Neonatal Med.
2022 Aug;29(3):117-122. 10.5385/nm.2022.29.3.117.
Case Series of Isolated Deep Gray Matter Injuries in Preterm Infants
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Children’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2533094
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5385/nm.2022.29.3.117
Abstract
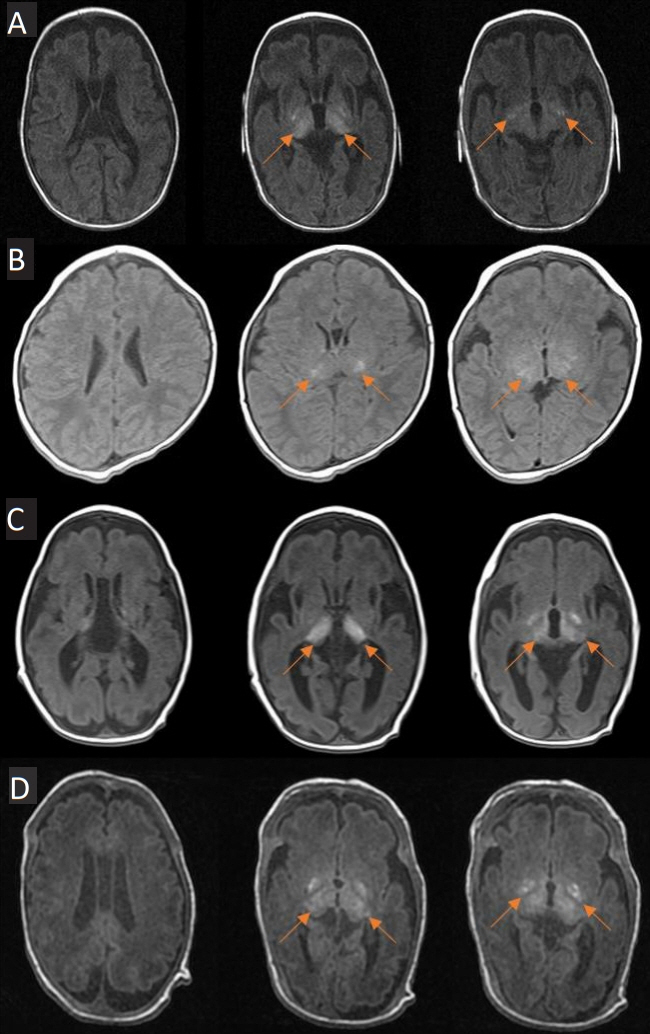
- Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates is an important cause of brain damage that leads to severe neurological sequelae or death. Brain injury patterns on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are used to predict neurodevelopmental outcome severity. This case series describes the clinical manifestations and neurologic outcomes of four preterm infants with isolated deep gray matter injuries. Basal ganglia and thalamic lesions were noted without white matter and cerebral cortex lesion on brain MRI. All patients were preterm infants born at less than 33 weeks’ gestation and required resuscitation in the delivery room. All had seizures during the neonatal period requiring anti-seizure medications. Severe neurologic disability was identified in three patients using neurodevelopmental assessment tools. Another patient has not been evaluated with assessment tools yet as he was 2 months’ corrected age, but he was supported by home ventilation via a tracheostomy due to insufficient self-respiration. This case series demonstrates that isolated deep gray matter injuries in preterm infants could predict severe neurodevelopmental outcomes.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schmidt JW, Walsh WF. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in preterm infants. J Neonatal Perinat Med. 2010; 3:277–84.2. Chalak LF, Rollins N, Morriss MC, Brion LP, Heyne R, Sanchez PJ. Perinatal acidosis and hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in preterm infants of 33 to 35 weeks’ gestation. J Pediatr. 2012; 160:388–94.3. Lawn JE, Cousens S, Zupan J; Lancet Neonatal Survival Steering Team. 4 Million neonatal deaths: when? where? why? Lancet. 2005; 365:891–900.4. Shankaran S, Laptook AR, McDonald SA, Hintz SR, Barnes PD, Das A, et al. Acute perinatal sentinel events, neonatal brain injury pattern, and outcome of infants undergoing a trial of hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Pediatr. 2017; 180:275–8.5. Shankaran S, Barnes PD, Hintz SR, Laptook AR, Zaterka-Baxter KM, McDonald SA, et al. Brain injury following trial of hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2012; 97:F398–404.6. Jacobs SE, Berg M, Hunt R, Tarnow-Mordi WO, Inder TE, Davis PG. Cooling for newborns with hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013; 2013:CD003311.7. Utter AA, Basso MA. The basal ganglia: an overview of circuits and function. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2008; 32:333–42.8. Nelson AB, Kreitzer AC. Reassessing models of basal ganglia function and dysfunction. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2014; 37:117–35.9. Martinez-Biarge M, Diez-Sebastian J, Rutherford MA, Cowan FM. Outcomes after central grey matter injury in term perinatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Early Hum Dev. 2010; 86:675–82.10. Miller SP, Ramaswamy V, Michelson D, Barkovich AJ, Holshouser B, Wycliffe N, et al. Patterns of brain injury in term neonatal encephalopathy. J Pediatr. 2005; 146:453–60.11. Martinez-Biarge M, Diez-Sebastian J, Kapellou O, Gindner D, Allsop JM, Rutherford MA, et al. Predicting motor outcome and death in term hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Neurology. 2011; 76:2055–61.12. Rutherford MA, Pennock JM, Counsell SJ, Mercuri E, Cowan FM, Dubowitz LM, et al. Abnormal magnetic resonance signal in the internal capsule predicts poor neurodevelopmental outcome in infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 1998; 102(2 Pt 1):323–8.13. Logitharajah P, Rutherford MA, Cowan FM. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in preterm infants: antecedent factors, brain imaging, and outcome. Pediatr Res. 2009; 66:222–9.14. Inder TE, Perlman JM, Volpe JJ. Preterm intraventricular hemorrhage/posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus. In : Volpe JJ, Inder TE, Darras BT, de Vries LS, du Plessis AJ, Neil J, editors. Volpe's Neurology of the Newborn. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier;2018. p. 637–98.e21.15. Martinez-Biarge M, Bregant T, Wusthoff CJ, Chew AT, Diez-Sebastian J, Rutherford MA, et al. White matter and cortical injury in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: antecedent factors and 2-year outcome. J Pediatr. 2012; 161:799–807.16. Okereafor A, Allsop J, Counsell SJ, Fitzpatrick J, Azzopardi D, Rutherford MA, et al. Patterns of brain injury in neonates exposed to perinatal sentinel events. Pediatrics. 2008; 121:906–14.17. Jeong SY, Choi SY, Chang YP, Lee YS. Neurodevelopmental outcomes according to brain injury patterns in neonates with postasphyxial hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Neonatal Med. 2017; 24:32–9.18. Gopagondanahalli KR, Li J, Fahey MC, Hunt RW, Jenkin G, Miller SL, et al. Preterm hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Front Pediatr. 2016; 4:114.19. Chao CP, Zaleski CG, Patton AC. Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: multimodality imaging findings. Radiographics. 2006; 26 Suppl 1:S159–72.20. Borch K, Greisen G. Blood flow distribution in the normal human preterm brain. Pediatr Res. 1998; 43:28–33.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Perinatal Hypoxic-lschemic Brain Injury: MR Findings
- Prevention and Therapeutic Strategies for Brain Injury in Extreme Prematurity
- Diffusion Tensor Imaging of Heterotopia: Changes of Fractional Anisotropy during Radial Migration of Neurons
- MR findings in Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis in Children
- Chronological Changes of the Signal Intensities of White Matter on the FLAIR Images of Infants