Prog Med Phys.
2022 Dec;33(4):63-71. 10.14316/pmp.2022.33.4.63.
Effect of Bead Device Diameter on Z-Resolution Measurement in Tomosynthesis Images: A Simulation Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiological Technology, Faculty of Health Sciences, Okayama University, Okayama, Japan
- 2Department of Radiological Technology, Okayama University Hospital, Okayama, Japan
- KMID: 2537873
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2022.33.4.63
Abstract
- Purpose
To clarify the relationship between the diameter of the simulated bead and the Z-resolution of the tomosynthesis image.
Methods
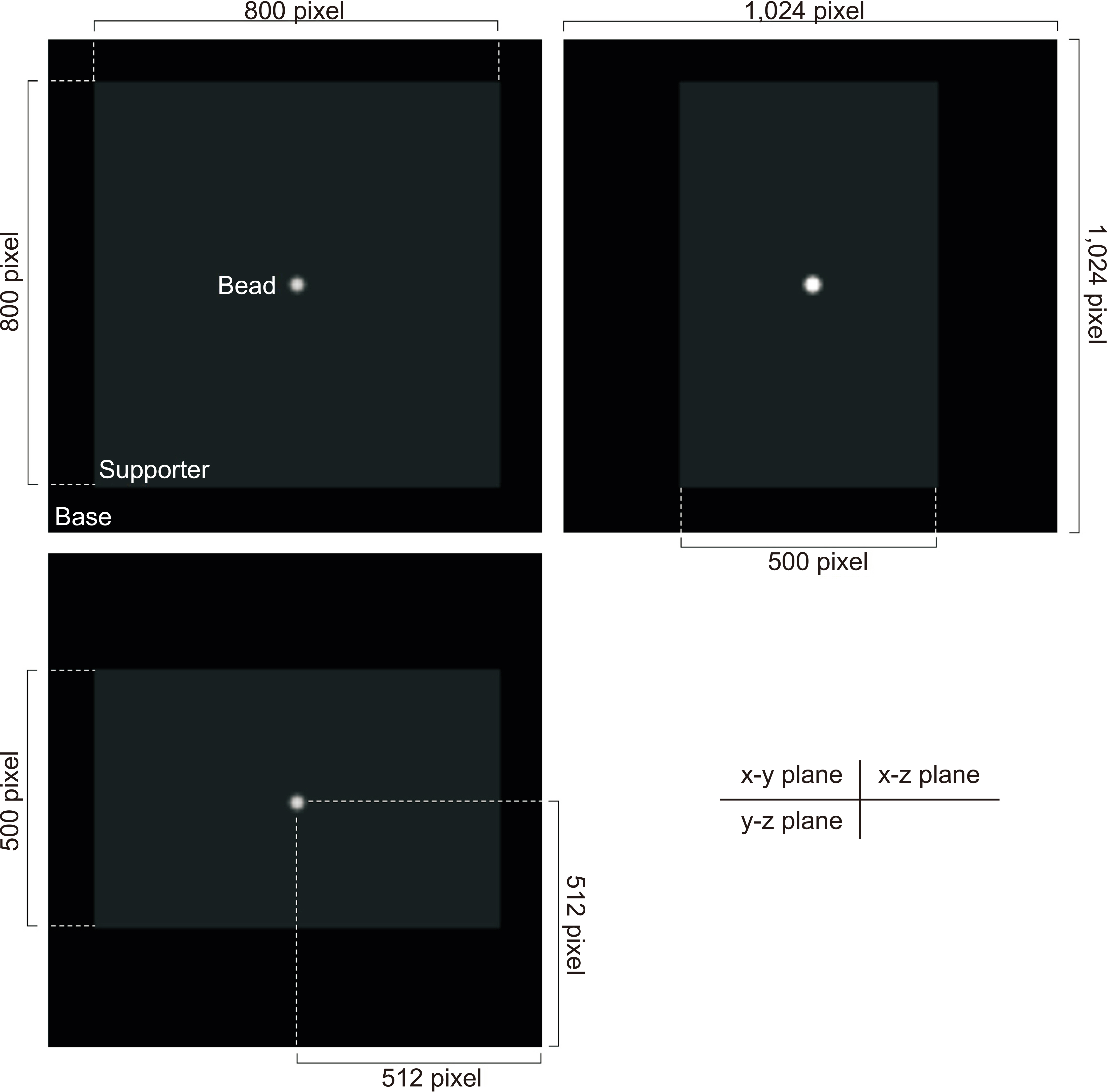
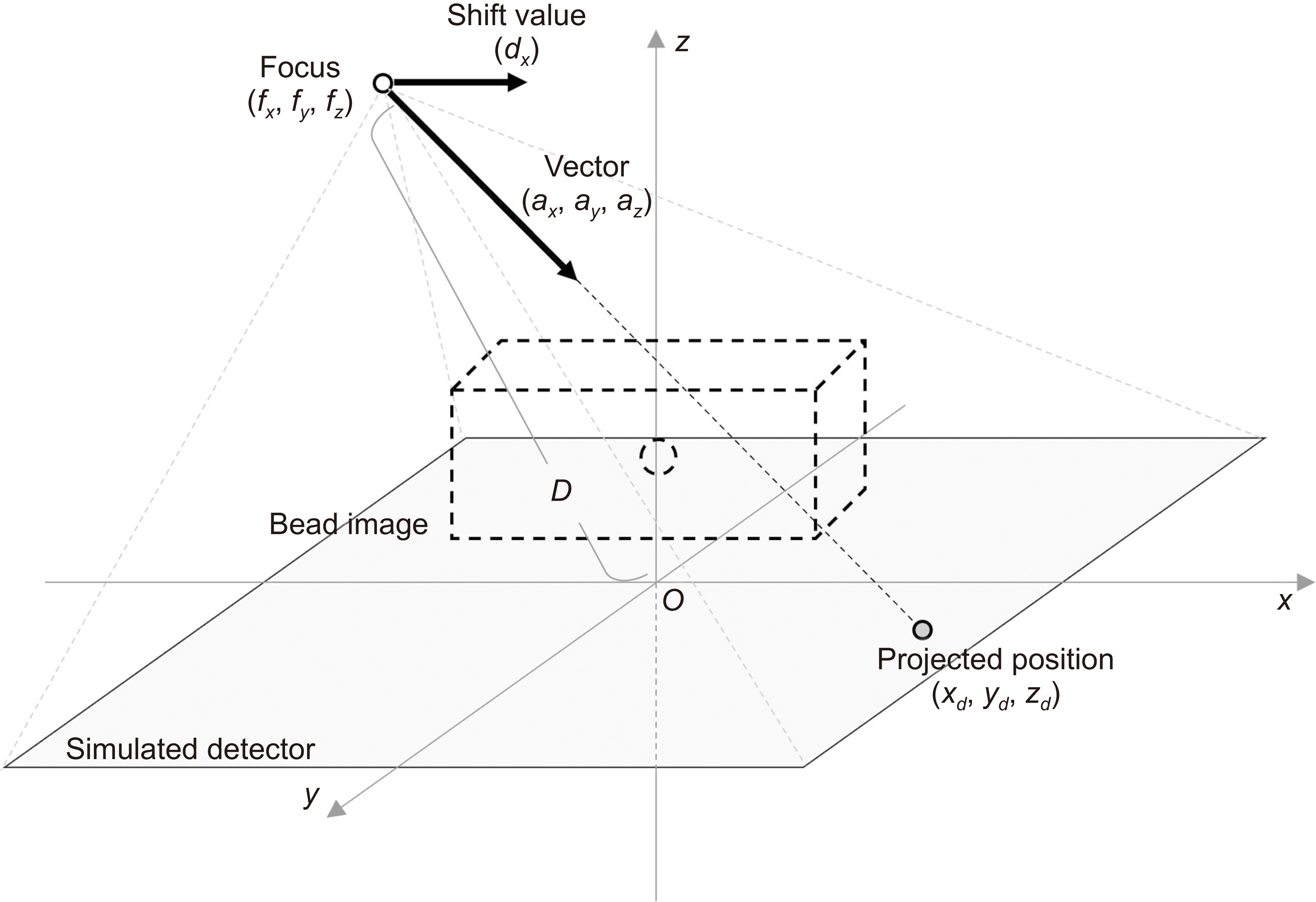
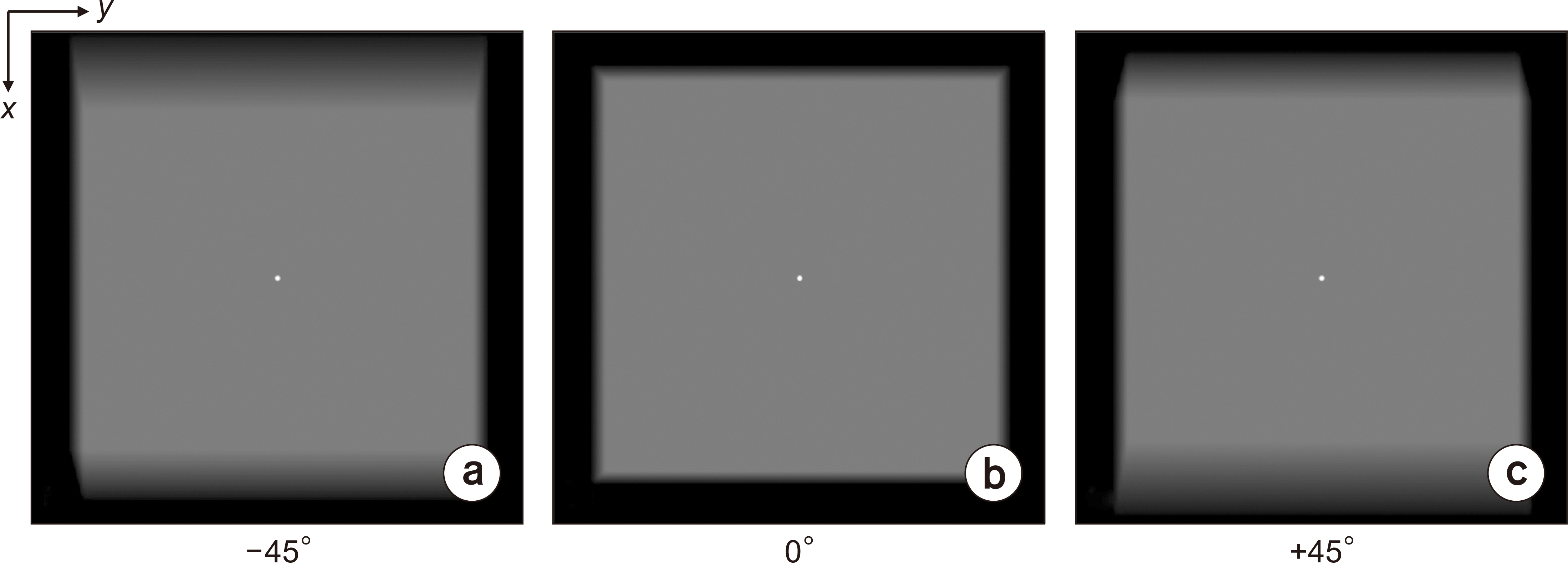
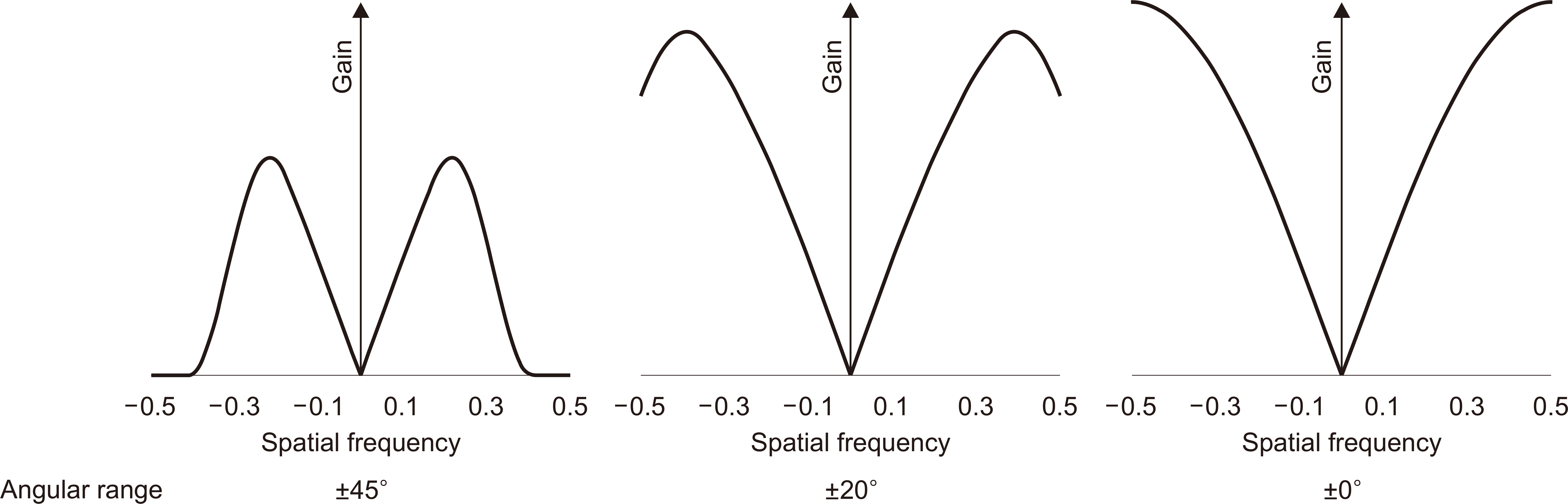
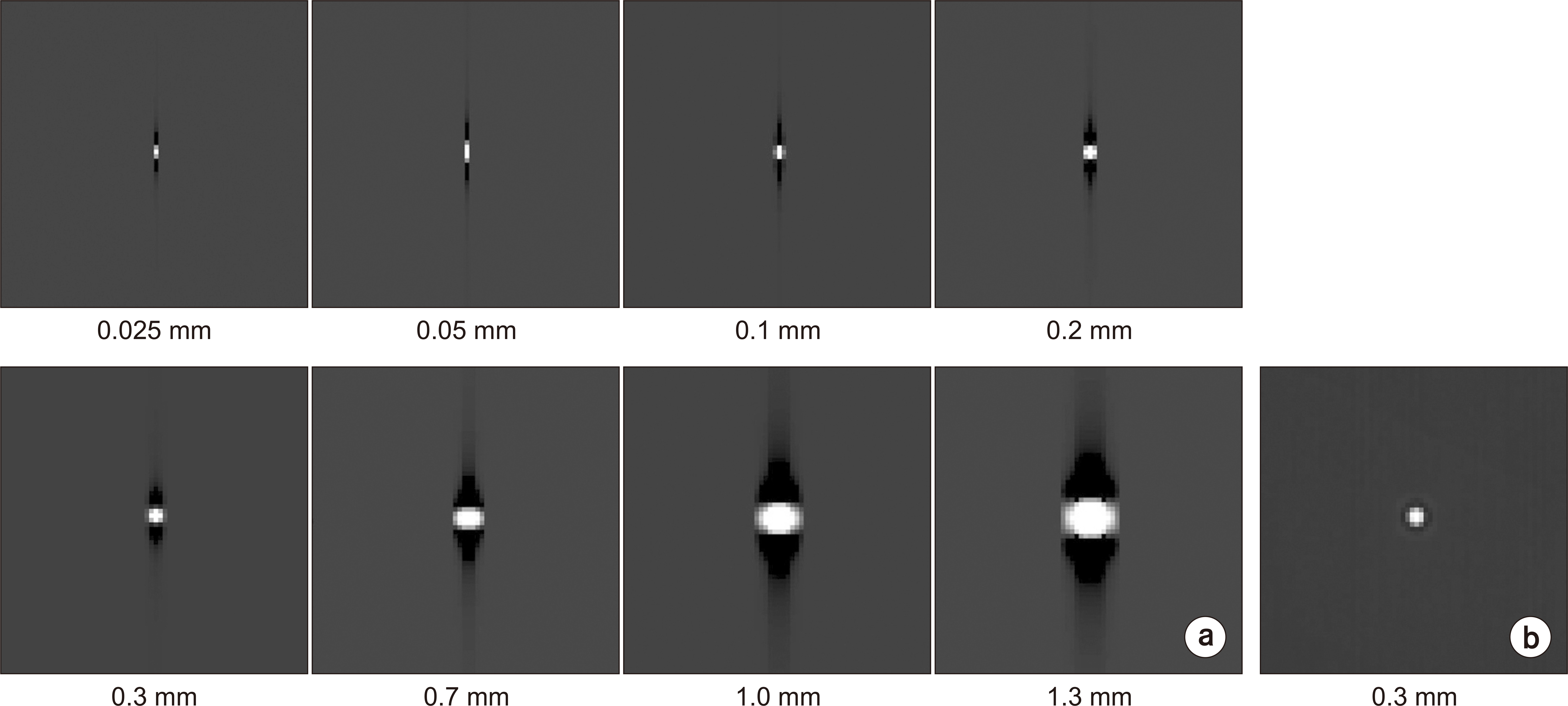
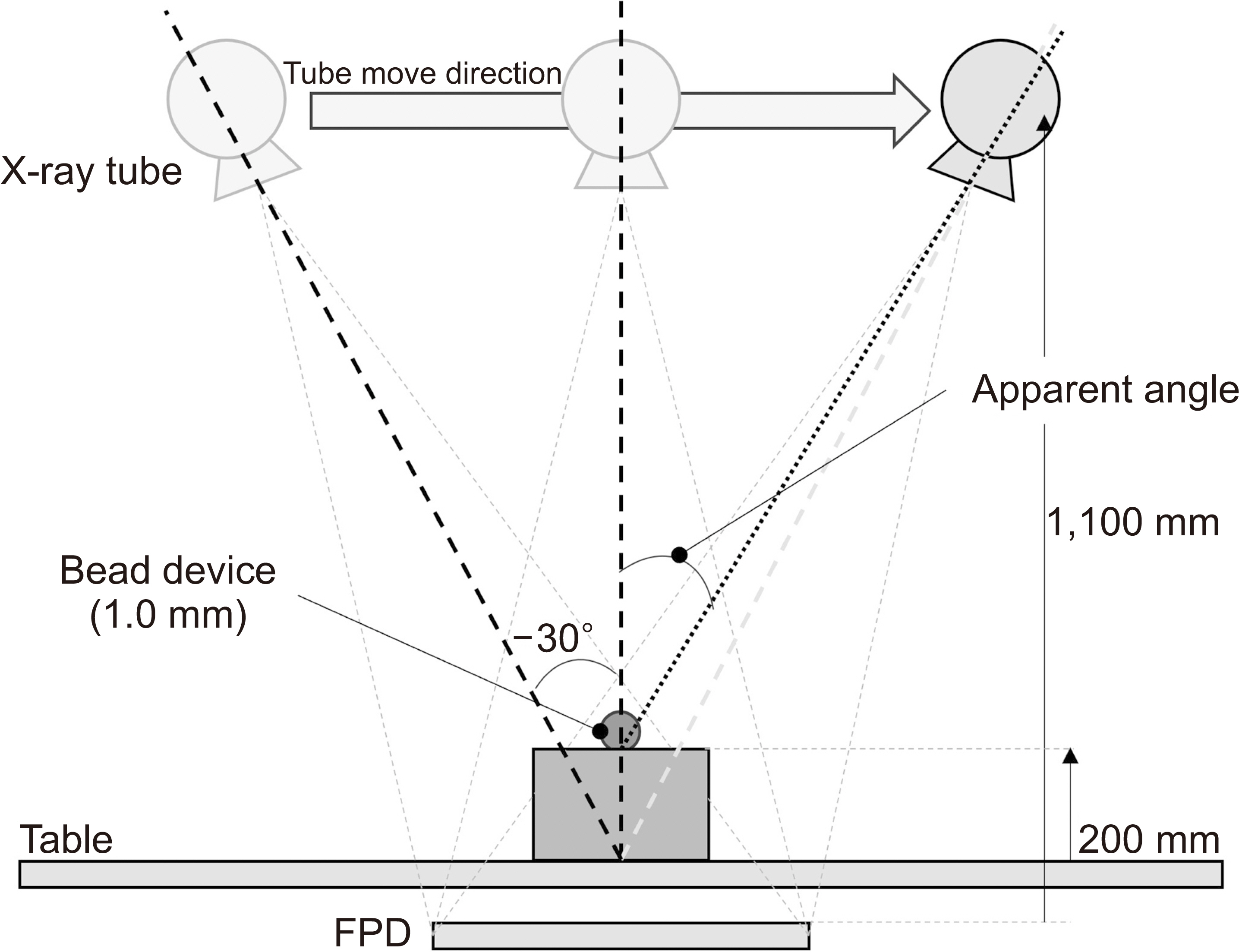
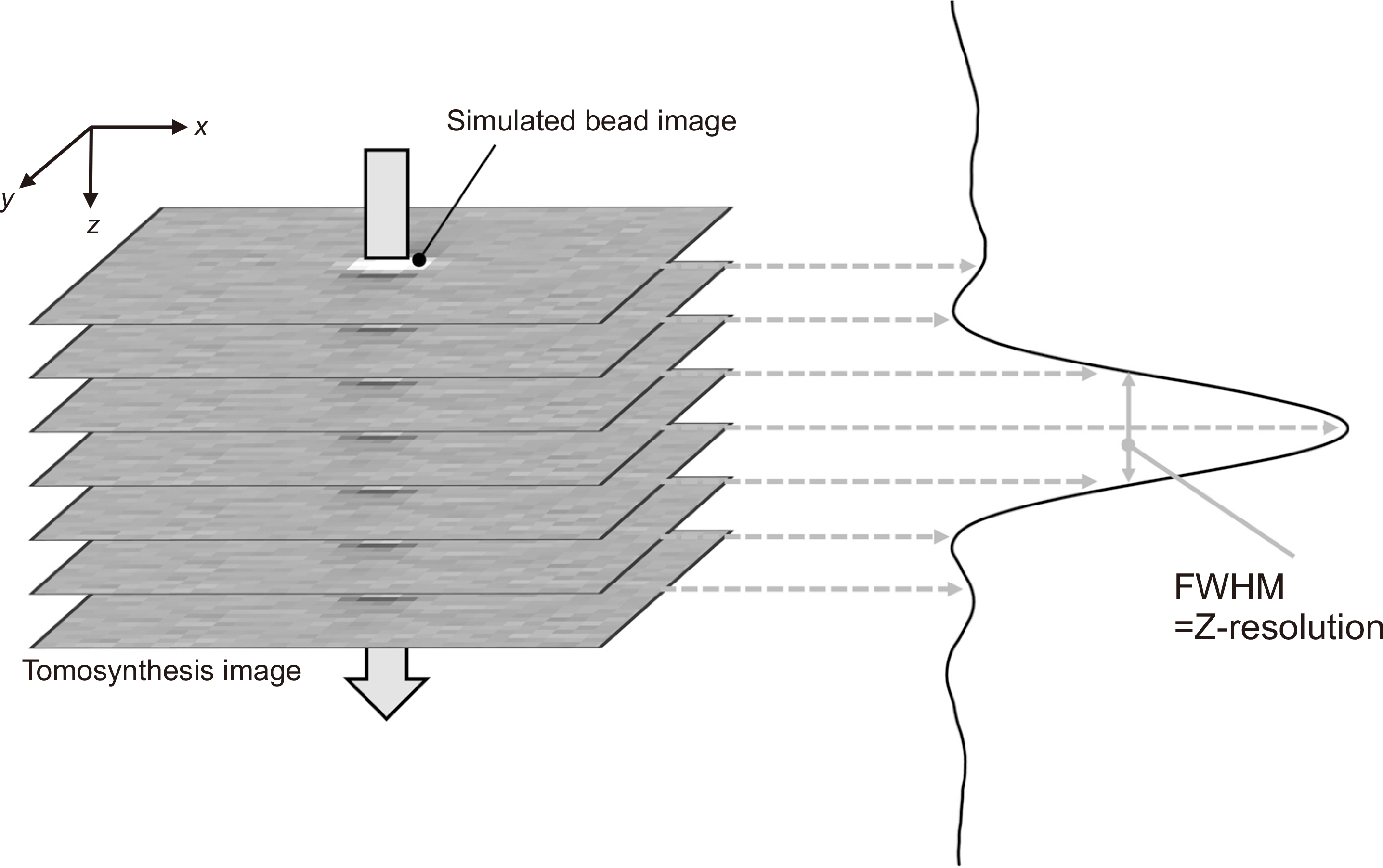
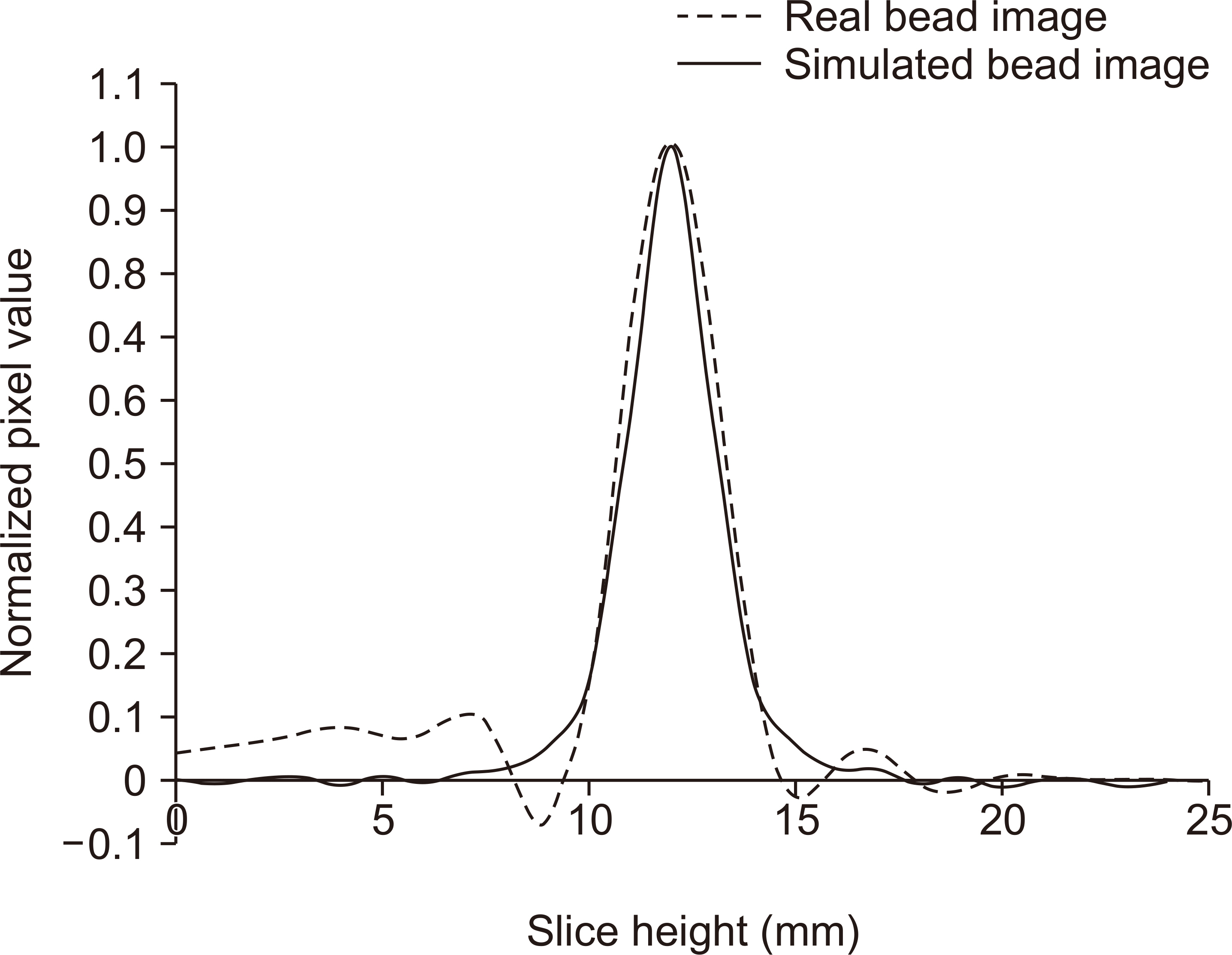
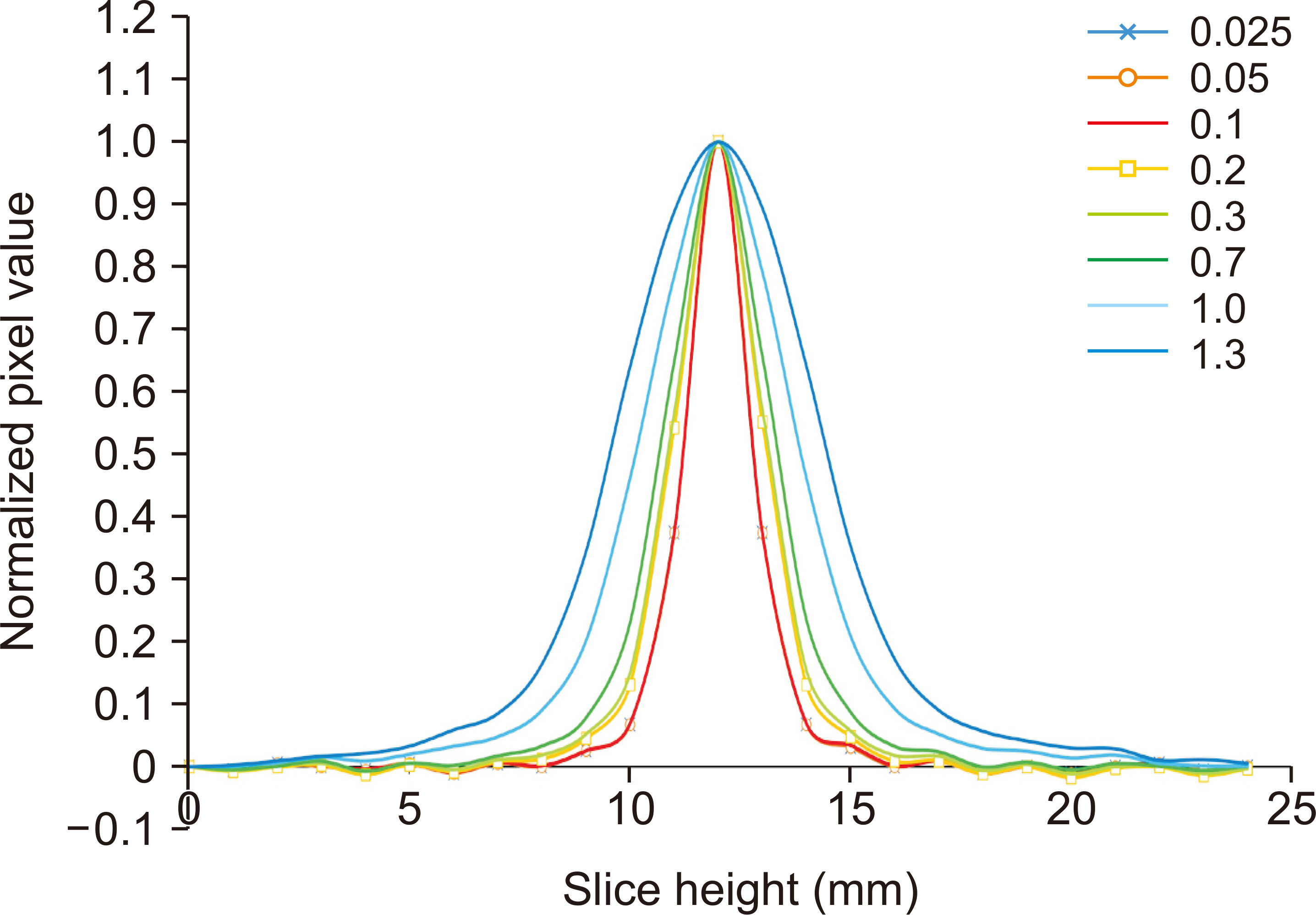
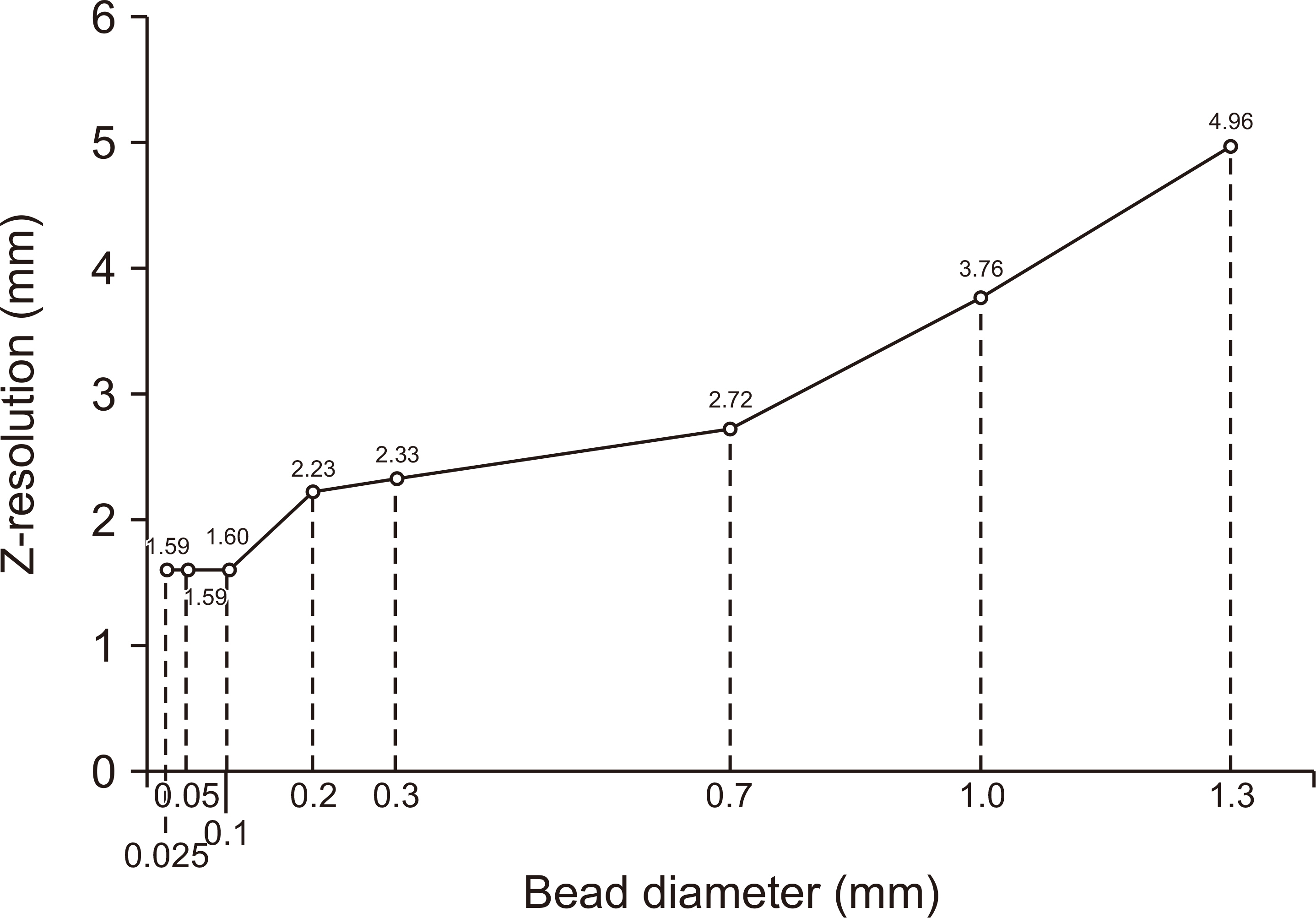
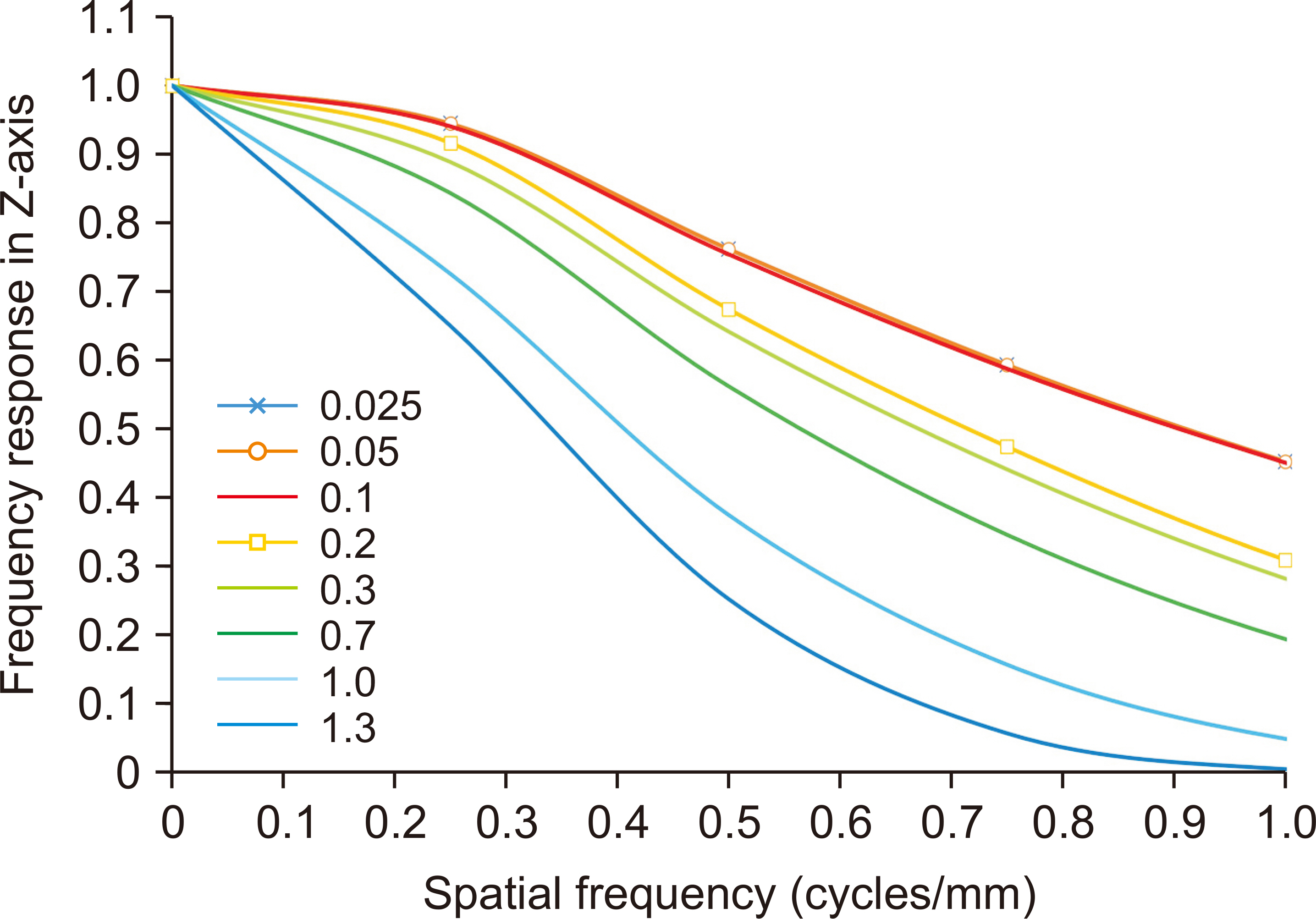
A simulated bead was placed on a 1,024×1,024×1,024-pixel base image. The diameters were set to 0.025, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.7, 1.0, and 1.3 mm. A bead was placed at the center of the base image and projected at a simulated X-ray angle range of ±45° to obtain a projected image. A region of interest was placed at the center of the bead image and the slice sensitivity profile (SSP) was obtained by acquiring pixel values in the z-direction. The full width at half maximum of the SSP was defined as the Z-resolution and the frequency response was obtained by the 1-D Fourier transform of the SSP.
Results
Z-resolution increased with increasing bead diameter. However, there was no change in Z-resolution between 0.025 and 0.1 mm. The frequency response was similar to that of the Z-resolution, with a significant difference between 0.1 and 0.2 mm diameter.
Conclusions
Z-resolution is dependent on the diameter of the bead, which should be selected considering the pixel size of the tomosynthesis image.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Yaffe MJ. 2014; Research in digital mammography and tomosynthesis at the University of Toronto. Radiol Phys Technol. 7:191–202. DOI: 10.1007/s12194-014-0277-y. PMID: 24961727.
Article2. Johnsson AA, Vikgren J, Bath M. 2014; Chest tomosynthesis: technical and clinical perspectives. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 35:17–26. DOI: 10.1055/s-0033-1363448. PMID: 24481756.
Article3. Livingston KS, Edwards EA, Griffin M, MacKenzie JD, Zapala MA. 2021; Use of digital tomosynthesis in assessing accurate medial epicondyle fracture displacement as compared with conventional radiography and computed tomography. J Pediatr Orthop. 41:e877–e883. DOI: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000001917. PMID: 34419980. PMCID: PMC8508716.
Article4. Hu YH, Zhao B, Zhao W. 2008; Image artifacts in digital breast tomosynthesis: investigation of the effects of system geometry and reconstruction parameters using a linear system approach. Med Phys. 35:5242–5252. DOI: 10.1118/1.2996110. PMID: 19175083. PMCID: PMC2673612.
Article5. Zheng J, Fessler JA, Chan HP. 2019; Effect of source blur on digital breast tomosynthesis reconstruction. Med Phys. 46:5572–5592. DOI: 10.1002/mp.13801. PMID: 31494953. PMCID: PMC6899200.
Article6. van Engen RE, Bosmans H, Bouwman RW, Dance DR, Heid P, Lazzari B, et al. 2018. Protocol for the quality control of the physical and technical aspects of digital breast tomosynthesis systems (version 1. EUREF;Berlin: p. 30–44. DOI: 10.1055/s-0033-1363448.7. Fukui R, Ishii R, Kishimoto J, Yamato S, Takahata A, Kohama C. 2014; Evaluation of the effect of geometry for measuring section thickness in tomosynthesis. Radiol Phys Technol. 7:141–147. DOI: 10.1007/s12194-013-0243-0. PMID: 24254729.
Article8. Maldera A, De Marco P, Colombo PE, Origgi D, Torresin A. 2017; Digital breast tomosynthesis: dose and image quality assessment. Phys Med. 33:56–67. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2016.12.004. PMID: 28010921.
Article9. Sage J, Fezzani KL, Fitton I, Hadid L, Moussier A, Pierrat N, et al. 2019; Experimental evaluation of seven quality control phantoms for digital breast tomosynthesis. Phys Med. 57:137–144. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2018.12.031. PMID: 30738517.
Article10. Mertelmeier T, Orman J, Haerer W, Dudam MK. 2006. Optimizing filtered backprojection reconstruction for a breast tomosynthesis prototype device. Paper presented at: Medical Imaging 2006: Physics of Medical Imaging; 2006 Feb 11-16; San Diego, USA. DOI: 10.1117/12.651380.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of the Number of Projected Images on the Noise Characteristics in Tomosynthesis Imaging
- Compressed-sensing (CS)-based Image Deblurring Scheme with a Total Variation Regularization Penalty for Improving Image Characteristics in Digital Tomosynthesis (DTS)
- Digital tomography in the diagnosis of a posterior pneumothorax in the intensive care unit
- Clinical Application of Artificial Intelligence in Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
- Estimation of Validity for the Trabecular Bone Indentation by FEA