Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2022 Aug;15(3):273-282. 10.21053/ceo.2022.00206.
Induction of the BRAFV600E Mutation in Thyroid Cells Leads to Frequent Hypermethylation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Inha University Hospital, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- 2Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Transdisciplinary Department of Medicine and Advanced Technology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- KMID: 2532991
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2022.00206
Abstract
Objectives
. The BRAFV600E mutation is a major driver mutation in papillary thyroid cancer. The aim of this study was to elucidate the correlation between DNA methylation and gene expression changes induced by the BRAFV600E mutation in thyroid cells.
Methods
. We used Nthy/BRAF cell lines generated by transfection of Nthy/ori cells with the wild-type BRAF gene (Nthy/WT cells) and the V600E mutant-type BRAF gene (Nthy/V600E cells). We performed gene expression microarray and DNA methylation array analyses for Nthy/WT and Nthy/V600E cells. Two types of array data were integrated to identify inverse correlations between methylation and gene expression. The results were verified in silico using data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and in vivo through pyrosequencing and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
Results
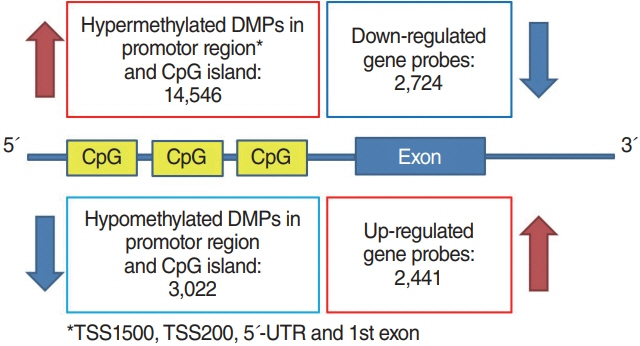
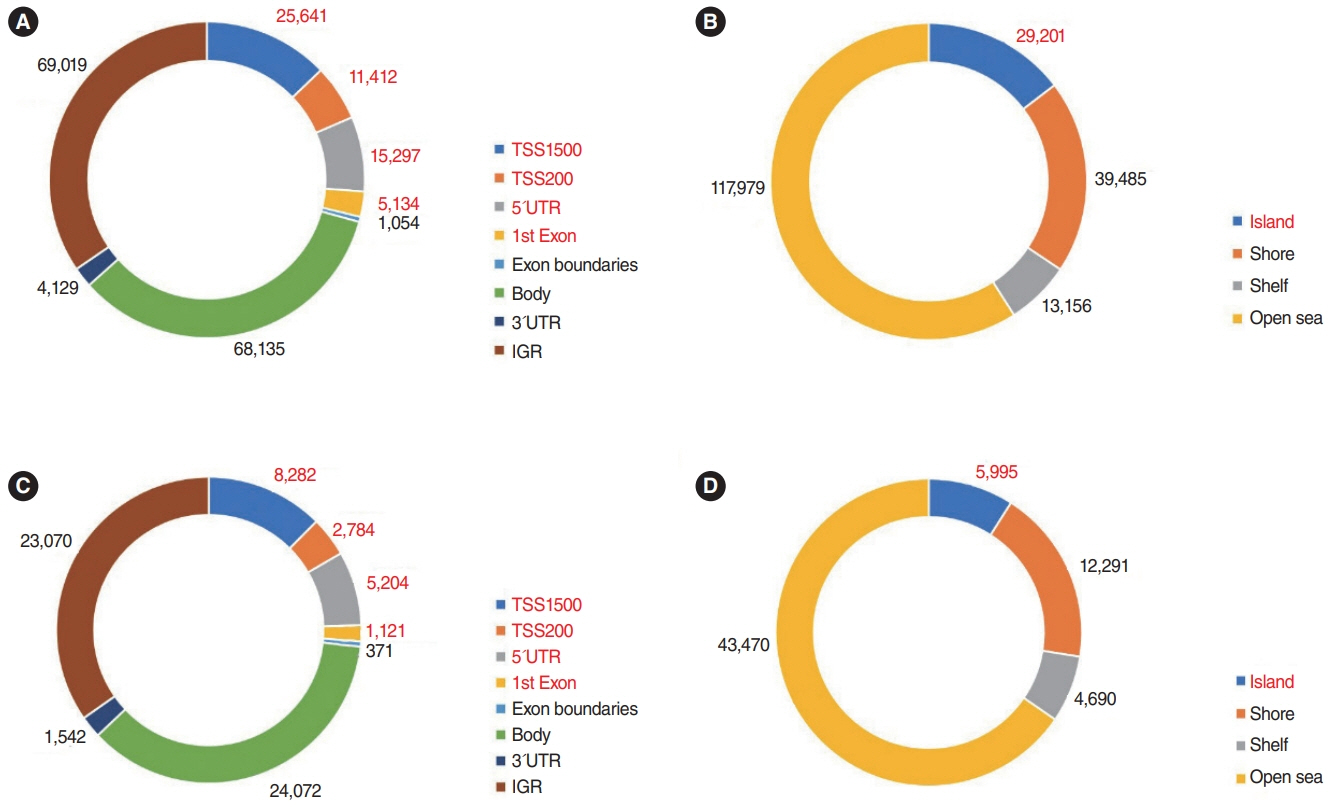
. In the Nthy/V600E cells, 199,821 probes were significantly hypermethylated, and 697 genes showed a “hypermethylation-downregulation” pattern in Nthy/V600E. Tumor suppressor genes and apoptosis-related genes were included. In total, 66,446 probes were significantly hypomethylated, and 227 genes showed a “hypomethylation-upregulation” pattern in Nthy/V600E cells. Protooncogenes and developmental protein-coding genes were included. In the TCGA analysis, 491/697 (70.44%) genes showed a hypermethylation-downregulation pattern, and 153/227 (67.40%) genes showed a hypomethylation-upregulation pattern. Ten selected genes showed a similar methylation-gene expression pattern in pyrosequencing and qRT-PCR.
Conclusion
. Induction of the BRAFV600E mutation in thyroid cells led to frequent hypermethylation. Anticancer genes, such as those involved in tumor suppression or apoptosis, were downregulated by upstream hypermethylation, whereas carcinogenic genes, such as protooncogenes, were upregulated by hypomethylation. Our results suggest that the BRAFV600E mutation in thyroid cells modulates DNA methylation and results in cancer-related gene expression.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Mitochondrial Ribosomal Protein L14 Promotes Cell Growth and Invasion by Modulating Reactive Oxygen Species in Thyroid Cancer
Hae Jong Kim, Quoc Khanh Nguyen, Seung-Nam Jung, Mi Ae Lim, Chan Oh, Yudan Piao, YanLi Jin, Ju-Hui Kim, Young Il Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Jae Won Chang, Ho-Ryun Won, Bon Seok Koo
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2023;16(2):184-197. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2022.01760.
Reference
-
1. Kitahara CM, Sosa JA. The changing incidence of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016; Nov. 12(11):646–53.2. Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Lee ES; Community of PopulationBased Regional Cancer Registries. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2015. Cancer Res Treat. 2018; Apr. 50(2):303–16.3. Xing M. BRAF mutation in thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005; Jun. 12(2):245–62.4. Li C, Lee KC, Schneider EB, Zeiger MA. BRAF V600E mutation and its association with clinicopathological features of papillary thyroid cancer: a meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012; Dec. 97(12):4559–70.5. Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic characterization of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell. 2014; Oct. 159(3):676–90.6. Faam B, Ghaffari MA, Ghadiri A, Azizi F. Epigenetic modifications in human thyroid cancer. Biomed Rep. 2015; Jan. 3(1):3–8.7. Bird A. DNA methylation patterns and epigenetic memory. Genes Dev. 2002; Jan. 16(1):6–21.8. Xing M. Gene methylation in thyroid tumorigenesis. Endocrinology. 2007; Mar. 148(3):948–53.9. Chen YC, Gotea V, Margolin G, Elnitski L. Significant associations between driver gene mutations and DNA methylation alterations across many cancer types. PLoS Comput Biol. 2017; Nov. 13(11):e1005840.10. Ellis RJ, Wang Y, Stevenson HS, Boufraqech M, Patel D, Nilubol N, et al. Genome-wide methylation patterns in papillary thyroid cancer are distinct based on histological subtype and tumor genotype. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; Feb. 99(2):E329–37.11. Beltrami CM, Dos Reis MB, Barros-Filho MC, Marchi FA, Kuasne H, Pinto CA, et al. Integrated data analysis reveals potential drivers and pathways disrupted by DNA methylation in papillary thyroid carcinomas. Clin Epigenetics. 2017; May. 9:45.12. Kikuchi Y, Tsuji E, Yagi K, Matsusaka K, Tsuji S, Kurebayashi J, et al. Aberrantly methylated genes in human papillary thyroid cancer and their association with BRAF/RAS mutation. Front Genet. 2013; Dec. 4:271.13. White MG, Nagar S, Aschebrook-Kilfoy B, Jasmine F, Kibriya MG, Ahsan H, et al. Epigenetic alterations and canonical pathway disruption in papillary thyroid cancer: a genome-wide methylation analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016; Jul. 23(7):2302–9.14. Hou P, Liu D, Xing M. Genome-wide alterations in gene methylation by the BRAF V600E mutation in papillary thyroid cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2011; Nov. 18(6):687–97.15. Ozer B, Sezerman OU. A novel analysis strategy for integrating methylation and expression data reveals core pathways for thyroid cancer aetiology. BMC Genomics. 2015; 16(Suppl 12):S7.16. Saiselet M, Floor S, Tarabichi M, Dom G, Hebrant A, van Staveren WC, et al. Thyroid cancer cell lines: an overview. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2012; Nov. 3:133.17. Kim BA, Jee HG, Yi JW, Kim SJ, Chai YJ, Choi JY, et al. Expression profiling of a human thyroid cell line stably expressing the BRAFV600E mutation. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2017; Jan. 14(1):53–67.18. Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW, Shi W, et al. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015; Apr. 43(7):e47.19. Morris TJ, Butcher LM, Feber A, Teschendorff AE, Chakravarthy AR, Wojdacz TK, et al. ChAMP: 450k chip analysis methylation pipeline. Bioinformatics. 2014; Feb. 30(3):428–30.20. Nikiforova MN, Kimura ET, Gandhi M, Biddinger PW, Knauf JA, Basolo F, et al. BRAF mutations in thyroid tumors are restricted to papillary carcinomas and anaplastic or poorly differentiated carcinomas arising from papillary carcinomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003; Nov. 88(11):5399–404.21. Hilger RA, Scheulen ME, Strumberg D. The Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway in the treatment of cancer. Onkologie. 2002; Dec. 25(6):511–8.22. Peyssonnaux C, Eychene A. The Raf/MEK/ERK pathway: new concepts of activation. Biol Cell. 2001; Sep. 93(1-2):53–62.23. Giordano TJ, Kuick R, Thomas DG, Misek DE, Vinco M, Sanders D, et al. Molecular classification of papillary thyroid carcinoma: distinct BRAF, RAS, and RET/PTC mutation-specific gene expression profiles discovered by DNA microarray analysis. Oncogene. 2005; Oct. 24(44):6646–56.24. Yoo SK, Lee S, Kim SJ, Jee HG, Kim BA, Cho H, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the transcriptional and mutational landscape of follicular and papillary thyroid cancers. PLoS Genet. 2016; Aug. 12(8):e1006239.25. Jones PA, Baylin SB. The epigenomics of cancer. Cell. 2007; Feb. 128(4):683–92.26. Lee EK, Chung KW, Yang SK, Park MJ, Min HS, Kim SW, et al. DNA methylation of MAPK signal-inhibiting genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2013; Nov. 33(11):4833–9.27. Rodriguez-Rodero S, Fernandez AF, Fernandez-Morera JL, CastroSantos P, Bayon GF, Ferrero C, et al. DNA methylation signatures identify biologically distinct thyroid cancer subtypes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; Jul. 98(7):2811–21.28. Cai LL, Liu GY, Tzeng CM. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling and its involved molecular pathways from one individual with thyroid malignant/benign tumor and hyperplasia: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; Aug. 95(35):e4695.29. Noreen F, Kung T, Tornillo L, Parker H, Silva M, Weis S, et al. DNA methylation instability by BRAF-mediated TET silencing and lifestyle-exposure divides colon cancer pathways. Clin Epigenetics. 2019; Dec. 11(1):196.30. Fang M, Ou J, Hutchinson L, Green MR. The BRAF oncoprotein functions through the transcriptional repressor MAFG to mediate the CpG Island Methylator phenotype. Mol Cell. 2014; Sep. 55(6):904–15.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Implication of BRAF Mutation in Thyroid Cancer
- Clinicopathological Implications of the BRAF(V600E) Mutation in PTC with Concurrent Hashimoto Thyroiditis
- Association of BRAF(V600E) Mutation with Poor Clinical Prognostic Factors and Ultrasonographic Findings in Cases of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Expressions of miRNAs in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Their Associations with the BRAFV600EMutation and Clinicopathological Features.
- Relation between RASSF1A Methylation and BRAF Mutation in Thyroid Tumor