J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2022 Sep;26(3):143-147. 10.14193/jkfas.2022.26.3.143.
A Fibular Lengthening Osteotomy Combined with Calcaneal Osteotomy for Post-Traumatic Valgus Ankle Arthritis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Orthopaedic Surgery, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea
- KMID: 2533197
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2022.26.3.143
Abstract
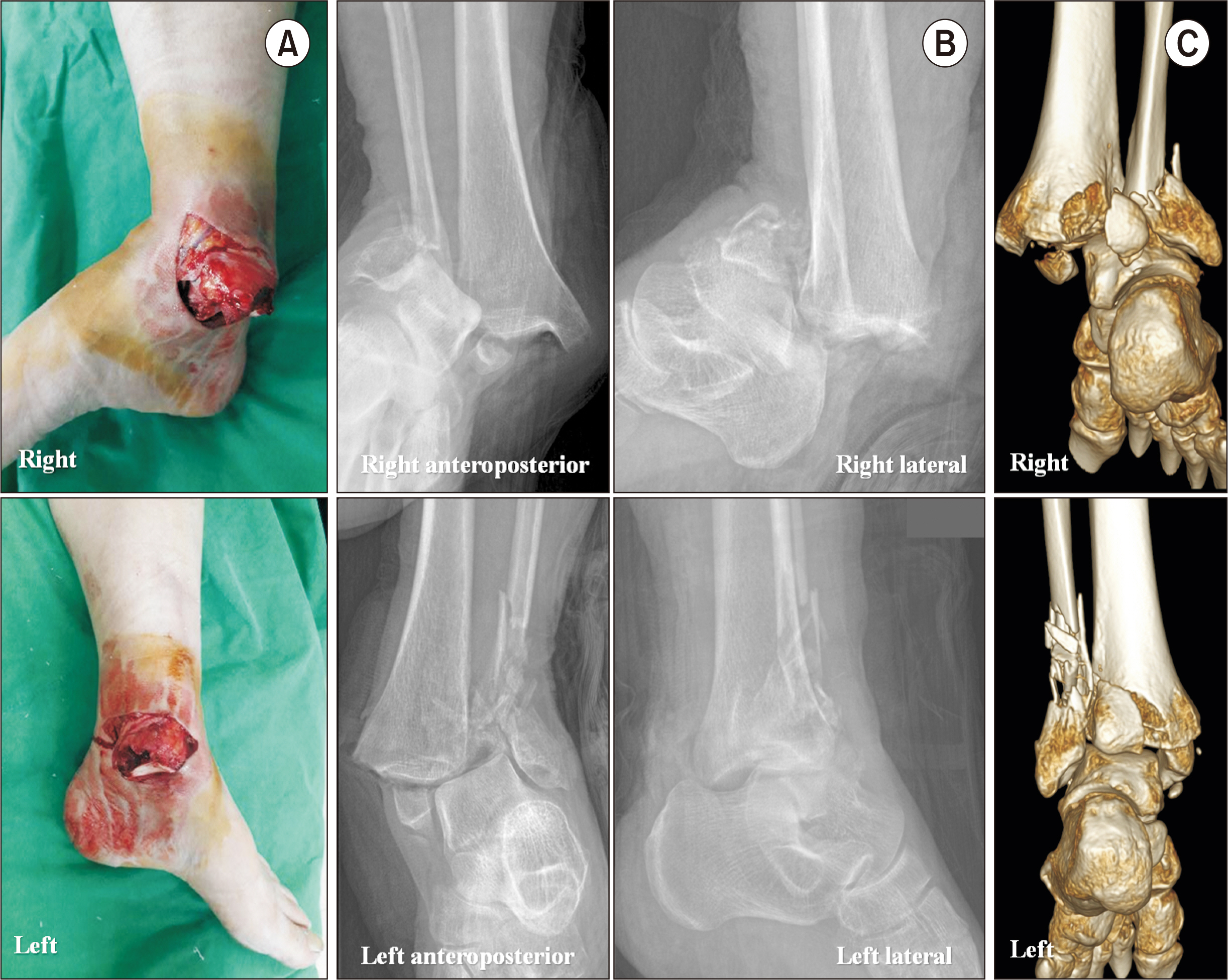
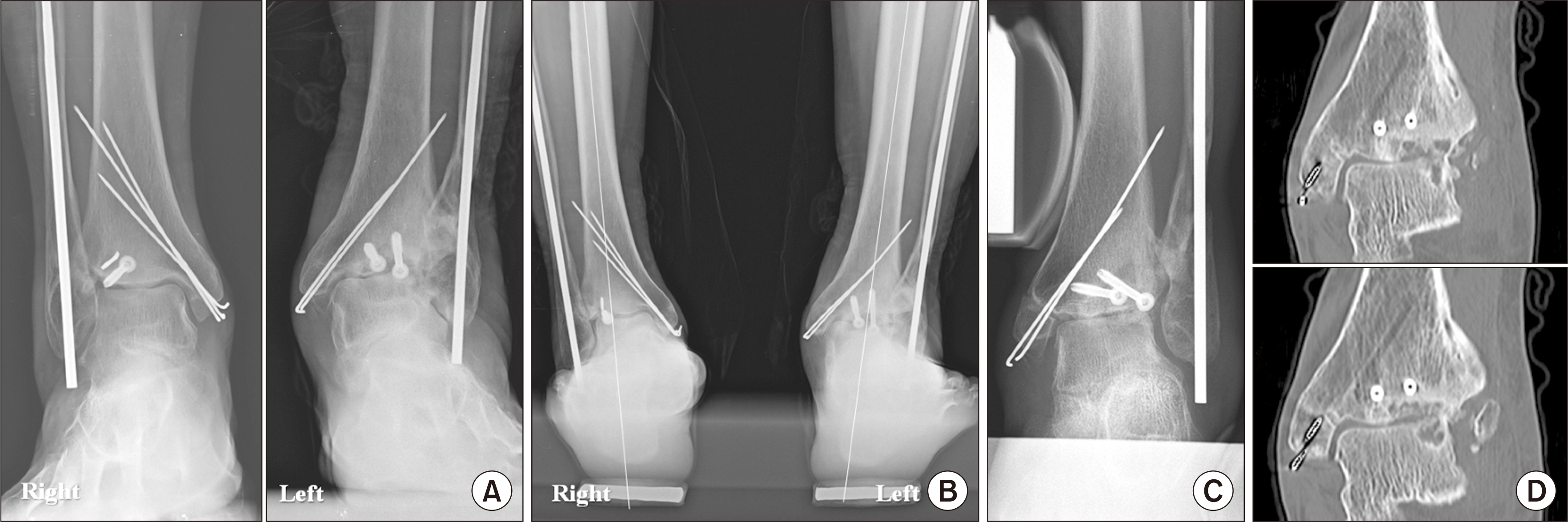
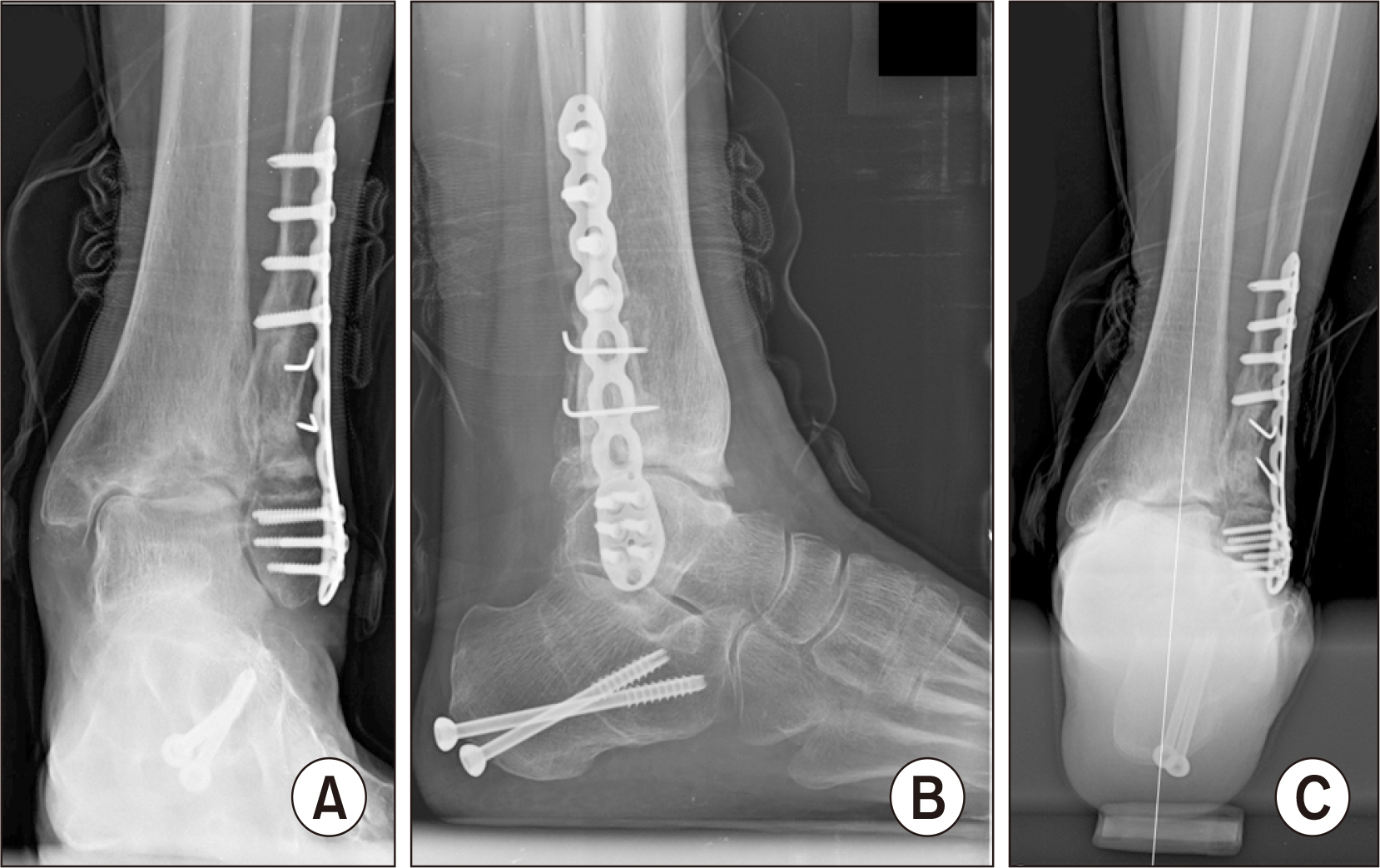
- Past research has reported that the common causes of ankle arthritis include trauma, congenital deformity, and degeneration. Among them, fracture-induced post-traumatic arthritis is most common. For patients with ankle fractures, an anatomical reduction is performed through surgical treatment. However, insufficient reduction or malunion of the fracture site may change the alignment of the ankle joint, resulting in valgus or varus deformities. Currently, most operative options for valgus arthritis aim to either restore joint alignment and/or reduce the uneven load on the cartilage. In this report, we would like to share our clinical experience of a patient with posttraumatic valgus ankle arthritis caused by severely comminuted fracture and dislocation. A satisfactory outcome could be obtained with combined fibular lengthening osteotomy and medial displacement calcaneal osteotomy.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Choi JY, Kim JH, Ko HT, Suh JS. 2015; Single oblique posterolateral approach for open reduction and internal fixation of posterior malleolar fractures with an associated lateral malleolar fracture. J Foot Ankle Surg. 54:559–64. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2014.09.043. DOI: 10.1053/j.jfas.2014.09.043. PMID: 25459093.2. Barg A, Pagenstert GI, Leumann AG, Müller AM, Henninger HB, Valderrabano V. 2012; Treatment of the arthritic valgus ankle. Foot Ankle Clin. 17:647–63. doi: 10.1016/j.fcl.2012.08.007. DOI: 10.1016/j.fcl.2012.08.007. PMID: 23158375.
Article3. Gómez-Palomo JM, Martínez-Crespo A, Rodríguez-Delourme I, García-Pérez JR, Martínez-Espinosa M, Montañez-Heredia E. 2020; Fibular-lengthening osteotomy in patient with progressive valgus deformity after an ankle fracture. Am J Case Rep. 21:e920460. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.920460. DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.920460. PMID: 32047142. PMCID: PMC7038640.
Article4. Weber D, Friederich NF, Müller W. 1998; Lengthening osteotomy of the fibula for post-traumatic malunion. Indications, technique and results. Int Orthop. 22:149–52. doi: 10.1007/s002640050229. DOI: 10.1007/s002640050229. PMID: 9728305. PMCID: PMC3619596.5. Bluman EM, Chiodo CP. 2008; Valgus ankle deformity and arthritis. Foot Ankle Clin. 13:443–70. ixdoi: 10.1016/j.fcl.2008.04.008. DOI: 10.1016/j.fcl.2008.04.008. PMID: 18692009.
Article6. Knupp M, Stufkens SA, Bolliger L, Barg A, Hintermann B. 2011; Classification and treatment of supramalleolar deformities. Foot Ankle Int. 32:1023–31. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2011.1023. DOI: 10.3113/FAI.2011.1023. PMID: 22338950.
Article7. Kim J, Kim JB, Lee WC. 2021; Outcomes of joint preservation surgery in valgus ankle arthritis without deltoid ligament insufficiency. Foot Ankle Int. 42:1419–30. doi: 10.1177/10711007211016001. DOI: 10.1177/10711007211016001. PMID: 34109853.
Article8. Brilhault J. 2022; Calcaneal osteotomy for hindfoot deformity. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 108(1S):103121. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2021.103121. DOI: 10.1016/j.otsr.2021.103121. PMID: 34687951.
Article9. Schon LC, de Cesar Netto C, Day J, Deland JT, Hintermann B, Johnson JE, et al. 2020; Consensus for the indication of a medializing displacement calcaneal osteotomy in the treatment of progressive collapsing foot deformity. Foot Ankle Int. 41:1282–5. doi: 10.1177/1071100720950747. DOI: 10.1177/1071100720950747. PMID: 32844661.
Article10. Ju DG, Debbi EM, Neustein AZ, Moon CN. 2019; Fibular lengthening osteotomy with revision syndesmotic repair for ankle fracture malunion. J Orthop Trauma. 33 Suppl 1:S38–9. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000001534. DOI: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000001534. PMID: 31290833.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pseudoaneurysm after Proximal Metatarsal Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus Correction: A Case Report
- Operative Treatment for Fibular Shortening after Trauma: A Case Report
- High Tibial Osteotomy With Fibular Shaft Osteotomy
- Surgical treatments of the ankle arthritis
- Hindfoot Alignment Change after High Tibial Valgization Osteotomy in a Patient with an Ipsilateral Fused Ankle: A Case Report