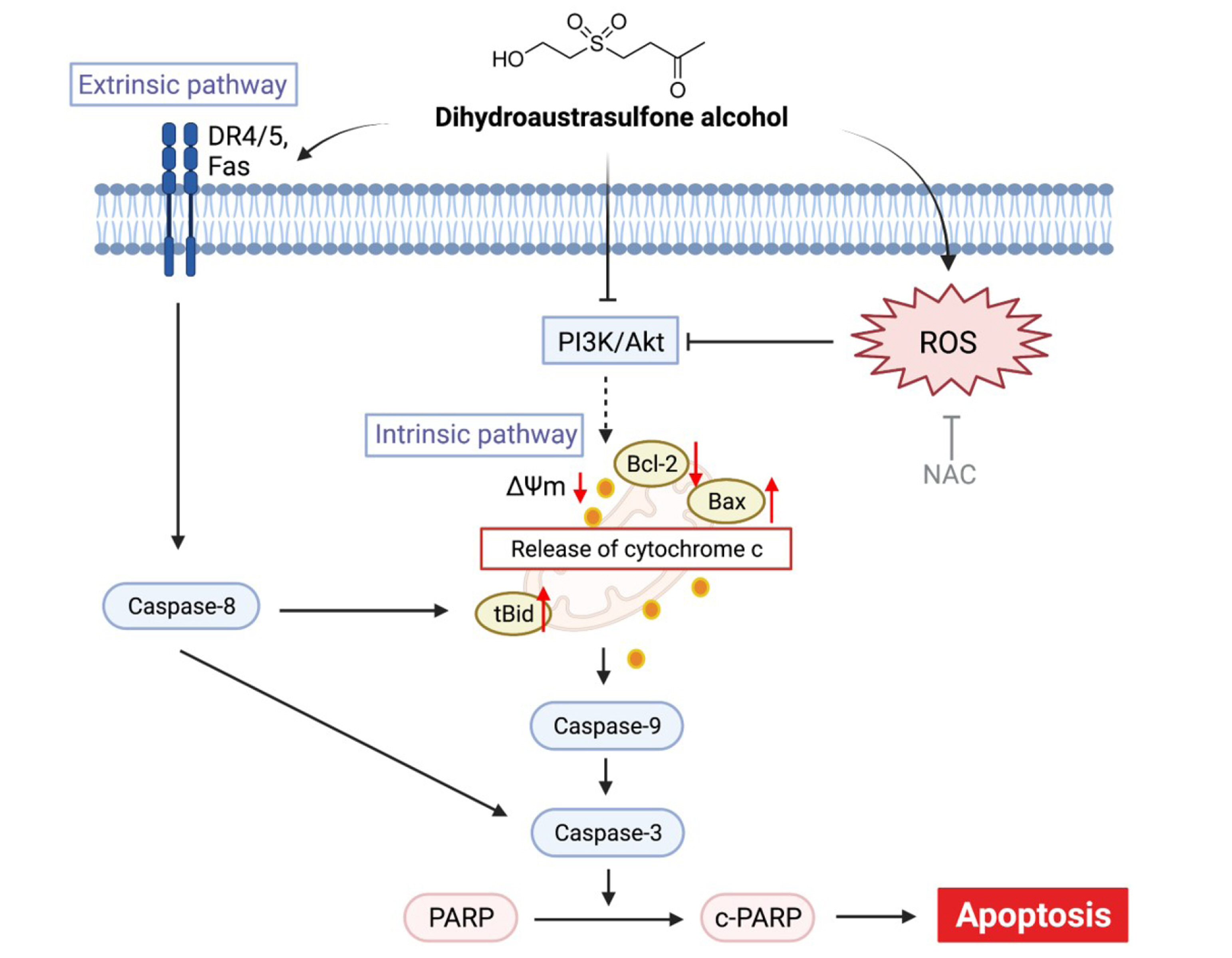
- Dihydroaustrasulfone alcohol (DA), the synthetic precursor of a natural compound (austrasulfone) isolated from the coral species Cladiella australis, has shown cytotoxic effects against cancer cells. However, it is unknown whether DA has antitumor effects on nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). In this study, we determined the antitumor effects of DA and investigated its mechanism of action on human NPC cells. The MTT assay was used to determine the cytotoxic effect of DA. Subsequently, apoptosis and reactive oxygen species (ROS) analyses were performed by using flow cytometry. Apoptotic and PI3K/AKT pathway-related protein expression was determined using Western blotting. We found that DA significantly reduced the viability of NPC-39 cells and determined that apoptosis was involved in DA-induced cell death. The activity of caspase-9, caspase-8, caspase-3, and PARP induced by DA suggested caspase-mediated apoptosis in DA-treated NPC-39 cells. Apoptosis-associated proteins (DR4, DR5, FAS) in extrinsic pathways were also elevated by DA. The enhanced expression of proapoptotic Bax and decreased expression of antiapoptotic BCL-2 suggested that DA mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. DA reduced the expression of pPI3K and p-AKT in NPC-39 cells. DA also reduced apoptosis after introducing an active AKT cDNA, indicating that DA could block the PI3K/AKT pathway from being activated. DA increased intracellular ROS, but N-acetylcysteine (NAC), a ROS scavenger, reduced DA-induced cytotoxicity. NAC also reversed the chances in pPI3K/AKT expression and reduced DA-induced apoptosis. These findings suggest that ROSmediates DA-induced apoptosis and PI3K/AKT signaling inactivation in human NPC cells.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. 2018; Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. Erratum in: CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:313. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21492. PMID: 30207593.
Article2. Chan AT, Leung SF, Ngan RK, Teo PM, Lau WH, Kwan WH, Hui EP, Yiu HY, Yeo W, Cheung FY, Yu KH, Chiu KW, Chan DT, Mok TS, Yau S, Yuen KT, Mo FK, Lai MM, Ma BB, Kam MK, et al. 2005; Overall survival after concurrent cisplatin-radiotherapy compared with radiotherapy alone in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 97:536–539. DOI: 10.1093/jnci/dji084. PMID: 15812080.
Article3. Lee AWM, Tung SY, Ng WT, Lee V, Ngan RKC, Choi HCW, Chan LLK, Siu LL, Ng AWY, Leung TW, Yiu HHY, O'Sullivan B, Chappell R. 2017; A multicenter, phase 3, randomized trial of concurrent chemoradiotherapy plus adjuvant chemotherapy versus radiotherapy alone in patients with regionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: 10-year outcomes for efficacy and toxicity. Cancer. 123:4147–4157. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.30850. PMID: 28662313.
Article4. Lin JC, Jan JS, Hsu CY, Liang WM, Jiang RS, Wang WY. 2003; Phase III study of concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: positive effect on overall and progression-free survival. J Clin Oncol. 21:631–637. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2003.06.158. PMID: 12586799.
Article5. Wee J, Tan EH, Tai BC, Wong HB, Leong SS, Tan T, Chua ET, Yang E, Lee KM, Fong KW, Tan HS, Lee KS, Loong S, Sethi V, Chua EJ, Machin D. 2005; Randomized trial of radiotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy followed by adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with American Joint Committee on Cancer/International Union against cancer stage III and IV nasopharyngeal cancer of the endemic variety. J Clin Oncol. 23:6730–6738. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2005.16.790. PMID: 16170180.
Article6. Lai SZ, Li WF, Chen L, Luo W, Chen YY, Liu LZ, Sun Y, Lin AH, Liu MZ, Ma J. 2011; How does intensity-modulated radiotherapy versus conventional two-dimensional radiotherapy influence the treatment results in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 80:661–668. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.03.024. PMID: 20643517.
Article7. Lee AW, Ng WT, Chan LL, Hung WM, Chan CC, Sze HC, Chan OS, Chang AT, Yeung RM. 2014; Evolution of treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer--success and setback in the intensity-modulated radiotherapy era. Radiother Oncol. 110:377–384. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2014.02.003. PMID: 24630534.
Article8. Jean YH, Chen WF, Duh CY, Huang SY, Hsu CH, Lin CS, Sung CS, Chen IM, Wen ZH. 2008; Inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 participate in anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of the natural marine compound lemnalol from Formosan soft coral Lemnalia cervicorni. Eur J Pharmacol. 578:323–331. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.08.048. PMID: 17916350.
Article9. Jean YH, Chen WF, Sung CS, Duh CY, Huang SY, Lin CS, Tai MH, Tzeng SF, Wen ZH. 2009; Capnellene, a natural marine compound derived from soft coral, attenuates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 158:713–725. DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00323.x. PMID: 19663884. PMCID: PMC2765592.
Article10. Huang HW, Tang JY, Ou-Yang F, Wang HR, Guan PY, Huang CY, Chen CY, Hou MF, Sheu JH, Chang HW. 2018; Sinularin selectively kills breast cancer cells showing G2/M arrest, apoptosis, and oxidative DNA damage. Molecules. 23:849. Erratum in: Molecules. 2018;23:1670. DOI: 10.3390/molecules23071670. PMID: 29987258. PMCID: PMC6099670. PMID: 369b8cb3979044019e84e63bbde2a8ef.
Article11. Liang CH, Wang GH, Chou TH, Wang SH, Lin RJ, Chan LP, So EC, Sheu JH. 2012; 5-epi-Sinuleptolide induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through tumor necrosis factor/mitochondria-mediated caspase signaling pathway in human skin cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1820:1149–1157. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.02.003. PMID: 22348919.
Article12. Wang SC, Li RN, Lin LC, Tang JY, Su JH, Sheu JH, Chang HW. 2021; Comparison of antioxidant and anticancer properties of soft coral-derived sinularin and dihydrosinularin. Molecules. 26:3853. DOI: 10.3390/molecules26133853. PMID: 34202721. PMCID: PMC8270243. PMID: b3e838ba6c3a41f2826da3e39070a956.
Article13. Wen ZH, Chao CH, Wu MH, Sheu JH. 2010; A neuroprotective sulfone of marine origin and the in vivo anti-inflammatory activity of an analogue. Eur J Med Chem. 45:5998–6004. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.09.067. PMID: 20980079.
Article14. Chen SC, Chien YC, Pan CH, Sheu JH, Chen CY, Wu CH. 2014; Inhibitory effect of dihydroaustrasulfone alcohol on the migration of human non-small cell lung carcinoma A549 cells and the antitumor effect on a Lewis lung carcinoma-bearing tumor model in C57BL/6J mice. Mar Drugs. 12:196–213. DOI: 10.3390/md12010196. PMID: 24413802. PMCID: PMC3917270. PMID: 5bb8f9944e914dbea81e9d80c3dc8670.
Article15. Hung HC, Feng CW, Lin YY, Chen CH, Tsui KH, Chen WF, Pan CY, Sheu JH, Sung CS, Wen ZH. 2018; Nucleophosmin modulates the alleviation of atopic dermatitis caused by the marine-derived compound dihydroaustrasulfone alcohol. Exp Mol Med. 50:e446. DOI: 10.1038/emm.2017.272. PMID: 29504608. PMCID: PMC5903824.
Article16. Lin SW, Huang SC, Kuo HM, Chen CH, Ma YL, Chu TH, Bee YS, Wang EM, Wu CY, Sung PJ, Wen ZH, Wu DC, Sheu JH, Tai MH. 2015; Coral-derived compound WA-25 inhibits angiogenesis by attenuating the VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling pathway. Mar Drugs. 13:861–878. DOI: 10.3390/md13020861. PMID: 25668036. PMCID: PMC4344606. PMID: bf30b232d81d4ef1bba9bd8436bf166a.
Article17. Lu IT, Lin SC, Chu YC, Wen Y, Lin YC, Cheng WC, Sheu JH, Lin CC. 2022; (-)-Agelasidine A induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mar Drugs. 20:109. DOI: 10.3390/md20020109. PMID: 35200638. PMCID: PMC8875608. PMID: a3993e8833984e0aba9daf1ef02e9cbc.
Article18. Blunt JW, Copp BR, Hu WP, Munro MH, Northcote PT, Prinsep MR. 2007; Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep. 24:31–86. DOI: 10.1039/b603047p. PMID: 17268607.
Article19. Calcabrini C, Catanzaro E, Bishayee A, Turrini E, Fimognari C. 2017; Marine sponge natural products with anticancer potential: an updated review. Mar Drugs. 15:310. DOI: 10.3390/md15100310. PMID: 29027954. PMCID: PMC5666418. PMID: f02079e829634c7aaed5cd0ff5c1b35b.
Article20. Rateb ME, Ebel R. 2011; Secondary metabolites of fungi from marine habitats. Nat Prod Rep. 28:290–344. DOI: 10.1039/c0np00061b. PMID: 21229157.
Article21. Wei J, Gou Z, Wen Y, Luo Q, Huang Z. 2020; Marine compounds targeting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Biomed Pharmacother. 129:110484. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110484. PMID: 32768966.
Article22. Ye J, Zhou F, Al-Kareef AM, Wang H. 2015; Anticancer agents from marine sponges. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 17:64–88. DOI: 10.1080/10286020.2014.970535. PMID: 25402340.
Article23. Guicciardi ME, Gores GJ. 2009; Life and death by death receptors. FASEB J. 23:1625–1637. DOI: 10.1096/fj.08-111005. PMID: 19141537. PMCID: PMC2698650.
Article24. Schneider-Brachert W, Heigl U, Ehrenschwender M. 2013; Membrane trafficking of death receptors: implications on signalling. Int J Mol Sci. 14:14475–14503. DOI: 10.3390/ijms140714475. PMID: 23852022. PMCID: PMC3742255. PMID: 057d0d23540a44d5b5dcd90bc4ea621c.
Article25. Wang S, El-Deiry WS. 2003; TRAIL and apoptosis induction by TNF-family death receptors. Oncogene. 22:8628–8633. DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207232. PMID: 14634624.
Article26. Adams JM, Cory S. 1998; The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. DOI: 10.1126/science.281.5381.1322. PMID: 9735050.
Article27. Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A, Adams JM. 2014; Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:49–63. DOI: 10.1038/nrm3722. PMID: 24355989.
Article28. Green DR. 2000; Apoptotic pathways: paper wraps stone blunts scissors. Cell. 102:1–4. DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00003-9. PMID: 10929706.29. Hunt A, Evan G. 2001; Apoptosis. Till death us do part. Science. 293:1784–1785. DOI: 10.1126/science.11546862. PMID: 11546862.30. Hardwick JM, Soane L. 2013; Multiple functions of BCL-2 family proteins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5:a008722. DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008722. PMID: 23378584. PMCID: PMC3552500.
Article31. Wu H, Medeiros LJ, Young KH. 2018; Apoptosis signaling and BCL-2 pathways provide opportunities for novel targeted therapeutic strategies in hematologic malignances. Blood Rev. 32:8–28. DOI: 10.1016/j.blre.2017.08.004. PMID: 28802908.
Article32. Noorolyai S, Shajari N, Baghbani E, Sadreddini S, Baradaran B. 2019; The relation between PI3K/AKT signalling pathway and cancer. Gene. 698:120–128. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.076. PMID: 30849534.
Article33. Tewari D, Patni P, Bishayee A, Sah AN, Bishayee A. 2022; Natural products targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in cancer: a novel therapeutic strategy. Semin Cancer Biol. 80:1–17. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.12.008. PMID: 31866476.
Article34. Ci Y, Shi K, An J, Yang Y, Hui K, Wu P, Shi L, Xu C. 2014; ROS inhibit autophagy by downregulating ULK1 mediated by the phosphorylation of p53 in selenite-treated NB4 cells. Cell Death Dis. 5:e1542. DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.506. PMID: 25429619. PMCID: PMC4260759.
Article35. Galadari S, Rahman A, Pallichankandy S, Thayyullathil F. 2017; Reactive oxygen species and cancer paradox: to promote or to suppress? Free Radic Biol Med. 104:144–164. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.01.004. PMID: 28088622.
Article36. Tafani M, Sansone L, Limana F, Arcangeli T, De Santis E, Polese M, Fini M, Russo MA. 2016; The interplay of reactive oxygen species, hypoxia, inflammation, and Sirtuins in cancer initiation and progression. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:3907147. DOI: 10.1155/2016/3907147. PMID: 26798421. PMCID: PMC4699039.
Article37. Huynh DTN, Jin Y, Myung CS, Heo KS. 2021; Ginsenoside Rh1 induces MCF-7 cell apoptosis and autophagic cell death through ROS-mediated Akt signaling. Cancers (Basel). 13:1892. DOI: 10.3390/cancers13081892. PMID: 33920802. PMCID: PMC8071122. PMID: 3d574bb3dd284183891a415a6d6f849d.
Article38. Kim SO, Cha HJ, Park C, Lee H, Hong SH, Jeong SJ, Park SH, Kim GY, Leem SH, Jin CY, Hwang EJ, Choi YH. 2019; Cordycepin induces apoptosis in human bladder cancer T24 cells through ROS-dependent inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biosci Trends. 13:324–333. DOI: 10.5582/bst.2019.01214. PMID: 31527329.
Article39. Li X, Zhu F, Jiang J, Sun C, Wang X, Shen M, Tian R, Shi C, Xu M, Peng F, Guo X, Wang M, Qin R. 2015; Synergistic antitumor activity of withaferin A combined with oxaliplatin triggers reactive oxygen species-mediated inactivation of the PI3K/AKT pathway in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 357:219–230. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.11.026. PMID: 25444914.
Article40. Liu Y, Shi C, He Z, Zhu F, Wang M, He R, Zhao C, Shi X, Zhou M, Pan S, Gao Y, Li X, Qin R. 2021; Inhibition of PI3K/AKT signaling via ROS regulation is involved in Rhein-induced apoptosis and enhancement of oxaliplatin sensitivity in pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Biol Sci. 17:589–602. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.49514. PMID: 33613115. PMCID: PMC7893580.
Article41. Song X, Wang Z, Liang H, Zhang W, Ye Y, Li H, Hu Y, Zhang Y, Weng H, Lu J, Wang X, Li M, Liu Y, Gu J. 2017; Dioscin induces gallbladder cancer apoptosis by inhibiting ROS-mediated PI3K/AKT signalling. Int J Biol Sci. 13:782–793. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.18732. PMID: 28656003. PMCID: PMC5485633.
Article42. Wen C, Wang H, Wu X, He L, Zhou Q, Wang F, Chen S, Huang L, Chen J, Wang H, Ye W, Li W, Yang X, Liu H, Peng J. 2019; ROS-mediated inactivation of the PI3K/AKT pathway is involved in the antigastric cancer effects of thioredoxin reductase-1 inhibitor chaetocin. Cell Death Dis. 10:809. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-2035-x. PMID: 31649256. PMCID: PMC6813365.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Myricetin Inhibits Angiogenesis by Inducing Apoptosis and Suppressing PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling in Endothelial Cells
- Induction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by Dendropanax morbifera Leveille Leaf Extract via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway
- Erratum: Induction of apoptotic cell death in human bladder cancer cells by ethanol extract of Zanthoxylum schinifolium leaf, through ROSdependent inactivation of the PI3K/ Akt signaling pathway
- Induction of apoptotic cell death in human bladder cancer cells by ethanol extract of Zanthoxylum schinifolium leaf, through ROS-dependent inactivation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
- Dasatinib induces apoptosis and autophagy by suppressing the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in bladder cancer cells