J Rheum Dis.
2023 Apr;30(2):126-132. 10.4078/jrd.2023.0006.
The relationship between long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and kidney function in patients with ankylosing spondylitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Statistics and Data Science, Korea National Open University, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Rheumatology, Hanyang University Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2541056
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2023.0006
Abstract
Objective
Although nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the first-line treatment for ankylosing spondylitis (AS), their effect on kidney function remains unclear. This longitudinal study investigated the correlation between long-term NSAID use and kidney function in patients with AS using electronic medical records.
Methods
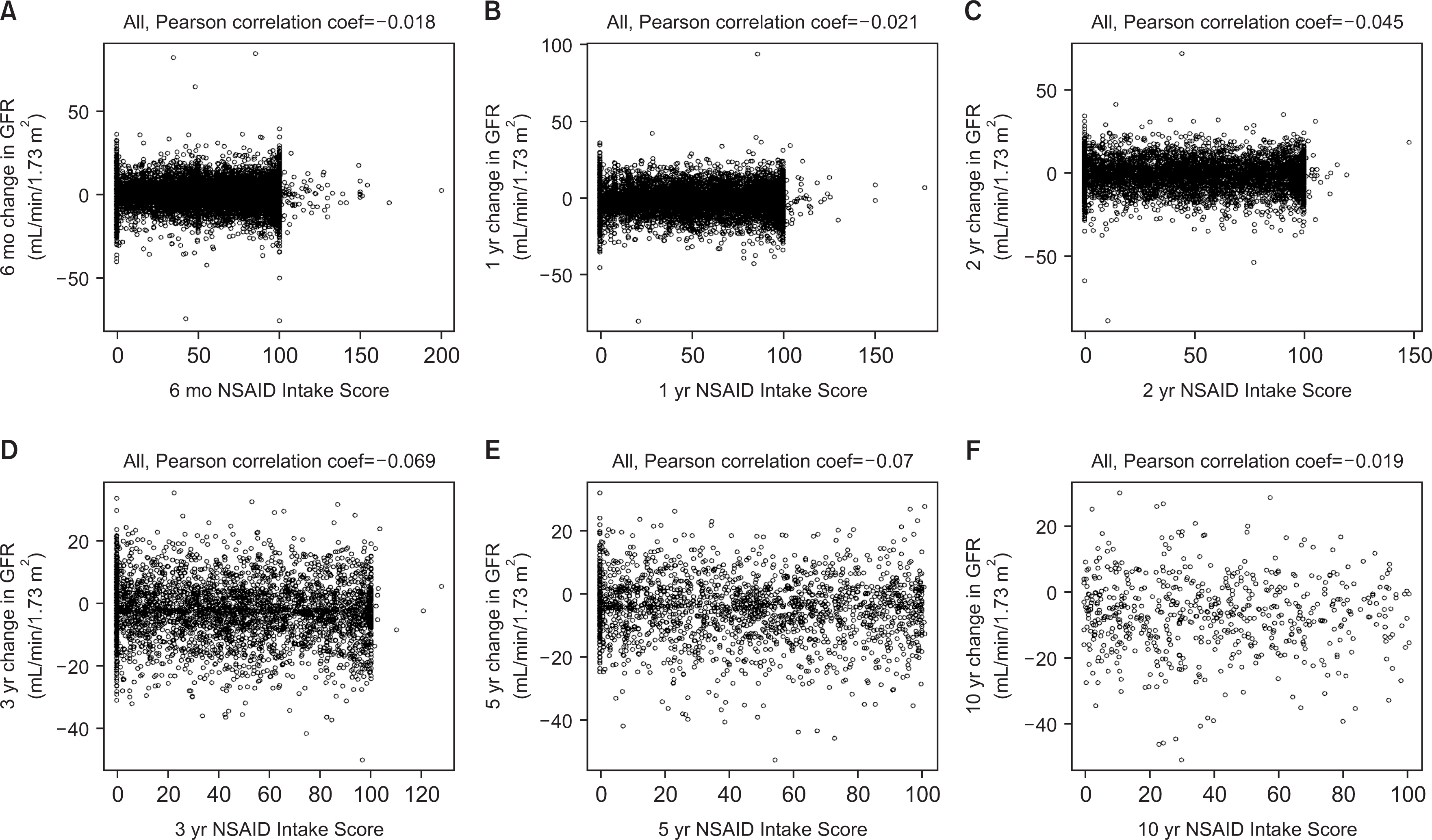
The electronic medical records of 1,280 patients with AS collected from a single center between January 2001 and December 2018 were reviewed. The Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society (ASAS) NSAID Intake Score was used to determine the cumulative dose of all NSAIDs prescribed for a different time intervals. Each ASAS NSAID Intake Score was obtained for intervals of 6 months, 1 year, 2 years, 3 years, 5 years, and 10 years. The correlation between the ASAS NSAID Intake Score and final estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) for each interval was investigated.
Results
The mean ASAS Intake Scores for 6-month, 1-year, 2-year, 3-year, 5-year, and 10-year intervals were 55.30, 49.28, 44.84, 44.14, 44.61, and 41.17, respectively. At each interval, the pearson correlation coefficients were −0.018 (95% CI: −0.031 to −0.006, p=0.004), −0.021 (95% CI: −0.039 to −0.004, p=0.018), −0.045 (95% CI: −0.071 to −0.019, p=0.001), −0.069 (95% CI: −0.102 to −0.037, p<0.001), −0.070 (95% CI: −0.114 to −0.026, p=0.002), −0.019 (95% CI: −0.099 to 0.062, p=0.645), respectively. There was a very weak negative relationship between ASAS Intake Score and eGFR at each interval.
Conclusion
Long-term NSAID use did not correlate with kidney function based on real-world data in patients with AS.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs safe for the kidney in ankylosing spondylitis?
Ji-Won Kim
J Rheum Dis. 2023;30(3):139-140. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2023.0033.Are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs safe for the kidney in ankylosing spondylitis?
Ji-Won Kim
J Rheum Dis. 2023;30(3):139-140. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2023.0033.
Reference
-
1. Inman RD. 2021; Axial spondyloarthritis: current advances, future challenges. J Rheum Dis. 28:55–9. DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.2.55.2. Robinson PC, van der Linden S, Khan MA, Taylor WJ. 2021; Axial spondyloarthritis: concept, construct, classification and implications for therapy. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 17:109–18. DOI: 10.1038/s41584-020-00552-4. PMID: 33361770.
Article3. Tam LS, Wei JC, Aggarwal A, Baek HJ, Cheung PP, Chiowchanwisawakit P, et al. 2019; 2018 APLAR axial spondyloarthritis treatment recommendations. Int J Rheum Dis. 22:340–56. DOI: 10.1111/1756-185X.13510. PMID: 30816645.
Article4. van der Heijde D, Ramiro S, Landewé R, Baraliakos X, Van den Bosch F, Sepriano A, et al. 2017; 2016 update of the ASAS-EULAR management recommendations for axial spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 76:978–91. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210770. PMID: 28087505.5. Ward MM, Deodhar A, Gensler LS, Dubreuil M, Yu D, Khan MA, et al. 2019; 2019 Update of the American College of Rheumatology/Spondylitis Association of America/Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network recommendations for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 71:1285–99. DOI: 10.1002/acr.24025. PMID: 31436026. PMCID: PMC6764857.
Article6. Wanders A, Heijde D, Landewé R, Béhier JM, Calin A, Olivieri I, et al. 2005; Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs reduce radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum. 52:1756–65. DOI: 10.1002/art.21054. PMID: 15934081.
Article7. Poddubnyy D, Rudwaleit M, Haibel H, Listing J, Märker-Hermann E, Zeidler H, et al. 2012; Effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on radiographic spinal progression in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: results from the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort. Ann Rheum Dis. 71:1616–22. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-201252. PMID: 22459541.8. Baker M, Perazella MA. 2020; NSAIDs in CKD: are they safe? Am J Kidney Dis. 76:546–57. DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.03.023. PMID: 32479922.
Article9. Eras J, Perazella MA. 2001; NSAIDs and the kidney revisited: are selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors safe? Am J Med Sci. 321:181–90. DOI: 10.1097/00000441-200103000-00005. PMID: 11269794.
Article10. Whelton A. 1999; Nephrotoxicity of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: physiologic foundations and clinical implications. Am J Med. 106(5B):13S–24S. DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9343(99)00113-8. PMID: 10390124.
Article11. Nelson DA, Marks ES, Deuster PA, O'Connor FG, Kurina LM. 2019; Association of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug prescriptions with kidney disease among active young and middle-aged adults. JAMA Netw Open. 2:e187896. DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.7896. PMID: 30768191. PMCID: PMC6484592.
Article12. Nderitu P, Doos L, Jones PW, Davies SJ, Kadam UT. 2013; Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and chronic kidney disease progression: a systematic review. Fam Pract. 30:247–55. DOI: 10.1093/fampra/cms086. PMID: 23302818.13. Gooch K, Culleton BF, Manns BJ, Zhang J, Alfonso H, Tonelli M, et al. 2007; NSAID use and progression of chronic kidney disease. Am J Med. 120:280.e1–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2006.02.015. PMID: 17349452.14. Zhan M, St Peter WL, Doerfler RM, Woods CM, Blumenthal JB, Diamantidis CJ, et al. 2017; Patterns of NSAIDs use and their association with other analgesic use in CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 12:1778–86. DOI: 10.2215/CJN.12311216. PMID: 28811297. PMCID: PMC5672983.
Article15. Lee TH, Koo BS, Nam B, Kim YJ, Son D, Lee S, et al. 2022; Age-stratified trends in the progression of spinal radiographic damage in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a longitudinal study. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 14:1759720X221100301. DOI: 10.1177/1759720X221100301. PMID: 35634353. PMCID: PMC9131377.
Article16. van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. 1984; Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 27:361–8. DOI: 10.1002/art.1780270401. PMID: 6231933.17. Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI, et al. 2009; A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 150:604–12. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-150-9-200905050-00006. PMID: 19414839. PMCID: PMC2763564.18. Dougados M, Simon P, Braun J, Burgos-Vargas R, Maksymowych WP, Sieper J, et al. 2011; ASAS recommendations for collecting, analysing and reporting NSAID intake in clinical trials/epidemiological studies in axial spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 70:249–51. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.133488. PMID: 20829199.
Article19. Levy AR, Szabo SM, Rao SR, Cifaldi M, Maksymowych WP. 2014; Estimating the occurrence of renal complications among persons with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 66:440–5. DOI: 10.1002/acr.22176. PMID: 24106183.
Article20. Ye W, Zhuang J, Yu Y, Li H, Leng X, Qian J, et al. 2019; Gender and chronic kidney disease in ankylosing spondylitis: a single-center retrospectively study. BMC Nephrol. 20:457. DOI: 10.1186/s12882-019-1658-6. PMID: 31818273. PMCID: PMC6902329.
Article21. Wu Y, Zhang G, Wang N, Xue Q. 2018; Risk factors of renal involvement based on different manifestations in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Kidney Blood Press Res. 43:367–77. DOI: 10.1159/000488071. PMID: 29539632.
Article22. Möller B, Pruijm M, Adler S, Scherer A, Villiger PM, Finckh A. 2015; Chronic NSAID use and long-term decline of renal function in a prospective rheumatoid arthritis cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. 74:718–23. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204078. PMID: 24356672.
Article23. Chiu HY, Huang HL, Li CH, Chen HA, Yeh CL, Chiu SH, et al. 2015; Increased risk of chronic kidney disease in rheumatoid arthritis associated with cardiovascular complications - a national population-based cohort study. PLoS One. 10:e0136508. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136508. PMID: 26406879. PMCID: PMC4583248.
Article24. Saigal R, Agrawal AK, Goyal L, Agrawal A, Gupta N. 2017; Renal function in ankylosing spondylitis. Indian J Rheumatol. 12:156–9. DOI: 10.4103/injr.injr_93_16.
Article25. Murray MD, Brater DC, Tierney WM, Hui SL, McDonald CJ. 1990; Ibuprofen-associated renal impairment in a large general internal medicine practice. Am J Med Sci. 299:222–9. DOI: 10.1097/00000441-199004000-00002. PMID: 2321664.
Article26. Wertheimer AI. 1986; The defined daily dose system (DDD) for drug utilization review. Hosp Pharm. 21:233–4.27. Mori S, Yoshitama T, Hirakata N, Ueki Y. 2017; Prevalence of and factors associated with renal dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a cross-sectional study in community hospitals. Clin Rheumatol. 36:2673–82. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-017-3804-5. PMID: 28884373. PMCID: PMC5681610.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs safe for the kidney in ankylosing spondylitis?
- Medical Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Analysis of Drug Utilization for Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Biologic therapies for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis
- Tailored Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis