J Stroke.
2022 Sep;24(3):335-344. 10.5853/jos.2022.01697.
Transcatheter Patent Foramen Ovale Closure in Stroke Patients with Thrombophilia: Current Status and Future Perspectives
- Affiliations
-
- 1Quebec Heart and Lung Institute, Laval University, Quebec City, QC, Canada
- 2Quebec University Hospital Center (Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Québec), Quebec City, QC, Canada
- KMID: 2534262
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2022.01697
Abstract
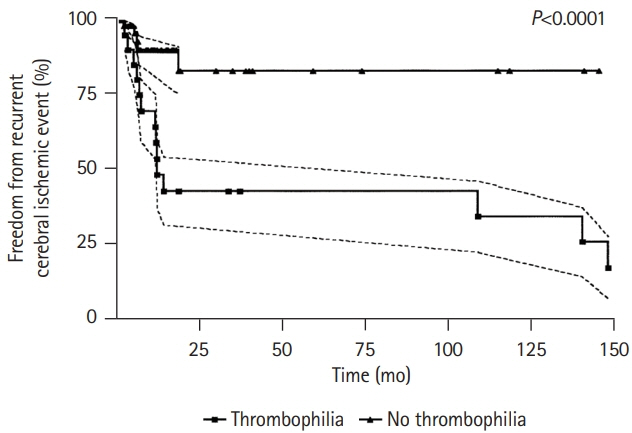
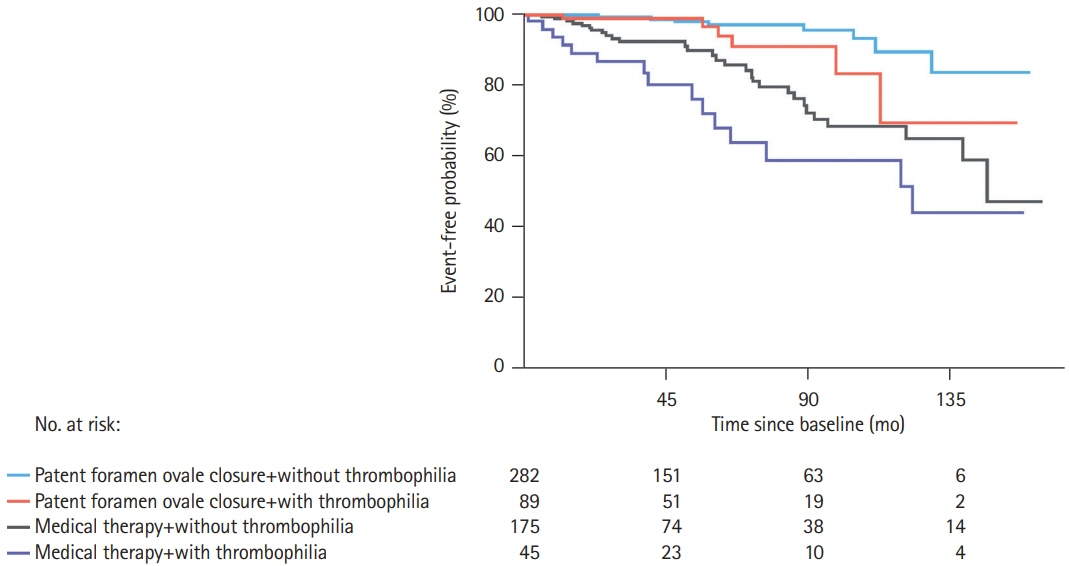
- Transcatheter patent foramen ovale (PFO) closure is a safe and effective treatment for secondary prevention after a PFO-associated stroke as demonstrated in multiple large randomized clinical trials. However, these trials excluded a significant proportion of patients who could have benefited from percutaneous PFO closure due to coexisting potential confounders such as additional thromboembolic risk factors, namely thrombophilia. Since scarce and conflicting data existed on such patients, current clinical management guidelines on patients with PFO mainly recommended against PFO closure in patients with thrombophilia and failed to provide any recommendation on the type and duration of antithrombotic treatment after transcatheter PFO closure. In the past 2 years, there has been new evidence supporting transcatheter PFO closure as a clinically meaningful alternative (vs. medical treatment) in this high-risk group of patients, along with additional data supporting the important role of systematic screening for thrombophilia in PFO-associated cerebrovascular events. This review article provides an updated overview of the incidence, clinical characteristics and outcomes of PFO closure in patients with thrombophilia, also commenting on the most appropriate medical treatment after PFO closure and future perspectives in the field.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Giacoppo D, Caronna N, Frangieh AH, Michel J, Andò G, Tarantini G, et al. Long-term effectiveness and safety of transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale compared with antithrombotic therapy alone: a meta-analysis of six randomised clinical trials and 3,560 patients with reconstructed time-to-event data. EuroIntervention. 2018; 14:857–867.2. Salehi Omran S, Hartman A, Zakai NA, Navi BB. Thrombophilia testing after ischemic stroke: why, when, and what? Stroke. 2021; 52:1874–1884.3. Thrombophilia and their detection. In : Wahed A, Quesada A, Dasgupta A, editors. Hematology and Coagulation. 2nd ed. Amsterdam (NL): Academic Press;2020. p. 265–276.4. Mac Grory B, Ohman EM, Feng W, Xian Y, Yaghi S, Kamel H, et al. Advances in the management of cardioembolic stroke associated with patent foramen ovale. BMJ. 2022; 376:e063161.5. Hviid CV, Simonsen CZ, Hvas AM. Recurrence risk in patients with cryptogenic stroke, patent foramen ovale, and thrombophilia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Haemost. 2019; 119:1839–1848.6. Giardini A, Donti A, Formigari R, Bronzetti G, Prandstraller D, Bonvicini M, et al. Comparison of results of percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale for paradoxical embolism in patients with versus without thrombophilia. Am J Cardiol. 2004; 94:1012–1016.7. Pristipino C, Sievert H, D’Ascenzo F, Louis Mas J, Meier B, Scacciatella P, et al. European position paper on the management of patients with patent foramen ovale: general approach and left circulation thromboembolism. Eur Heart J. 2019; 40:3182–3195.8. Messé SR, Gronseth GS, Kent DM, Kizer JR, Homma S, Rosterman L, et al. Practice advisory update summary: patent foramen ovale and secondary stroke prevention: report of the Guideline Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2020; 94:876–885.9. Liu K, Song B, Palacios IF, Inglessis-Azuaje I, Deng W, McMullin D, et al. Patent foramen ovale attributable cryptogenic embolism with thrombophilia has higher risk for recurrence and responds to closure. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2020; 13:2745–2752.10. Ben-Assa E, Herrero-Garibi J, Cruz-Gonzalez I, Elmariah S, Rengifo-Moreno P, Al-Bawardy R, et al. Efficacy and safety of percutaneous patent foramen ovale closure in patients with a hypercoagulable disorder. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2021; 98:800–807.11. Buber J, Guetta V, Orion D, Lubetsky A, Borik S, Vatury O, et al. Patent foramen ovale closure among patients with hypercoagulable states maintained on antithrombotic therapy. Cardiology. 2021; 146:375–383.12. Kalaria C, Kittner S. The therapeutic value of laboratory testing for hypercoagulable states in secondary stroke prevention. Neurol Clin. 2015; 33:501–513.13. Arachchillage DJ, Mackillop L, Chandratheva A, Motawani J, MacCallum P, Laffan M. Thrombophilia testing: a British Society for Haematology guideline. Br J Haematol. 2022; 198:443–458.14. Lim ST, Murphy SJ, Smith DR, Williams J, Navarro SG, McCabe J, et al. Clinical outcomes and a high prevalence of abnormalities on comprehensive arterial and venous thrombophilia screening in TIA or ischaemic stroke patients with a patent foramen ovale, an inter-atrial septal aneurysm or both. J Neurol Sci. 2017; 377:227–233.15. Elgendy AY, Saver JL, Amin Z, Boudoulas KD, Carroll JD, Elgendy IY, et al. Proposal for updated nomenclature and classification of potential causative mechanism in patent foramen ovale-associated stroke. JAMA Neurol. 2020; 77:878–886.16. Alsheikh-Ali AA, Thaler DE, Kent DM. Patent foramen ovale in cryptogenic stroke: incidental or pathogenic? Stroke. 2009; 40:2349–2355.17. Pezzini A, Del Zotto E, Magoni M, Costa A, Archetti S, Grassi M, et al. Inherited thrombophilic disorders in young adults with ischemic stroke and patent foramen ovale. Stroke. 2003; 34:28–33.18. Karttunen V, Hiltunen L, Rasi V, Vahtera E, Hillbom M. Factor V Leiden and prothrombin gene mutation may predispose to paradoxical embolism in subjects with patent foramen ovale. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2003; 14:261–268.19. Ford MA, Reeder GS, Lennon RJ, Brown RD, Petty GW, Cabalka AK, et al. Percutaneous device closure of patent foramen ovale in patients with presumed cryptogenic stroke or transient ischemic attack: the Mayo Clinic experience. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2009; 2:404–411.20. Pezzini A, Grassi M, Zotto ED, Giossi A, Volonghi I, Costa P, et al. Do common prothrombotic mutations influence the risk of cerebral ischaemia in patients with patent foramen ovale?: systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Haemost. 2009; 101:813–817.21. Debski M, Abdelrahman A, Alshehri H, Prince M, Wiper A, Chalil S, et al. Contemporary management of patent foramen ovale: a multinational survey on cardiologists’ perspective. J Interv Cardiol. 2021; 2021:6955791.22. Omran SS, Lerario MP, Gialdini G, Merkler AE, Moya A, Chen ML, et al. Clinical impact of thrombophilia screening in young adults with ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019; 28:882–889.23. Offelli P, Zanchetta M, Pedon L, Marzot F, Cucchini U, Pegoraro C, et al. Thrombophilia in young patients with cryptogenic stroke and patent foramen ovale (PFO). Thromb Haemost. 2007; 98:906–907.24. Kefer J, Sluysmans T, Hermans C, El Khoury R, Lambert C, Van de Wyngaert F, et al. Percutaneous transcatheter closure of interatrial septal defect in adults: procedural outcome and long-term results. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2012; 79:322–330.25. Giardini A, Donti A, Formigari R, Salomone L, Palareti G, Guidetti D, et al. Spontaneous large right-to-left shunt and migraine headache with aura are risk factors for recurrent stroke in patients with a patent foramen ovale. Int J Cardiol. 2007; 120:357–362.26. Ding WY, Protty MB, Davies IG, Lip GY. Relationship between lipoproteins, thrombosis, and atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res. 2022; 118:716–731.27. Galli M, Luciani D, Bertolini G, Barbui T. Lupus anticoagulants are stronger risk factors for thrombosis than anticardiolipin antibodies in the antiphospholipid syndrome: a systematic review of the literature. Blood. 2003; 101:1827–1832.28. Dodge SM, Hassell K, Anderson CA, Keller J, Groves B, Carroll JD. Antiphospholipid antibodies are common in patients referred for percutaneous patent foramen ovale closure. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2004; 61:123–127.29. Yan C, Li H. Preliminary investigation of in situ thrombus within patent foramen ovale in patients with and without stroke. JAMA. 2021; 325:2116–2118.30. Botto N, Spadoni I, Giusti S, Ait-Ali L, Sicari R, Andreassi MG. Prothrombotic mutations as risk factors for cryptogenic ischemic cerebrovascular events in young subjects with patent foramen ovale. Stroke. 2007; 38:2070–2073.31. Kar S, Noureddin N, Aboulhosn J, Mahmzi Y, Coluzzi A, Tobis JM. Percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale or atrial septal defect in the presence of thrombophilia. J Struct Heart Dis. 2017; 3:135–140.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Transcatheter Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale in a Stroke Patient under the Guidance of Transesophageal Echocardiography
- Patent Foramen Ovale and Cryptogenic Stroke
- Patent Foramen Ovale and Stroke-Current Status
- Transcatheter Treatment of Patent Foramen Ovale Combined with Abnormal Drainage of Left Superior Vena Cava to Left Upper Pulmonary Vein
- Intermediate and Long-Term Results of Transcatheter Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale Using the Amplatzer Patent Foramen Ovale Occluder: One Case of Pulmonary Embolism Irrespective of Patent Foramen Ovale Closure