Korean J Clin Microbiol.
2012 Jun;15(2):60-66. 10.5145/KJCM.2012.15.2.60.
Evaluation of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry for Identification of Aerobic Bacteria in a Clinical Microbiology Laboratory
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. deyong@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1434174
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/KJCM.2012.15.2.60
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) has been used for the identification of bacteria worldwide. To our knowledge, the evaluation of MALDI-TOF MS for the identification of bacteria in Korea has not been studied. In this paper we compared the identification results of aerobic bacteria using MALDI-TOF MS to those results using conventional biochemical methods.
METHODS
We evaluated the performance of a MALDI-TOF MS system (Bruker Daltonics, Leipzig, Germany) on consecutive aerobic isolates collected from January to February of 2011 which were identified using conventional methods (biochemical testing and commercial identification kits). Either directly smearing onto the target plate or protein extraction methods were additionally used if no reliable or discordant results were obtained.
RESULTS
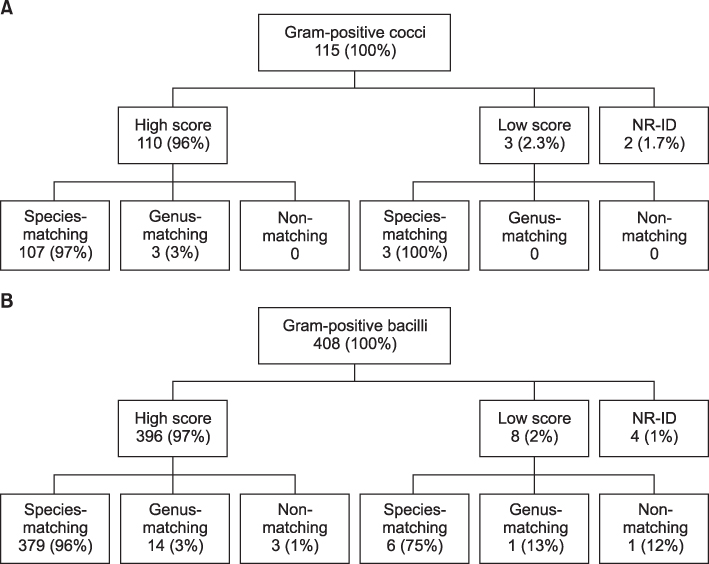
Among 523 isolates tested, 506 (97%) isolates had valid scores (> or =2.0), 11 (2%) isolates gave intermediate scores (1.7< or = score <2.0), and 6 (1%) isolates yielded no reliable identification (score <1.7). Of the 506 valid results (score > or =2.0) by MALDI-TOF MS, the identification matched at the species level in 486 (96%) isloates, matched at the genus level in 17 (3%) isloates, and was discordant at the genus and species levels in 3 (1%) isloates.
CONCLUSION
The overall matching rate at the species level of MALDI-TOF MS was very high. When MALDI-TOF MS did not yield reliable results by direct smear, additional direct smears or protein extraction methods could be used to obtain better results. Our results showed that MALDI-TOF MS is a very useful method for the identification of aerobic bacteria isolated in clinical microbiology laboratories.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Innovation in Clinical Microbiology Testing
Kyungwon Lee
Korean J Healthc Assoc Infect Control Prev. 2021;26(1):42-44. doi: 10.14192/kjicp.2021.26.1.42.Weissella confusa Bacteremia in an Immune-Competent Patient with Underlying Intramural Hematomas of the Aorta
Wonmok Lee, Sun-Mi Cho, Myungsook Kim, Young-Guk Ko, Dongeun Yong, Kyungwon Lee
Ann Lab Med. 2013;33(6):459-462. doi: 10.3343/alm.2013.33.6.459.
Reference
-
1. Petti CA, Weinstein MP, Carroll KC. Versalovic J, Carroll KC, editors. Systems for detection and identification of bacteria and yeasts. Manual of clinical microbiology. 2011. 10th ed. Washington, DC: ASM Press;15–26.2. Holland RD, Wilkes JG, Rafii F, Sutherland JB, Persons CC, Voorhees KJ, et al. Rapid identification of intact whole bacteria based on spectral patterns using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1996. 10:1227–1232.3. Seng P, Drancourt M, Gouriet F, La Scola B, Fournier PE, Rolain JM, et al. Ongoing revolution in bacteriology: routine identification of bacteria by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Clin Infect Dis. 2009. 49:543–551.4. Bizzini A, Durussel C, Bille J, Greub G, Prod'hom G. Performance of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for identification of bacterial strains routinely isolated in a clinical microbiology laboratory. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. 48:1549–1554.5. Stevenson LG, Drake SK, Shea YR, Zelazny AM, Murray PR. Evaluation of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for identification of clinically important yeast species. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. 48:3482–3486.6. Verroken A, Janssens M, Berhin C, Bogaerts P, Huang TD, Wauters G, et al. Evaluation of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for identification of nocardia species. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. 48:4015–4021.7. Cherkaoui A, Hibbs J, Emonet S, Tangomo M, Girard M, Francois P, et al. Comparison of two matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry methods with conventional phenotypic identification for routine identification of bacteria to the species level. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. 48:1169–1175.8. Stephan R, Ziegler D, Pflüger V, Vogel G, Lehner A. Rapid genus- and species-specific identification of Cronobacter spp. by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. 48:2846–2851.9. van Veen SQ, Claas EC, Kuijper EJ. High-throughput identification of bacteria and yeast by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry in conventional medical microbiology laboratories. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. 48:900–907.10. Prod'hom G, Bizzini A, Durussel C, Bille J, Greub G. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for direct bacterial identification from positive blood culture pellets. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. 48:1481–1483.11. Ferreira L, Sánchez-Juanes F, González-Avila M, Cembrero-Fuciños D, Herrero-Hernández A, González-Buitrago JM, et al. Direct identification of urinary tract pathogens from urine samples by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. 48:2110–2115.12. Christner M, Rohde H, Wolters M, Sobottka I, Wegscheider K, Aepfelbacher M. Rapid identification of bacteria from positive blood culture bottles by use of matrix-assisted laser desorption-ionization time of flight mass spectrometry fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. 48:1584–1591.13. Löffler FE, Sun Q, Li J, Tiedje JM. 16S rRNA gene-based detection of tetrachloroethene-dechlorinating Desulfuromonas and Dehalococcoides species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000. 66:1369–1374.14. Chun J, Lee JH, Jung Y, Kim M, Kim S, Kim BK, et al. EzTaxon: a web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2007. 57:2259–2261.15. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Interpretive criteria for identification of bacteria and fungi by DNA target sequencing; approved guideline MM-18A. 2007. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.16. Ivanova EP, Gorshkova NM, Sawabe T, Hayashi K, Kalinovskaya NI, Lysenko AM, et al. Pseudomonas extremorientalis sp. nov., isolated from a drinking water reservoir. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2002. 52:2113–2120.17. Anzai Y, Kim H, Park JY, Wakabayashi H, Oyaizu H. Phylogenetic affiliation of the pseudomonads based on 16S rRNA sequence. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2000. 50:1563–1589.18. La Scola B, Gundi VA, Khamis A, Raoult D. Sequencing of the rpoB gene and flanking spacers for molecular identification of Acinetobacter species. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. 44:827–832.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of VITEK Mass Spectrometry (MS), a Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-Flight MS System for Identification of Anaerobic Bacteria
- Reliability of Acinetobacter baumannii Identification with Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry
- Evaluation of two commercial kits for rapid pathogen identification directly from positive blood cultures by matrix-associated laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry
- MALDI-TOF-MS Fingerprinting Provides Evidence of Urosepsis caused by Aerococcus urinae
- Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Microbiology: What Are the Current Issues?