Cancer Res Treat.
2023 Apr;55(2):498-505. 10.4143/crt.2022.388.
EGFR Mutation–Positive Unresectable Stage III Non-Squamous Lung Cancer Is Associated with a High Incidence of Brain Metastasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea
- 2Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2541236
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2022.388
Abstract
- Purpose
The impact of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation in locally advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains controversial. This study was conducted to investigate the clinical outcomes and recurrence patterns after definitive chemoradiotherapy (CRT) in patients with unresectable stage III non-squamous-cell lung cancer according to EGFR mutation status.
Materials and Methods
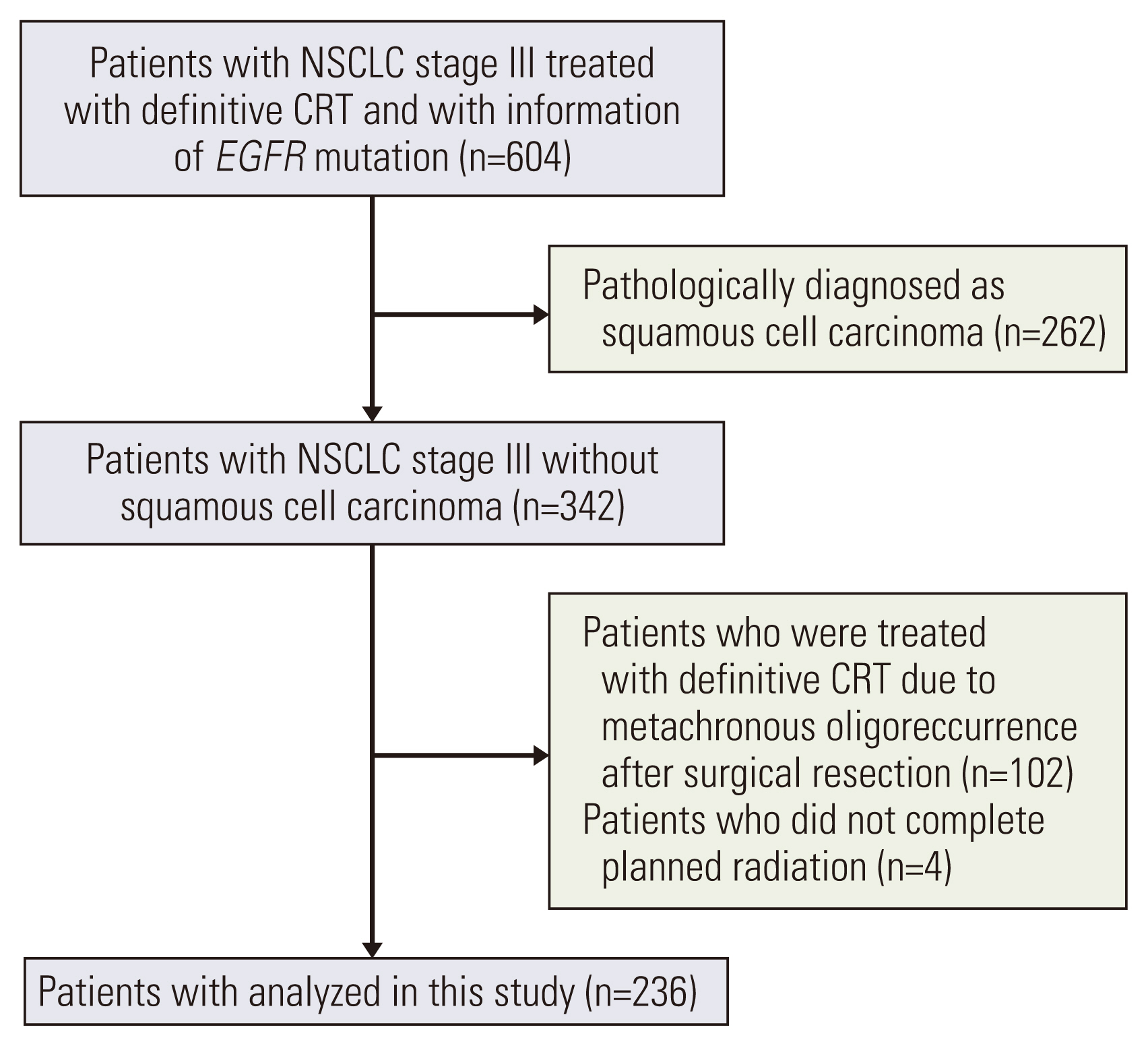
We retrospectively reviewed 604 patients with pathologically confirmed stage III NSCLC who were treated with definitive CRT and were examined for EGFR mutation at Samsung Medical Center, Korea, from January 2013 to December 2018. Among them, we identified 236 patients with stage III non-squamous-cell lung cancer who were treated with definitive CRT and were examined for EGFR mutation status. We analyzed the frequency of EGFR mutation, progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), objective response rate (ORR), and recurrence pattern.
Results
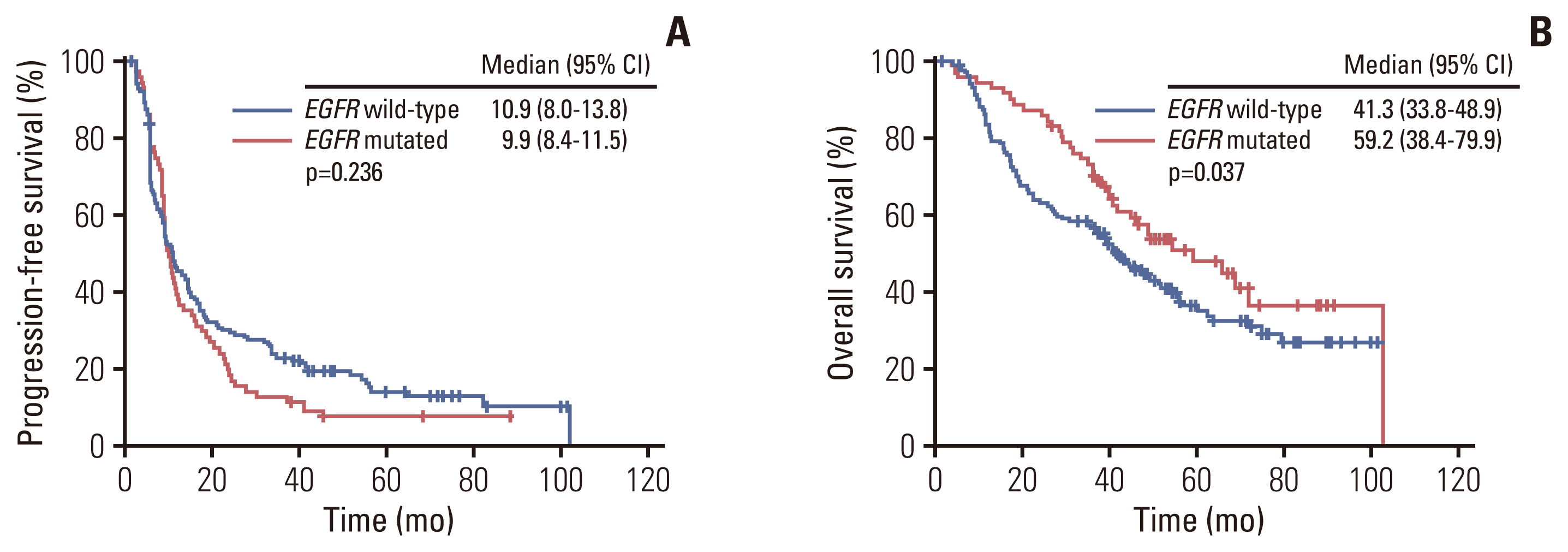
Among 236 patients, EGFR mutation was detected in 71 patients (30.1%) and the median follow-up duration was 41.7 months. There were no significant differences in PFS (9.9 vs. 10.9 months, p=0.236), and ORR to CRT (93.0% vs. 90.3%, p=0.623) according to EGFR mutation status. However, the EGFR mutant group showed significantly higher recurrence (88.7% vs. 75.2%, p=0.022), distant metastasis (76.1% vs. 61.2%, p=0.036) rates, especially brain (38.0% vs. 12.7%, p < 0.001), and better median OS (59.2 vs. 41.3 months, p=0.037) compared with patients without EGFR mutation.
Conclusion
Patients with EGFR mutation–positive unresectable stage III non-squamous lung cancer exhibited higher recurrence and distant metastasis rates, especially brain metastasis.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE, Adjei AA. Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008; 83:584–94.
Article2. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021; 71:7–33.
Article3. Auperin A, Le Pechoux C, Rolland E, Curran WJ, Furuse K, Fournel P, et al. Meta-analysis of concomitant versus sequential radiochemotherapy in locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:2181–90.
Article4. Blackstock AW, Govindan R. Definitive chemoradiation for the treatment of locally advanced non small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:4146–52.5. Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, Vicente D, Murakami S, Hui R, et al. Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:1919–29.6. Faivre-Finn C, Vicente D, Kurata T, Planchard D, Paz-Ares L, Vansteenkiste JF, et al. Four-year survival with durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III NSCLC: an update from the PACIFIC trial. J Thorac Oncol. 2021; 16:860–7.7. Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2129–39.
Article8. Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, Solomon B, Maki RG, et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:1693–703.9. Park SE, Noh JM, Kim YJ, Lee HS, Cho JH, Lim SW, et al. EGFR mutation is associated with short progression-free survival in patients with stage III non-squamous cell lung cancer treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Cancer Res Treat. 2019; 51:493–501.
Article10. Nakamura M, Kageyama SI, Niho S, Okumura M, Hojo H, Motegi A, et al. Impact of EGFR mutation and ALK translocation on recurrence pattern after definitive chemoradiotherapy for inoperable stage III non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2019; 20:e256–64.
Article11. Yagishita S, Horinouchi H, Katsui Taniyama T, Nakamichi S, Kitazono S, Mizugaki H, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation is associated with longer local control after definitive chemoradiotherapy in patients with stage III nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015; 91:140–8.12. Tanaka K, Hida T, Oya Y, Oguri T, Yoshida T, Shimizu J, et al. EGFR mutation impact on definitive concurrent chemoradiation therapy for inoperable stage III adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 2015; 10:1720–5.
Article13. Burel-Vandenbos F, Ambrosetti D, Coutts M, Pedeutour F. EGFR mutation status in brain metastases of non-small cell lung carcinoma. J Neurooncol. 2013; 111:1–10.
Article14. Shin DY, Na II, Kim CH, Park S, Baek H, Yang SH. EGFR mutation and brain metastasis in pulmonary adenocarcinomas. J Thorac Oncol. 2014; 9:195–9.
Article15. Komaki R, Allen PK, Wei X, Blumenschein GR, Tang X, Lee JJ, et al. Adding erlotinib to chemoradiation improves overall survival but not progression-free survival in stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015; 92:317–24.
Article16. Hotta K, Saeki S, Yamaguchi M, Harada D, Bessho A, Tanaka K, et al. Gefitinib induction followed by chemoradiotherapy in EGFR-mutant, locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: LOGIK0902/OLCSG0905 phase II study. ESMO Open. 2021; 6:100191.
Article17. Wu YL, Tsuboi M, He J, John T, Grohe C, Majem M, et al. Osimertinib in resected EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383:1711–23.
Article18. Lu S, Casarini I, Kato T, Cobo M, Ozguroglu M, Hodge R, et al. Osimertinib maintenance after definitive chemoradiation in patients with unresectable EGFR mutation positive stage III non-small-cell lung cancer: LAURA trial in progress. Clin Lung Cancer. 2021; 22:371–5.
Article19. Lee CK, Man J, Lord S, Links M, Gebski V, Mok T, et al. Checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. J Thorac Oncol. 2017; 12:403–7.20. Dong ZY, Zhang JT, Liu SY, Su J, Zhang C, Xie Z, et al. EGFR mutation correlates with uninflamed phenotype and weak immunogenicity, causing impaired response to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncoimmunology. 2017; 6:e1356145.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- EGFR Mutation Is Associated with Short Progression-Free Survival in Patients with Stage III Non-squamous Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy
- Clinical Relevance of EGFR Mutations in Colorectal Cancer Patients
- Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations in Colorectal Cancer Patients
- Brain Metastases Developed in Advanced Colorectal Cancer Patients who Underwent Multi-drug Chemotherapy
- Discordance of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation between Brain Metastasis and Primary Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer