Hanyang Med Rev.
2009 Nov;29(4):370-378. 10.7599/hmr.2009.29.4.370.
Prevention and Therapeutic Strategies for Brain Injury in Extreme Prematurity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea. neopark@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2053724
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7599/hmr.2009.29.4.370
Abstract
- As the evolution of neonatal intensive care has resulted in dramatic improvements in the survival of extremely preterm infants, there is major concern about the increasing rates of neurodisability among those at the limits of viability. Among the infants with parenchymal brain injury such as intraventricular hemorrhage grades III-IV, ventriculomegaly and cystic periventricular leukomalacia, more than 1 out of 3 have one of the cerebral palsy syndrome. However, research examining neuroprotection for brain injury in extremely preterm infants is limited. This review was focused on brain injury and recent strategies for neuroprotection addressing both white matter injury and gray matter dysfunction in infants born <26 weeks' gestation and/or with birth weight less than 750 g.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bloom RS, Boyle D, Kattwinkel J. Textbook of neonatal resuscitation. Elk Grove Village, U.S.A.: American Academy of Pediatrics;2006.2. Wilson-Costello D, Friedman H, Minich N, Siner B, Taylor G, Schluchter M, Hack M. Improved neurodevelopmental outcomes for extremely low birth weight infants in 2000-2002. Pediatrics. 2007; 119:37–45.
Article3. Anderson PJ, Doyle LW. Cognitive and educational deficits in children born extremely preterm. Semin Perinatol. 2008; 32:51–58.
Article4. Tommiska V, Heinonen K, Lehtonen L, Renlund M, Saarela T, Tammela O, Virtanen M, Fellman V. No improvement in outcome of nationwide extremely low birth weight infant populations between 1996-1997 and 1999-2000. Pediatrics. 2007; 119:29–36.
Article5. Hintz SR, Kendrick DE, Vohr BR, Poole WK, Higgins RD. Changes in neurodevelopmental outcomes at 18 to 22 months' corrected age among infants of less than 25 weeks' gestational age born in 1993-1999. Pediatrics. 2005; 115:1645–1651.
Article6. Msall ME. The limits of viability and the uncertainty of neuroprotection: challenges in optimizing outcomes in extreme prematurity. Pediatrics. 2007; 119:158–160.
Article7. Volpe JJ. Brain injury in premature infants: a complex amalgam of destructive and developmental disturbances. Lancet Neurol. 2009; 8:110–124.
Article8. Khwaja O, Volpe JJ. Pathogenesis of cerebral white matter injury of prematurity. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2008; 93:F153–F161.
Article9. Murata Y, Itakura A, Matsuzawa K, Okumura A, Wakai K, Mizutani S. Possible antenatal and perinatal related factors in development of cystic periventricular leukomalacia. Brain Dev. 2005; 27:17–21.
Article10. Ajayi-Obe M, Saeed N, Cowan FM, Rutherford MA, Edwards AD. Reduced development of cerebral cortex in extremely preterm infants. Lancet. 2000; 356:1162–1163.
Article11. Inder TE, Wells SJ, Mogridge NB, Spencer C, Volpe JJ. Defining the nature of the cerebral abnormalities in the premature infant: a qualitative magnetic resonance imaging study. J Pediatr. 2003; 143:171–179.
Article12. Dyet LE, Kennea N, Counsell SJ, Maalouf EF, Ajayi-Obe M, Duggan PJ, Harrison M, Allsop JM, Hajnal J, Herlihy AH, Edwards B, Laroche S, Cowan FM, Rutherford MA, Edwards AD. Natural history of brain lesions in extremely preterm infants studied with serial magnetic resonance imaging from birth and neurodevelopmental assessment. Pediatrics. 2006; 118:536–548.
Article13. Horsch S, Hallberg B, Leifsdottir K, Skiold B, Nagy Z, Mosskin M, Blennow M, Aden U. Brain abnormalities in extremely low gestational age infants: a Swedish population based MRI study. Acta Paediatr. 2007; 96:979–984.
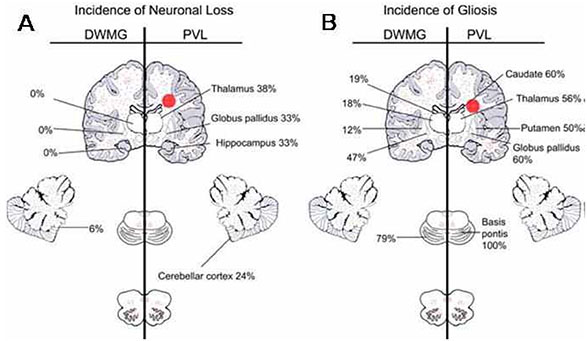
Article14. Pierson CR, Folkerth RD, Billiards SS, Trachtenberg FL, Drinkwater ME, Volpe JJ, Kinney HC. Gray matter injury associated with periventricular leukomalacia in the premature infant. Acta Neuropathol. 2007; 114:619–631.
Article15. Wilson-Costello D, Friedman H, Minich N, Fanaroff AA, Hack M. Improved survival rates with increased neurodevelopmental disability for extremely low birth weight infants in the 1990s. Pediatrics. 2005; 115:997–1003.
Article16. Chan K, Ohlsson A, Synnes A, Lee DS, Chien LY, Lee SK. Survival, morbidity, and resource use of infants of 25 weeks' gestational age or less. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001; 185:220–226.
Article17. Vanhaesebrouck P, Allegaert K, Bottu J, Debauche C, Devlieger H, Docx M, Francois A, Haumont D, Lombet J, Rigo J, Smets K, Vanherreweghe I, Van Overmeire B, Van Reempts P. The EPIBEL study: outcomes to discharge from hospital for extremely preterm infants in Belgium. Pediatrics. 2004; 114:663–675.
Article18. Lorenz JM. The outcome of extreme prematurity. Semin Perinatol. 2001; 25:348–359.
Article19. Costeloe K, Hennessy E, Gibson AT, Marlow N, Wilkinson AR. The EPICure study: outcomes to discharge from hospital for infants born at the threshold of viability. Pediatrics. 2000; 106:659–671.
Article20. Volpe JJ. Neurology of the newborn. 5th ed. Philadelphia, U.S.A.: Saunders/Elsevier;2008.21. Jensen FE. The role of glutamate receptor maturation in perinatal seizures and brain injury. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2002; 20:339–347.
Article22. Jensen FE. Developmental factors regulating susceptibility to perinatal brain injury and seizures. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2006; 18:628–633.
Article23. Dammann O, Leviton A. Inflammatory brain damage in preterm newborns--dry numbers, wet lab, and causal inferences. Early Human Development. 2004; 79:1–15.
Article24. Talos DM, Fishman RE, Park H, Folkerth RD, Follett PL, Volpe JJ, Jensen FE. Developmental regulation of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid receptor subunit expression in forebrain and relationship to regional susceptibility to hypoxic/ischemic injury. I. Rodent cerebral white matter and cortex. J Comp Neurol. 2006; 497:42–60.
Article25. Talos DM, Follett PL, Folkerth RD, Fishman RE, Trachtenberg FL, Volpe JJ, Jensen FE. Developmental regulation of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid receptor subunit expression in forebrain and relationship to regional susceptibility to hypoxic/ischemic injury. II. Human cerebral white matter and cortex. J Comp Neurol. 2006; 497:61–77.
Article26. Patra K, Wilson-Costello D, Taylor HG, Mercuri-Minich N, Hack M. Grades I-II intraventricular hemorrhage in extremely low birth weight infants: Effects on neurodevelopment. J Pediatr. 2006; 149:169–173.
Article27. deRegnier RA. Neurophysiologic evaluation of brain function in extremely premature newborn infants. Semin Perinatol. 2008; 32:2–10.
Article28. Wikstrom S, Ley D, Hansen-Pupp I, Rosen I, Hellstrom-Westas L. Early amplitude-integrated EEG correlates with cord TNF-alpha and brain injury in very preterm infants. Acta Paediatr. 2008; 97:915–919.29. Volpe JJ. Electroencephalography May Provide Insight Into Timing of Premature Brain Injury. Pediatrics. 2009; 124:e542–e544.
Article30. Hatzidaki E, Giahnakis E, Maraka S, Korakaki E, Manoura A, Saitakis E, Papamastoraki I, Margari KM, Giannakopoulou C. Risk factors for periventricular leukomalacia. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2009; 88:110–115.
Article31. Volpe JJ. Postnatal sepsis, necrotizing entercolitis, and the critical role of systemic inflammation in white matter injury in premature infants. J Pediatr. 2008; 153:160–163.
Article32. Laptook AR. Use of therapeutic hypothermia for term infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2009; 56:601–616.
Article33. Schmidt B, Davis P, Moddemann D, Ohlsson A, Roberts RS, Saigal S, Solimano A, Vincer M, Wright LL. Long-term effects of indomethacin prophylaxis in extremely-low-birth-weight infants. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:1966–1972.
Article34. Doyle LW, Crowther CA, Middleton P, Marret S. Antenatal magnesium sulfate and neurologic outcome in preterm infants: A systematic review. Obstet Gynecol. 2009; 113:1327–1333.
Article35. Juul SE, McPherson RJ, Bauer LA, Ledbetter KJ, Gleason CA, Mayock DE. A phase I/II trial of high-dose erythropoietin in extremely low birth weight infants: pharmacokinetics and safety. Pediatrics. 2008; 122:383–391.
Article36. Follett PL, Rosenberg PA, Volpe JJ, Jensen FE. NBQX attenuates excitotoxic injury in developing white matter. J Neurosci. 2000; 20:9235–9241.
Article37. Manning SM, Talos DM, Zhou C, Selip DB, Park HK, Park CJ, Volpe JJ, Jensen FE. NMDA receptor blockade with memantine attenuates white matter injury in a rat model of periventricular leukomalacia. J Neurosci. 2008; 28:6670–6678.
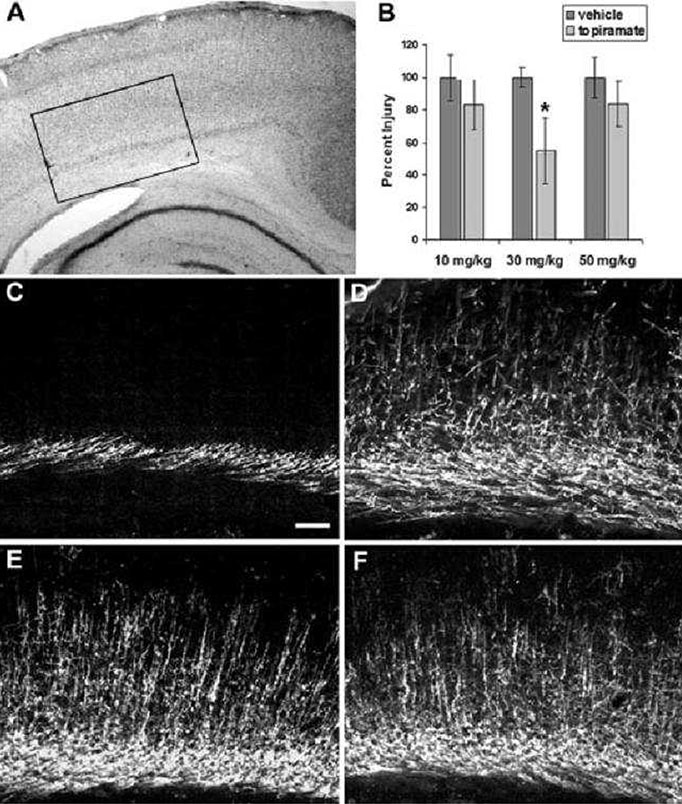
Article38. Follett PL, Deng W, Dai W, Talos DM, Massillon LJ, Rosenberg PA, Volpe JJ, Jensen FE. Glutamate receptor-mediated oligodendrocyte toxicity in periventricular leukomalacia: A protective role for topiramate. J Neurosci. 2004; 24:4412–4420.
Article39. Haynes RL, Baud O, Li J, Kinney HC, Volpe JJ, Folkerth DR. Oxidative and nitrative injury in periventricular leukomalacia: a review. Brain Pathol. 2005; 15:225–233.
Article40. Lechpammer M, Manning SM, Samonte F, Nelligan J, Sabo E, Talos DM, Volpe JJ, Jensen FE. Minocycline treatment following hypoxic/ischaemic injury attenuates white matter injury in a rodent model of periventricular leucomalacia. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2008; 34:379–393.
Article41. Gerstner B, DeSilva TM, Genz K, Armstrong A, Brehmer F, Neve RL, Felderhoff-Mueser U, Volpe JJ, Rosenberg PA. Hyperoxia causes maturation-dependent cell death in the developing white matter. J Neurosci. 2008; 28:1236–1245.
Article42. Gerstner B, Sifringer M, Dzietko M, Schuller A, Lee J, Simons S, Obladen M, Volpe JJ, Rosenberg PA, Felderhoff-Mueser U. Estradiol attenuates hyperoxia-induced cell death in the developing white matter. Ann Neurol. 2007; 61:562–573.
Article43. Gerstner B, Lee J, DeSilva TM, Jensen FE, Volpe JJ, Rosenberg PA. 17beta-estradiol protects against hypoxic/ischemic white matter damage in the neonatal rat brain. J Neurosci Res. 2009; 87:2078–2086.
Article44. Msall ME, Park JJ. The spectrum of behavioral outcomes after extreme prematurity: regulatory, attention, social, and adaptive dimensions. Semin Perinatol. 2008; 32:42–50.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cardiovascular Management for the Prevention of Insult on the Central Nervous System in Prematurity
- White Matter Injury of Prematurity: Its Mechanisms and Clinical Features
- Brain and Lung: Lung Injury in Patients with Brain Injury
- Perinatal Hypoxic-lschemic Brain Injury: MR Findings
- Possible Prevention of Neonatal Death: A Regional Population-Based Study in Japan