Korean J Schizophr Res.
2022 Oct;25(2):43-53. 10.16946/kjsr.2022.25.2.43.
Factors Affecting the Family Attitude Toward the Outpatients With Schizophrenia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2535944
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.16946/kjsr.2022.25.2.43
Abstract
Objectives
To identify various factors that might affect a high expressed emotion recognized by primary caregivers of the schizophrenic outpatients.
Methods
Of patients who had been receiving outpatient treatments at department of psychiatry of Dong-A university hospital, 154 patients with a DSM-V diagnosis of schizophrenia with stable symptoms and their primary caregivers were enrolled in this study. Family attitude (family attitude scale) was assessed through an interview with primary caregivers. In these patients, symptoms (brief psychiatric rating scale), problem behavior (behavior and symptom identification scale), general health status (shortform 36 health survey), recovery (recovery assessment scale), drug attitude (drug attitude inventory), insight (self-appraisal of illness questionnaire) were assessed through a self reporting questionnaire. Multiple regression analysis were performed in consideration of 15 factors (age, sex, the level of education, marital status, job status, age of onset, duration of illness, number of hospitalization, chlorpromazine equivalent dose, symptoms, problem behavior, general health status, recovery, drug attitude, insight) as explanatory variables for a family attitude.
Results
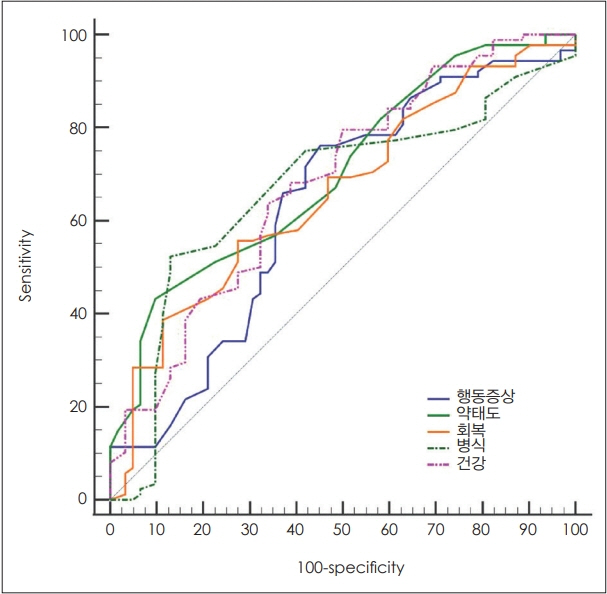
On a multiple regression analysis, the following five factors were found to be significant explanatory variables for a family attitude that is experienced by primary caregivers of the schizophrenic outpatients: job status, duration of illness, number of hospitalization, problem behavior, and drug attitude. A coefficient of determination for these five explanatory variables was 0.58. The high expressed emotion group had significantly higher number of hospitalizations and problem behavior, but lower employment, poorer genral health status, negative drug attitude, and lack of insight compared to the low expressed emotion group.
Conclusion
Our results showed that five factors such as job status, duration of illness, number of hospitalization, problem behavior, and drug attitude were found to be significant explanatory variables for family attitude that is experience by primary caregivers of the schizophrenic outpatients. Because these five variables account for 58% of total family attitude, however, further studies are needed to identify other factors that might affect a family attitude.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lefley HP. Family burden and family stigma in major mental illness. Am Psychol. 1989; 44:556–560.2. Kreisman DE, Joy VD. Family response to the mental illness of a relative: a review of the literature. Schizophr Bull. 1974; 1:34–57.3. Gibbons J, Horn S, Powell J, Gibbons J. Schizophrenic patients and their families. A survey in a psychiatric service based on a DGH Unit. Br J Psychiatry. 1984; 144:70–77.4. Hatfield AB. The family as a partner in the treatment of mental illness. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1979; 30:338–340.5. Provencher HL, Mueser KT. Positive and negative symptom behaviors and caregiver burden in the relatives of persons with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 1997; 26:71–80.6. Schene AH, Van Wijngaarden B, Koeter MW. Family caregiving in schizophrenia: Domains and distress. Schizophr Bull. 1998; 24:609–618.7. Wolthaus J, Dingemans P, Schene A, Linszen D, Wiersma D, Van Den Bosch R, et al. Caregiver burden in recent-onset schizophrenia and spectrum disorders: the influence of symptoms and personality traits. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2002; 190:241–247.8. Dyck DG, Short R, Vitaliano PP. Predictors of burden and infectious illness in schizophrenia caregivers. Psychosomatic Medicine. 1999; 61:411–419.9. Grandón P, Jenaro C, Lemos S. Primary caregivers of schizophrenia outpatients: Burden and predictor variables. Psychiatry Res. 2008; 158:335–343.10. Webb C, Pfeiffer M, Mueser KT, Gladis M, Mensch E, DeGirolamo J, et al. Burden and well-being of caregivers for the severely mentally ill: the role of coping style and social support. Schizophr Res. 1998; 34:169–180.11. Roick C, Heider D, Toumi M, Angermeyer MC. The impact of caregivers’c haracteristics, patients’conditions and regional differences on family burden in schizophrenia: a longitudinal analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2006; 114:363–374.12. Lowyck B, De Hert M, Peeters E, Wampers M, Gilis P, Peuskens J. A study of the family burden of 150 family members of schizophrenic patients. Eur Psychiatry. 2004; 19:395–401.13. Jones SL, Roth D, Jones PK. Effect of demographic and behavioral variables on burden of caregivers of chronic mentally ill persons. Psychiatr Serv. 1995; 46:141–145.14. Baronet AM. Factors associated with caregiver burden in mental illness: a critical review of the research literature. Clin Psychol Rev. 1999; 19:819–841.15. Gibbons JS, Horn SH, Powell JM, Gibbons JL. Schizophrenic patients and their families. A survey in a psychiatric service based on a DGH unit. Br J Psychiatry. 1984; 144:70–77.16. Kim CK, Seo JM, Lee GZ, Kim JW, Kim GJ, Byun WT. Family Burden of Schizophrenics in the Primary Caregivers and Siblings. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2000; 39:113–127.17. Kim JW, Kim CK. Factors Influencing Burden on the Primary Caregivers of Remitted Schizophrenic Outpatients. Korean J Schizophr Res. 2017; 20:44–54.18. Maeng SR, Kim WH, Kim JH, Bae JN, Lee JS, Kim CE. Factors Affecting Quality of Life and Family Burden among the Families of Patients with Schizophrenia. Korean J Schizophr Res. 2016; 19:78–88.19. Gang DH, Kim CK, Byun WT. The Objective and Subjective Family Burden of Schizophrenic Patient. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1995; 34:193–203.20. Brown G. Experiences of discharged chronic schizophrenic mental hospital patients in various types of living groups. Millbank Memorial Fund Quarterly. 1959; 37:105–131.21. Butzlaff RL, Hooley JM. Expressed emotion and psychiatric relapse: a meta-analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998; 55:547–552.22. King S, Dixon MJ. Expressed emotion and relapse in young schizophrenia outpatients. Schizophr Bull. 1999; 25:377–386.23. Bhugra D, McKenzie K. Expressed emotion across cultures. Adv. Psychiatr Treat. 2003; 9:342–348.24. Scazufca M, Kuipers E. Links between expressed emotion and burden of care in relatives of patients with schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 1996; 168:580–587.25. Barrowclough C, Parle M. Appraisal, psychological adjustment and expressed emotion in relatives of patients suffering from schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 1997; 171:26–30.26. Smith J, Birchwood M, Cochrane R, George S. The needs of high and low expressed emotion families: a normative approach. Social Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 1993; 28:11–16.27. Scazufca M, Kuipers E. Links between expressed emotion and burden of care in relatives of patients with schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 1996; 168:580–587.28. Boye B, Bentsen H, Ulstein I, Notland TH, Lersbryggen A, Lingjærde O, et al. Relatives’distress and patients’symptoms and behaviours: a prospective study of patients with schizophrenia and their relatives. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2001; 104:42–50.29. Miura Y, Mizuno M, Yamashita C, Watanabe K, Murakami M, Kashima H. Expressed emotion and social functioning in chronic schizophrenia. Compr Psychiatry. 2004; 45:469–474.30. Chung YC, Chung AJ, Hwang IK. The expressed emotion of the relatives of schizophrenics. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Ass. 1988; 27:535–541.31. Kang KS, Lee YS. Relatives’expressed emotion perceived by schizophrenic patients. Chonnam J Nursing Sciences. 1999; 4:71–87.32. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5). 5th ed. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association;2013.33. Vaughn C, Leff JP. The measurement of expressed emotion in families of psychiatric patients. Br J Soc Clin Psychol. 1976; 15:157–165.34. Kavanagh DJ, O’Halloran P, Manicavasagar V, Clark D, Piatkowska O, Tennant C, et al. The family attitude scale: reliability and validity of a new scale for measuring the emotional climate of families. Psychiatry Res. 1997; 70:185–195.35. Overall JE, Gorham DR. The brief psychiatric rating scale (BPRS): recent developments in ascertainment and scaling. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1988; 24:97–99.36. Overall JE, Klett CJ. Applied multivariate analysis. New York: McGraw-Hill;1972.37. Eisen SV, Dill DL, Grob MC. Reliability and validity of a brief patient-report instrument for psychiatric outcome evaluation. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1994; 45:242–247.38. Bae A, Hong CH, Shin J. Validation Study of the Behavior and Symptom Identification Scale (BASIS-32). Korean Journal of Clinical Psychology. 2011; 30:929–941.39. Ware JE, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-Item Short-Form Health Status Survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992; 30:253–265.40. Koh SB, Jang SJ, Kang MG, Cha BS, Park JG. Reliability and validity on measurement instrument for health status assessment in occupational workers. J Prev Med Public Health. 1997; 30:251–265.41. Corrigan PW, Salzer M, Ralph RO, Sangster Y, Keck L. Examining the factor structure of the recovery assessment scale. Schizophr Bull. 2004; 30:1035–1041.42. Lim KM, Shin ES, Shim SH, Jeong YJ. Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of the Recovery Assessment Scale (RAS) for Psychiatric Patients. J Korea Contents Association. 2014; 628–638.43. Lee JM, Kim CK. Opinions on the Recovery of Outpatients with Schizophrenia and Their Wills to Recover. Korean J Schizophr Res. 2021; 24:17–25.44. Hogan TP, Awad AG, Eastwood MR. A self-report scale predictive of drug compliance in schizophrenics: Reliability and discriminative validity. Psychol Med. 1983; 13:177–183.45. Marks KA, Fastenau PS, Lysaker PH, Bond GR. Self-appraisal of illness questionnaire (SAIQ): Relationship to researcher-rated insight and neuropsychological function in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2000; 45:203–211.46. Taylor DM, Barnes TRE, Young AH. The Maudsley Prescribing Guidelines in Psychiatry. 13th ed. WILEY Blackwell;2018. p.15.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors Affecting the Empowerment Experienced by Outpatients with Schizophrenia
- The Comparison of Clinical Variables Among Competitive Employment, Partial Employment, and Unemployment Group in Schizophrenic Outpatients
- Factors Affecting Quality of Life and Family Burden among the Families of Patients with Schizophrenia
- Factors Influencing Burden on the Primary Caregivers of Remitted Schizophrenic Outpatients
- Factors Influencing the Personal Recovery in Outpatients With Schizophrenia