Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Korea
- 5Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2539813
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.102
Abstract
- The Korean National Health Information Database (NHID) contains big data combining information obtained from the National Health Insurance Service and health examinations. Data are provided in the form of a cohort, and the NHID can be used to conduct longitudinal studies and research on rare diseases. Moreover, data on the cause and date of death are provided by Statistics Korea. Research and publications based on the NHID have increased explosively in the field of endocrine disorders. However, because the data were not collected for research purposes, studies using the NHID have limitations, particularly the need for the operational definition of diseases. In this review, we describe the characteristics of the Korean NHID, operational definitions of endocrine diseases used for research, and an overview of recent studies in endocrinology using the Korean NHID.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 9 articles
-
Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):525-537. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2023.1765.Long-Term Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Levels and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Han-Sang Baek, Bongseong Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Sang-Ah Chang, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):770-781. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2023.1726.Different Associations between Lipid Levels and Risk for Heart Failure according to Diabetes Progression
Seung-Hwan Lee, Kyu Na Lee, Jong-Chan Youn, Hun Sung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2025;49(1):105-116. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0066.Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea 2024
Se Eun Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ji Yoon Kim, Kyuho Kim, Joon Ho Moon, Nam Hoon Kim, Kyung Do Han, Sung Hee Choi, Bong Soo Cha
Diabetes Metab J. 2025;49(1):24-33. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0818.Big Data Research for Diabetes-Related Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Kyung-Soo Kim, Bongseong Kim, Kyungdo Han
Diabetes Metab J. 2025;49(1):13-21. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0780.Prevalence, Incidence, and Metabolic Characteristics of Young Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in South Korea (2010–2020)
Ji Yoon Kim, Jiyoon Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Se Eun Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Sung Hee Choi, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2025;49(2):172-182. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0826.Effects of Pancreatitis and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Development of Pancreatic Cancer: A Nationwide Nested Case-Control Study
Young-eun Kim, Min Heui Yu, Chung Mo Nam, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes Metab J. 2025;49(2):252-263. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0277.Risk of Osteoporotic Fractures among Patients with Thyroid Cancer: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Eu Jeong Ku, Won Sang Yoo, Yu Been Hwang, Subin Jang, Jooyoung Lee, Shinje Moon, Eun Kyung Lee, Hwa Young Ahn
Endocrinol Metab. 2025;40(2):225-235. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2024.2101.Prevalence and Current Status of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Korean Adults Based on Fact Sheets 2024
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinol Metab. 2025;40(2):174-184. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2025.2398.
Reference
-
1. Kim MK, Han K, Lee SH. Current trends of big data research using the Korean National Health Information Database. Diabetes Metab J. 2022; 46:552–63.
Article2. Choi EK. Cardiovascular research using the Korean National Health Information Database. Korean Circ J. 2020; 50:754–72.
Article3. Shin DW, Cho J, Park JH, Cho B. National General Health Screening Program in Korea: history, current status, and future direction. Precis Future Med. 2022; 6:9–31.
Article4. Kim HK, Song SO, Noh J, Jeong IK, Lee BW. Data configuration and publication trends for the Korean National Health Insurance and Health Insurance Review & Assessment Database. Diabetes Metab J. 2020; 44:671–8.
Article5. National Health Insurance Service. 2021 National Health Insurance statistical yearbook [Internet]. Wonju: National Health Insurance Service;2022. [cited 2023 Jan 29]. Available from: https://www.nhis.or.kr/nhis/together/wbhaec06300m01.do?mode=view&articleNo=10829400&article.offset=0&articleLimit=10.6. Won JH, Byun SJ, Oh BM, Park SJ, Seo HG. Risk and mortality of aspiration pneumonia in Parkinson’s disease: a nationwide database study. Sci Rep. 2021; 11:6597.
Article7. Yang MS, Park M, Back JH, Lee GH, Shin JH, Kim K, et al. Validation of cancer diagnosis based on the National Health Insurance Service Database versus the National Cancer Registry Database in Korea. Cancer Res Treat. 2022; 54:352–61.
Article8. Lee HR, Yoo JE, Choi H, Han K, Jung JH, Park J, et al. Tuberculosis and risk of ischemic stroke: a nationwide cohort study. Stroke. 2022; 53:3401–9.
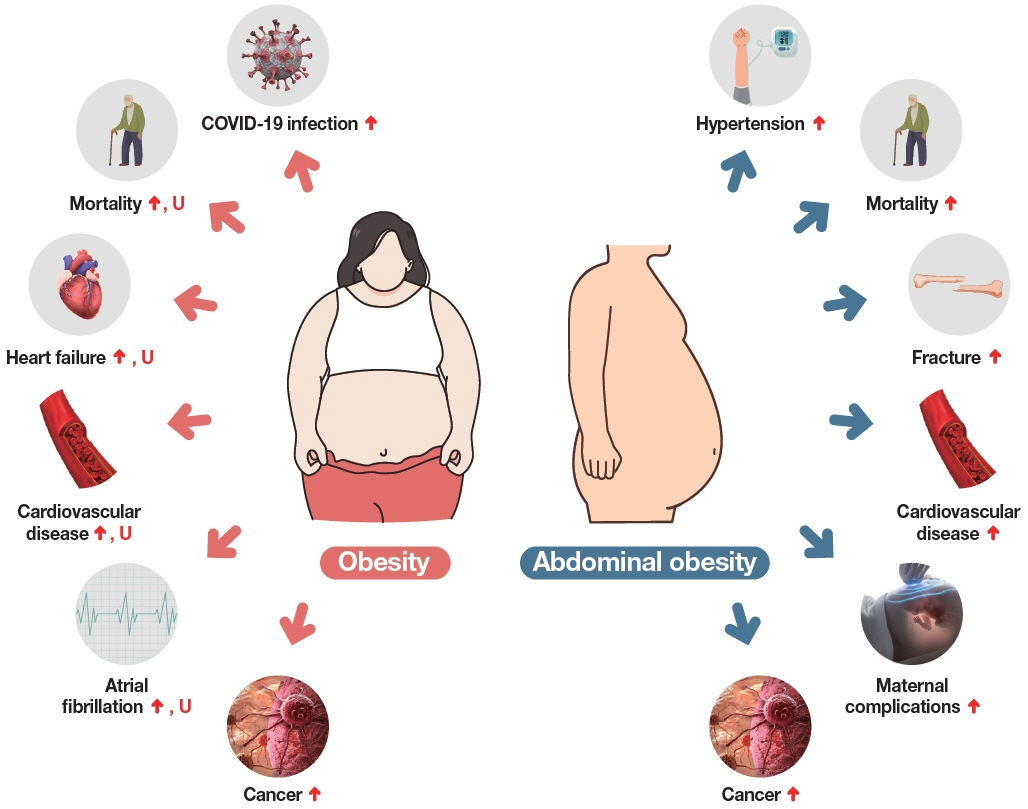
Article9. Kim BY, Kang SM, Kang JH, Kang SY, Kim KK, Kim KB, et al. 2020 Korean Society for the Study of Obesity guidelines for the management of obesity in Korea. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2021; 30:81–92.
Article10. Kim YH, Han K, Son JW, Lee SS, Oh SW, Kwon HS, et al. Data analytic process of a nationwide population-based study on obesity using the National Health Information Database presented by the National Health Insurance Service 2006-2015. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2017; 26:23–7.
Article11. World Health Organization; Regional Office for the Western Pacific. The Asia-Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment. Sydney: Health Communications Australia;2000.12. Yang YS, Han BD, Han K, Jung JH, Son JW; Taskforce Team of the Obesity Fact Sheet of the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. Obesity fact sheet in Korea, 2021: trends in obesity prevalence and obesity-related comorbidity incidence stratified by age from 2009 to 2019. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2022; 31:169–77.
Article13. Kim YH, Kim SM, Han KD, Son JW, Lee SS, Oh SW, et al. Change in weight and body mass index associated with allcause mortality in Korea: a nationwide longitudinal study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 102:4041–50.
Article14. Kim YH, Kim SM, Han KD, Jung JH, Lee SS, Oh SW, et al. Waist circumference and all-cause mortality independent of body mass index in Korean population from the National Health Insurance Health Checkup 2009-2015. J Clin Med. 2019; 8:72.
Article15. Cho JH, Rhee EJ, Park SE, Kwon H, Jung JH, Han KD, et al. Maintenance of body weight is an important determinant for the risk of ischemic stroke: a nationwide populationbased cohort study. PLoS One. 2019; 14:e0210153.
Article16. Cho JH, Rhee EJ, Park SE, Kwon H, Jung JH, Han KD, et al. The risk of myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke according to waist circumference in 21,749,261 Korean adults: a nationwide population-based study. Diabetes Metab J. 2019; 43:206–21.
Article17. Yoo JE, Han K, Jung JH, Hur YI, Kim YH, Kim ES, et al. Body mass index, waist circumference and cardiovascular diseases in transitional ages (40 and 66 years). J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022 Dec 15 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.13138.
Article18. ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, Bannuru RR, Brown FM, Bruemmer D, et al. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of care in diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. 2023; 46(Suppl 1):S140–57.19. Rhee EJ, Kwon H, Park SE, Han KD, Park YG, Kim YH, et al. Associations among obesity degree, glycemic status, and risk of heart failure in 9,720,220 Korean adults. Diabetes Metab J. 2020; 44:592–601.
Article20. Kim YG, Han KD, Choi JI, Boo KY, Kim DY, Oh SK, et al. The impact of body weight and diabetes on new-onset atrial fibrillation: a nationwide population based study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019; 18:128.
Article21. Choi JB, Moon HW, Park YH, Bae WJ, Cho HJ, Hong SH, et al. The impact of diabetes on the risk of prostate cancer development according to body mass index: a 10-year nationwide cohort study. J Cancer. 2016; 7:2061–6.
Article22. Choi JB, Myong JP, Lee Y, Kim I, Kim JH, Hong SH, et al. Does increased body mass index lead to elevated prostate cancer risk?: it depends on waist circumference. BMC Cancer. 2020; 20:589.
Article23. Choi JB, Lee EJ, Han KD, Hong SH, Ha US. Estimating the impact of body mass index on bladder cancer risk: stratification by smoking status. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:947.
Article24. Choi JB, Kim JH, Hong SH, Han KD, Ha US. Association of body mass index with bladder cancer risk in men depends on abdominal obesity. World J Urol. 2019; 37:2393–400.
Article25. Hwang S, Park YM, Han KD, Yun JS, Ko SH, Ahn YB, et al. Associations of general obesity and central obesity with the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a Korean population: a national population-based cohort study. Int J Cancer. 2021; 148:1144–54.26. Lee JE, Nam CM, Lee SG, Park S, Kim TH, Park EC. The economic burden of cancer attributable to obesity in Korea: a population-based cohort study. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2019; 28:e13084.
Article27. Rhee EJ, Cho JH, Kwon H, Park SE, Jung JH, Han KD, et al. Association between abdominal obesity and increased risk for the development of hypertension regardless of physical activity: a nationwide population-based study. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2018; 20:1417–26.
Article28. Lim J, Han K, Kim SY, Cho YH, Yoon YS, Park HS, et al. Effects of central obesity on maternal complications in Korean women of reproductive age. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2019; 13:156–63.
Article29. Park GR, Kim HS, Kim YT, Chung HJ, Ha SJ, Kim DW, et al. Waist circumference and the risk of lumbar and femur fractures: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021; 25:1198–205.30. Jung CY, Park H, Kim DW, Lim H, Chang JH, Choi YJ, et al. Association between body mass index and risk of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a nationwide case-control study in South Korea. Clin Infect Dis. 2021; 73:e1855–62.
Article31. Lee SH, Kim MK, Rhee EJ. Effects of cardiovascular risk factor variability on health outcomes. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020; 35:217–26.
Article32. Nam GE, Cho KH, Han K, Han B, Cho SJ, Roh YK, et al. Impact of body mass index and body weight variabilities on mortality: a nationwide cohort study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2019; 43:412–23.
Article33. Kim DH, Nam GE, Han K, Kim YH, Park KY, Hwang HS, et al. Variabilities in weight and waist circumference and risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and mortality: a nationwide cohort study. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020; 35:933–42.
Article34. Park KY, Hwang HS, Cho KH, Han K, Nam GE, Kim YH, et al. Body weight fluctuation as a risk factor for type 2 diabetes: results from a nationwide cohort study. J Clin Med. 2019; 8:950.
Article35. Nam GE, Park YG, Han K, Kim MK, Koh ES, Kim ES, et al. BMI, weight change, and dementia risk in patients with new-onset type 2 diabetes: a nationwide cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2019; 42:1217–24.
Article36. Yeo Y, Shin DW, Han K, Kim D, Kim TH, Chun S, et al. Smoking, alcohol consumption, and the risk of thyroid cancer: a population-based Korean cohort study of 10 million people. Thyroid. 2022; 32:440–8.
Article37. Song Y, Lee HS, Park G, Kang SW, Lee JW. Dyslipidemia risk in thyroid cancer patients: a nationwide populationbased cohort study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022; 13:893461.
Article38. Park JH, Cho HS, Yoon JH. Thyroid cancer in patients with metabolic syndrome or its components: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Cancers (Basel). 2022; 14:4106.
Article39. Kim J, Kim MK, Baek KH, Song KH, Han K, Kwon HS. Repeated low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and the risk of thyroid cancer: a nationwide population-based study in Korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2022; 37:303–11.40. Park JH, Choi M, Kim JH, Kim J, Han K, Kim B, et al. Metabolic syndrome and the risk of thyroid cancer: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Thyroid. 2020; 30:1496–504.
Article41. An SY, Kim SY, Oh DJ, Min C, Sim S, Choi HG. Obesity is positively related and tobacco smoking and alcohol consumption are negatively related to an increased risk of thyroid cancer. Sci Rep. 2020; 10:19279.
Article42. Lee YK, Hwangbo Y, Lee S, Lee DE, Lee EK, Yeom MS, et al. Aspirin use is not associated with lower thyroid cancer risk: a nationwide nested case-control study. Thyroid. 2020; 30:829–37.
Article43. Yeo Y, Han K, Shin DW, Kim D, Jeong SM, Chun S, et al. Changes in smoking, alcohol consumption, and the risk of thyroid cancer: a population-based Korean cohort study. Cancers (Basel). 2021; 13:2343.
Article44. Kim ES, Han K, Kwon HS. The association between metabolic syndrome, obesity phenotype, and the risk of thyroid cancer. Diabetes. 2019; 68(Supplement_1):2107-P.45. Son H, Lee H, Kang K, Lee I. The risk of thyroid cancer and obesity: a nationwide population-based study using the Korea National Health Insurance Corporation cohort database. Surg Oncol. 2018; 27:166–71.
Article46. An J, Kim T, Kim N, Kim H, Choi D, Park Y, et al. Demographic and clinical risk factors for thyroid cancer in Korea: Korean National Health Insurance Database study. Thyroid. 2015; 25(Supp 1):A114–5.47. Cho YY, Kang MJ, Kim SK, Jung JH, Hahm JR, Kim TH, et al. Protective effect of metformin against thyroid cancer development: a population-based study in Korea. Thyroid. 2018; 28:864–70.
Article48. Kim SY, Song YS, Wee JH, Min C, Yoo DM, Lee CH, et al. Evaluation of the relationship between previous statin use and thyroid cancer using Korean National Health Insurance Service-Health Screening Cohort data. Sci Rep. 2021; 11:7912.
Article49. Choi JH, Lee JY, Lim YC, Kim JK, Han KD, Cho JH. Association between obstructive sleep apnea and thyroid cancer incidence: a national health insurance data study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021; 278:4569–74.
Article50. Kim M, Kim BH, Lee H, Nam H, Park S, Jang MH, et al. Thyroid cancer after hysterectomy and oophorectomy: a nationwide cohort study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2021; 184:143–51.
Article51. Hyun MK, Kim J, Kwon JW, Park YJ. PSU2 The incidence of complications after its thyroidectomy in patients with thyroid cancer in Korea: using health claim database. Value Health. 2012; 15:A402.52. Jee E, Park SY, Ahn SV, Lee S. Incidence and prevalence of post-surgical hypoparathyroidism in Korea. J Bone Miner Res. 2017; 32:S120.53. Suh B, Shin DW, Park Y, Lim H, Yun JM, Song SO, et al. Increased cardiovascular risk in thyroid cancer patients taking levothyroxine: a nationwide cohort study in Korea. Eur J Endocrinol. 2019; 180:11–20.
Article54. Shin DW, Suh B, Lim H, Yun JM, Song SO, Park Y. Jshaped association between postoperative levothyroxine dosage and fracture risk in thyroid cancer patients: a retrospective cohort study. J Bone Miner Res. 2018; 33:1037–43.
Article55. Shin DW, Suh B, Yoon JM, Park Y. Risk of coronary heart disease and ischemic stroke in thyroid cancer patients taking levothyroxine. J Clin Oncol. 2017; 35(5_suppl):105.
Article56. Seo GH, Cho YY, Chung JH, Kim SW. Increased risk of leukemia after radioactive iodine therapy in patients with thyroid cancer: a nationwide, population-based study in Korea. Thyroid. 2015; 25:927–34.
Article57. Kim KJ, Song JE, Kim JY, Bae JH, Kim NH, Yoo HJ, et al. Effects of radioactive iodine treatment on cardiovascular disease in thyroid cancer patients: a nationwide cohort study. Ann Transl Med. 2020; 8:1235.
Article58. Kim KJ, Choi J, Kim JY, Kim NH, Kim HY, Baek SK, et al. The paradox of decreased all-cause mortality in patients with thyroid cancer compared to general population in Korea: a nationwide case-control cohort study. Thyroid. 2022; 32(Suppl 1):A61.59. Kim KJ, Jang S, Kim KJ, An JH, Kim NH, Shin DY, et al. Actual causes of death in thyroid cancer patients in Korea: a nationwide case control cohort study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2020; 182:103–10.
Article60. Kim M, Kim H, Park S, Joo J, Kim IJ, Kim BH. Risk factors for second primary malignancies following thyroid cancer: a nationwide cohort study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2022; 186:561–71.
Article61. Kim KJ, Choi J, Kim JY, Kim KJ, Bae JH, Kim JH, et al. Increased risk of second primary malignancy in patients with thyroid cancer: is it a real phenomenon or a detection bias? Thyroid. 2021; 31(Suppl 1):A24.62. Jin YJ, Kwon MJ, Kim JH, Kim JH, Choi HG. Association between thyroid cancer and breast cancer: two longitudinal follow-up studies using a national health screening cohort. J Pers Med. 2022; 12:133.
Article63. Ahn HY, Chae JE, Moon H, Noh J, Park YJ, Kim SG. Trends in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with medullary thyroid carcinoma in Korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020; 35:811–9.
Article64. Choi HG, Kim TJ, Hong SK, Min C, Yoo DM, Kim H, et al. Thyroid diseases and chronic rhinosinusitis: a nested casecontrol study using a national health screening cohort. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022; 19:8372.
Article65. Seo GH, Kim TH, Chung JH. Antithyroid drugs and congenital malformations: a nationwide Korean cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2018; 168:405–13.66. Cho YY, Kim B, Choi D, Kim CH, Shin DW, Kim JS, et al. Graves’ disease, its treatments, and the risk of atrial fibrillation: a Korean population-based study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022; 13:1032764.
Article67. Song E, Kim M, Park S, Park MJ, Kim JA, Roh E, et al. Treatment modality and risk of heart failure in patients with long-standing Graves’ disease: a nationwide populationbased cohort study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021; 12:761782.
Article68. Kim HJ, Kang T, Kang MJ, Ahn HS, Sohn SY. Incidence and mortality of myocardial infarction and stroke in patients with hyperthyroidism: a nationwide cohort study in Korea. Thyroid. 2020; 30:955–65.
Article69. Sohn SY, Seo GH, Chung JH. Risk of all-cause mortality in levothyroxine-treated hypothyroid patients: a nationwide Korean cohort study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021; 12:680647.
Article70. Ahn HY, Choi HS, Ha S, Cho SW. Incidence of subacute thyroiditis during the COVID-19 pandemic in South Korea using the National Health Insurance Service Database. Thyroid. 2022; 32:1299–306.
Article71. Kim SY, Yoo DM, Min CY, Choi HG. The effects of previous thyroid disease on the susceptibility to, morbidity of, and mortality due to COVID-19: a nationwide cohort study in South Korea. J Clin Med. 2021; 10:3522.
Article72. Baek YH, Cho SW, Jeong HE, Kim JH, Hwang Y, Lange JL, et al. 10-Year fracture risk in postmenopausal women with osteopenia and osteoporosis in South Korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2021; 36:1178–88.
Article73. Yu TY, Cho H, Kim TY, Ha YC, Jang S, Kim HY. Utilization of osteoporosis-related health services: use of data from the Korean National Health Insurance Database 2008-2012. J Korean Med Sci. 2018; 33:e20.
Article74. Lee YK, Yoo JI, Kim TY, Ha YC, Koo KH, Choi H, et al. Validation of operational definition to identify patients with osteoporotic hip fractures in administrative claims data. Healthcare (Basel). 2022; 10:1724.
Article75. Park SM, Ahn SH, Kim HY, Jang S, Ha YC, Lee YK, et al. Incidence and mortality of subsequent vertebral fractures: analysis of claims data of the Korea National Health Insurance Service from 2007 to 2016. Spine J. 2020; 20:225–33.
Article76. Jung HS, Nho JH, Ha YC, Jang S, Kim HY, Yoo JI, et al. Incidence of osteoporotic refractures following proximal humerus fractures in adults aged 50 years and older in Korea. J Bone Metab. 2019; 26:105–11.
Article77. Kwon GD, Jang S, Lee A, Park CM, Lee YK, Kim TY, et al. Incidence and mortality after distal radius fractures in adults aged 50 years and older in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:630–4.
Article78. Kong SH, Kim JH, Park MY, Kim SW, Shin CS. Residual risks of comorbidities after parathyroidectomy in a nationwide cohort of patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. Endocrine. 2023; 79:190–9.
Article79. Kim SH, Rhee Y, Kim YM, Won YJ, Noh J, Moon H, et al. Prevalence and complications of nonsurgical hypoparathyroidism in Korea: a nationwide cohort study. PLoS One. 2020; 15:e0232842.
Article80. Ahn SH, Park SM, Park SY, Yoo JI, Jung HS, Nho JH, et al. Osteoporosis and osteoporotic fracture fact sheet in Korea. J Bone Metab. 2020; 27:281–90.
Article81. Kim JH, Moon H, Noh J, Lee J, Kim SG. Epidemiology and prognosis of pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma in Korea: a nationwide study based on the National Health Insurance Service. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020; 35:157–64.
Article82. Ahn CH, Kim JH, Park MY, Kim SW. Epidemiology and comorbidity of adrenal Cushing syndrome: a nationwide cohort study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021; 106:e1362–72.
Article83. Kim JH, Choi S, Lee YA, Lee J, Kim SG. Epidemiology and long-term adverse outcomes in Korean patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia: a nationwide study. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2022; 37:138–47.
Article84. Kim KJ, Hong N, Yu MH, Lee H, Lee S, Lim JS, et al. Time-dependent risk of atrial fibrillation in patients with primary aldosteronism after medical or surgical treatment initiation. Hypertension. 2021; 77:1964–73.
Article85. Park KH, Lee EJ, Seo GH, Ku CR. Risk for acromegaly-related comorbidities by sex in Korean acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020; 105:dgz317.
Article86. Yun SJ, Lee JK, Park SY, Chin SO. Descriptive epidemiology and survival analysis of acromegaly in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2021; 36:e159.
Article87. Hong S, Kim KS, Han K, Park CY. Acromegaly and cardiovascular outcomes: a cohort study. Eur Heart J. 2022; 43:1491–9.
Article88. Hong S, Han K, Kim KS, Park CY. Risk of neurodegenerative diseases in patients with acromegaly: a cohort study. Neurology. 2022; 99:e1875–85.89. Oh JS, Kim HJ, Hann HJ, Kang TU, Kim DS, Kang MJ, et al. Incidence, mortality, and cardiovascular diseases in pituitary adenoma in Korea: a nationwide population-based study. Pituitary. 2021; 24:38–47.
Article90. Park JS, Yun SJ, Lee JK, Park SY, Chin SO. Descriptive epidemiology and survival analysis of prolactinomas and Cushing’s disease in Korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2021; 36:688–96.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Introducing big data analysis using data from National Health Insurance Service
- Big Data Research for Diabetes-Related Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
- Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
- Pediatric Cancer Research using Healthcare Big Data
- Real World Data and Artificial Intelligence in Diabetology