Ann Clin Microbiol.
2023 Mar;26(1):19-27. 10.5145/ACM.2023.26.1.3.
Evaluation of two commercial kits for rapid pathogen identification directly from positive blood cultures by matrix-associated laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2540715
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2023.26.1.3
Abstract
- Background
A bloodstream infection is a life-threatening medical emergency, with a mortality rate of up to 30%. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) can be used to identify pathogens directly from positive blood cultures. Two commercial preparation kits, SepsiTyper (Bruker Daltonics, Germany) and SepsiPrep (ASTA Corp., Korea), and two MALDI-TOF MS systems, MALDI Biotyper Sirius (Bruker Daltonics, Germany) and VITEK MS PRIME (bioMérieux, France), are available in Korea. We examined these kits and MALDI-TOF MS systems to analyze their performance.
Methods
We assessed the effectiveness of direct identification using 47 blood cultures and 3 bile cultures positive for microbial growth. The VIRTUO system (bioMérieux, France) was used to incubate the samples after they were collected in Bact/ALERT aerobic and anaerobic bottles. The manufacturers’ protocols were followed for both the SepsiTyper and SepsiPrep kits.
Results
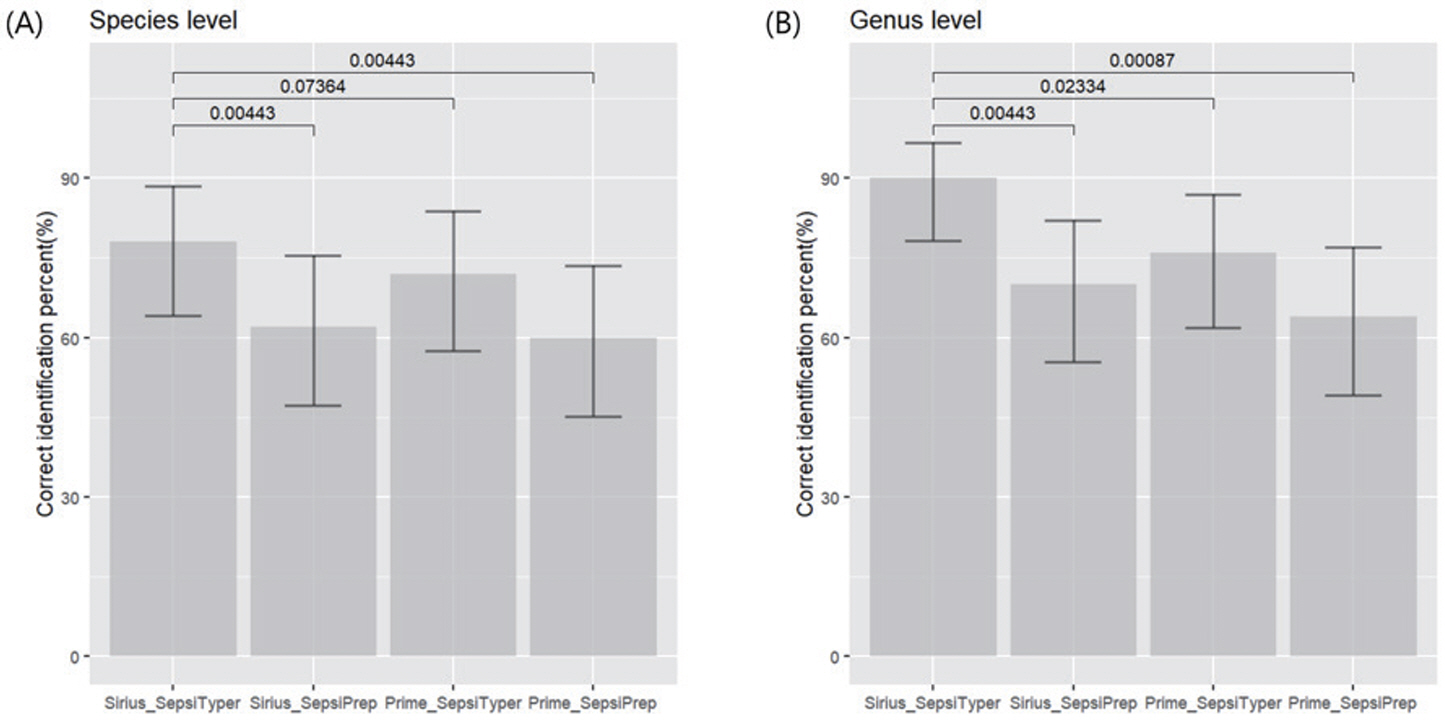
The SepsiTyper yielded considerably more accurate identifications than did the SepsiPrep, when utilized in MALDI-TOF MS systems (P = 0.0044). However, the SepsiPrep was easier to use and the results more quickly obtained than with the SepsiTyper. The MALDI Biotyper Sirius produced more accurate identifications with the SepsiTyper than did the VITEK MS PRIME (P = 0.0736). The SepsiTyper enabled the accurate identification of five of six polymicrobial cases, utilizing either the MALDI-TOF MS systems.
Conclusions
Among the pathogen ID kits tested in this study, the SepsiTyper with MALDI Biotyper Sirius performed the best. In clinical laboratories utilizing VITEK MS PRIME, it is recommended that the either the SepsiTyper or SepsiPrep kit be used for direct identification, while considering certain limitations in terms of performance.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hattori H, Maeda M, Nagatomo Y, Takuma T, Niki Y, Naito Y, et al. Epidemiology and risk factors for mortality in bloodstream infections: a single-center retrospective study in Japan. Am J Infect Control 2018;46:e75–9. .2. Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, Antonelli M, Coopersmith CM, French C, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intens Care Med 2021;47:1181–247. .3. Yoon EJ, Kim D, Jeong SH. Bloodstream infections and carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in South Korea. Lancet Infect Dis 2019;19:931–2. .4. Fre´de´ric S, Antoine M, Bodson A, Lissoir B. Bacterial rapid identification with matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry: development of an ‘inhouse method’ and comparison with Bruker Sepsityper® kit. Acta Clin Belg 2015;70:325–30. .5. Yoo IY, Han J, Ha SI, Cha YJ, Pil SD, Park Y. Clinical performance of ASTA SepsiPrep kit in direct bacterial identification and antimicrobial susceptibility test using MicroIDSys Elite and VITEK-2 system. J Clin Lab Anal 2021;35:e23744. .6. Ponderand L, Pavese P, Maubon D, Giraudon E, Girard T, Landelle C, et al. Evaluation of Rapid Sepsityper® protocol and specific MBT-Sepsityper module (Bruker Daltonics) for the rapid diagnosis of bacteremia and fungemia by MALDI-TOF-MS. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 2020;19:60. .7. Lin HH, Tseng KH, Tien N, Lin YT, Yu J, Hsueh PR, et al. Evaluation of the Rapid Sepsityper protocol and specific MBT-Sepsityper module for the identification of bacteremia and fungemia using Bruker Biotyper MALDI-TOF MS. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2022;55:1330-3. .8. Pranada AB, Cordovana M, Meyer M, Hubert H, Abdalla M, Ambretti S, et al. Identification of micro-organism from positive blood cultures: comparison of three different short culturing methods to the Rapid Sepsityper workflow. J Med Microbiol 2022;71:001571. .9. Fothergill A, Kasinathan V, Hyman J, Walsh J, Drake T, Wang YFW. Rapid identification of bacteria and yeasts from positive-blood-culture bottles by using a lysis-filtration method and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrum analysis with the SARAMIS database. J Clin Microbiol 2013;51:805–9. .10. Morgenthaler NG and Kostrzewa M. Rapid identification of pathogens in positive blood culture of patients with sepsis: review and meta-analysis of the performance of the Sepsityper kit. Int J Microbiol 2015;2015:1-10. .11. Godmer A, Benzerara Y, Normand AC, Veziris N, Gallah S, Eckert C, et al. Revisiting species identification within the Enterobacter cloacae complex by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry. Microbiol Spectr 2021;9:e00661-21. .12. Brady M, Oza A, Cunney R, Burns K. Attributable mortality of hospital-acquired bloodstream infections in Ireland. J Hosp Infect 2017;96:35–41. .13. Dat VQ, Vu HN, Nguyen The H, Nguyen HT, Hoang LB, Vu Tien Viet D, et al. Bacterial bloodstream infections in a tertiary infectious diseases hospital in Northern Vietnam: aetiology, drug resistance, and treatment outcome. BMC Infect Dis 2017;17:493. .14. Goto M and Al-Hasan MN. Overall burden of bloodstream infection and nosocomial bloodstream infection in North America and Europe. Clin Microbiol Infect 2013;19:501–9. .15. Chen JHK, Ho PL, Kwan GSW, She KKK, Siu GKH, Cheng VCC, et al. Direct bacterial identification in positive blood cultures by use of two commercial matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry systems. J Clin Microbiol 2013;51:1733–9. .16. Schieffer KM, Tan KE, Stamper PD, Somogyi A, Andrea SB, Wakefield T, et al. Multicenter evaluation of the SepsityperTM extraction kit and MALDI-TOF MS for direct identification of positive blood culture isolates using the BD BACTECTM FX and VersaTREK® diagnostic blood culture systems. J Appl Microbiol 2014;116:934–41. .17. Jamal W, Saleem R, Rotimi VO. Rapid identification of pathogens directly from blood culture bottles by Bruker matrix-assisted laser desorption laser ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry versus routine methods. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2013;76:404–8. .18. Prod’hom G, Bizzini A, Durussel C, Bille J, Greub G. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for direct bacterial identification from positive blood culture pellets. J Clin Microbiol 2010;48:1481–3. .19. Tadros M and Petrich A. Evaluation of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and Sepsityper Kit™ for the direct identification of organisms from sterile body fluids in a Canadian pediatric hospital. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol 2013;24:191–4. .
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry for Identification of Aerobic Bacteria in a Clinical Microbiology Laboratory
- Rapid Diagnosis of Mycobacterium abscessus Bacteremia Using Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry
- Reliability of Acinetobacter baumannii Identification with Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry
- MALDI-TOF-MS Fingerprinting Provides Evidence of Urosepsis caused by Aerococcus urinae
- Application of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Imaging Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF IMS) for Premalignant Gastrointestinal Lesions