J Pathol Transl Med.
2022 Jul;56(4):205-211. 10.4132/jptm.2022.04.22.
EGFL7 expression profile in IDH-wildtype glioblastomas is associated with poor patient outcome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Molecular Oncology Research Center, Barretos Cancer Hospital, Barretos, São Paulo, Brazil
- 2Barretos School of Health Sciences, Dr. Paulo Prata – FACISB, Barretos, São Paulo, Brazil
- 3The Ohio State University, Department of Radiation Oncology, Columbus, OH, USA
- 4Department of Pathology, School of Medicine of Ribeirao Preto, University of Sao Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Sao Paulo, Brazil
- 5UNESP – Univ. Estadual Paulista, School of Medicine, Department of Pathology, Botucatu, São Paulo, Brazil
- 6Department of Neurosurgery, Barretos Cancer Hospital, Barretos, São Paulo, Brazil
- 7Department of Pathology, Barretos Cancer Hospital, Barretos, São Paulo, Brazil
- 8Life and Health Sciences Research Institute (ICVS), School of Medicine, University of Minho, Braga, Portugal
- 9ICVS/3B’s – PT Government Associate Laboratory, Braga/Guimarães, Portugal
- KMID: 2531612
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.04.22
Abstract
- Background
Despite the advances in glioblastoma (GBM) treatment, the average life span of patients is 14 months. Therefore, it is urgent to identity biomarkers of prognosis, treatment response, or development of novel treatment strategies. We previously described the association of high epidermal growth factor-like domain multiple 7 (EGFL7) expression and unfavorable outcome of pilocytic astrocytoma patients. The present study aims to analyze the prognostic potential of EGFL7 in GBM isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH)-wildtype, using immunohistochemistry and in silico approaches.
Methods
Spearman’s correlation analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas RNA sequencing data was performed. The genes strongly correlated to EGFL7 expression were submitted to enrichment gene ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis. Additionally, EGFL7 expression was associated with patient overall survival. The expression of EGFL7 was analyzed through immunohistochemistry in 74 GBM IDH-wildtype patients’ samples, and was associated with clinicopathological data and overall survival.
Results
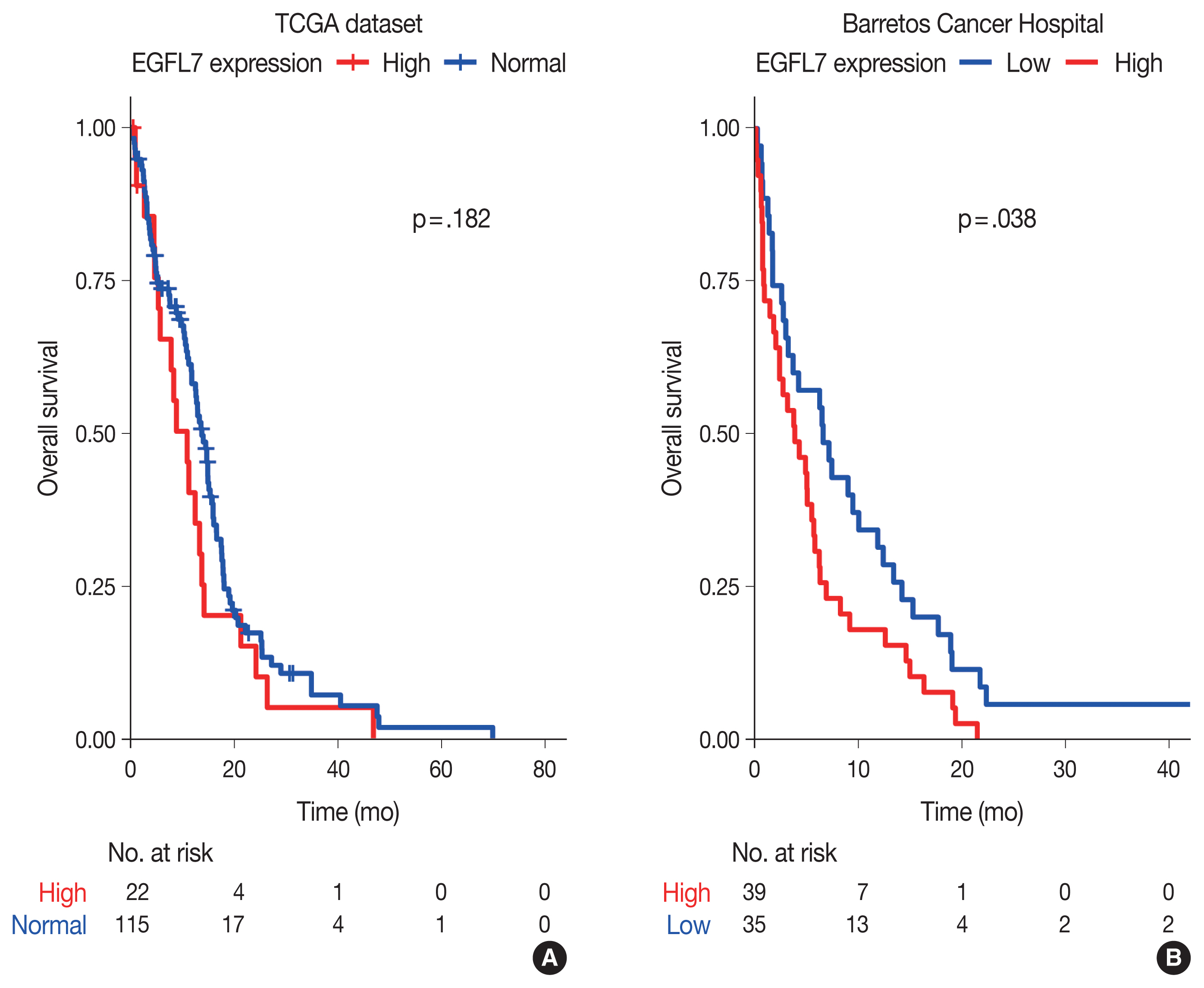
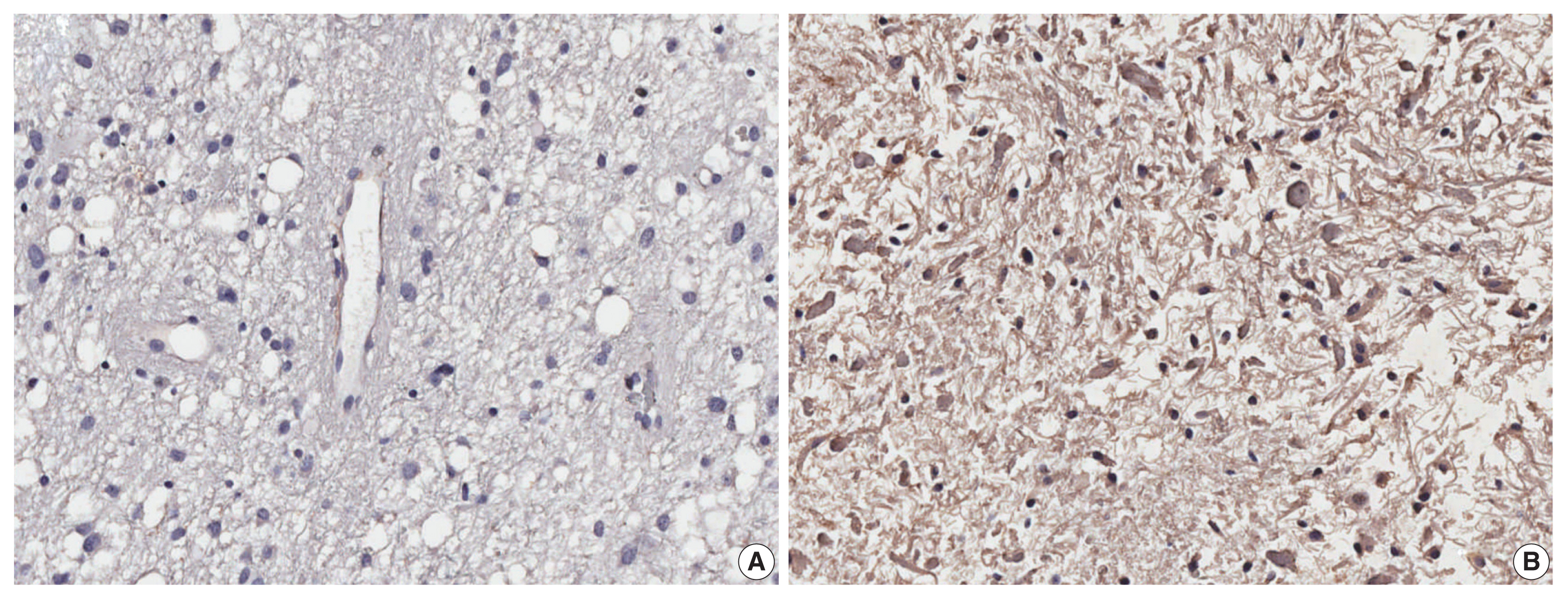
In silico analysis found 78 genes strongly correlated to EGFL7 expression. These genes were enriched in 40 biological processes and eight KEGG pathways, including angiogenesis/vasculogenesis, cell adhesion, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase–Akt, Notch, and Rap1 signaling pathways. The immunostaining showed high EGFL7 expression in 39 cases (52.7%). High immunolabelling was significantly associated with low Karnofsky Performance Status and poor overall survival. Cox analysis showed that GBMs IDH-wildtype with high EGFL7 expression presented a higher risk of death compared to low expression (hazard ratio, 1.645; 95% confidence interval, 1.021 to 2.650; p = .041).
Conclusions
This study gives insights regarding the genes that are correlated with EGFL7, as well as biological processes and signaling pathways, which should be further investigated in order to elucidate their role in glioblastoma biology.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board Central nervous system tumours. 5th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer;2021.2. Broniscer A, Gajjar A. Supratentorial high-grade astrocytoma and diffuse brainstem glioma: two challenges for the pediatric oncologist. Oncologist. 2004; 9:197–206.
Article3. Hadjipanayis CG, Van Meir EG. Brain cancer propagating cells: biology, genetics and targeted therapies. Trends Mol Med. 2009; 15:519–30.
Article4. Paugh BS, Qu C, Jones C, et al. Integrated molecular genetic profiling of pediatric high-grade gliomas reveals key differences with the adult disease. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:3061–8.
Article5. Ohgaki H. Epidemiology of brain tumors. Methods Mol Biol. 2009; 472:323–42.
Article6. Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:987–96.
Article7. Richter A, Alexdottir MS, Magnus SH, et al. EGFL7 mediates BMP9-induced sprouting angiogenesis of endothelial cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2019; 12:1250–9.
Article8. Parker LH, Schmidt M, Jin SW, et al. The endothelial-cell-derived secreted factor Egfl7 regulates vascular tube formation. Nature. 2004; 428:754–8.
Article9. Fitch MJ, Campagnolo L, Kuhnert F, Stuhlmann H. Egfl7, a novel epidermal growth factor-domain gene expressed in endothelial cells. Dev Dyn. 2004; 230:316–24.
Article10. Hansen TF, Andersen RF, Olsen DA, Sorensen FB, Jakobsen A. Prognostic importance of circulating epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with chemotherapy and bevacizumab. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:2388.
Article11. Shen X, Han Y, Xue X, et al. Epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 promotes cell invasion and angiogenesis in pancreatic carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016; 77:167–75.
Article12. Huang CH, Li XJ, Zhou YZ, Luo Y, Li C, Yuan XR. Expression and clinical significance of EGFL7 in malignant glioma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2010; 136:1737–43.
Article13. Wang FY, Kang CS, Wang-Gou SY, Huang CH, Feng CY, Li XJ. EGFL7 is an intercellular EGFR signal messenger that plays an oncogenic role in glioma. Cancer Lett. 2017; 384:9–18.
Article14. Brunhara BB, Becker AP, Neder L, et al. Evaluation of the prognostic potential of EGFL7 in pilocytic astrocytomas. Neuropathology. 2021; 41:21–8.
Article15. Fan C, Yang LY, Wu F, et al. The expression of Egfl7 in human normal tissues and epithelial tumors. Int J Biol Markers. 2013; 28:71–83.
Article16. Bidinotto LT, Torrieri R, Mackay A, et al. Copy number profiling of Brazilian astrocytomas. G3 (Bethesda). 2016; 6:1867–78.
Article17. Wan YW, Allen GI, Liu Z. TCGA2STAT: simple TCGA data access for integrated statistical analysis in R. Bioinformatics. 2016; 32:952–4.
Article18. Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012; 2:401–4.
Article19. Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009; 37:1–13.
Article20. Louis DN, Perry A, Wesseling P, et al. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021; 23:1231–51.
Article21. Cheng Z, Dai Y, Pang Y, et al. High EGFL7 expression may predict poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cancer Biol Ther. 2019; 20:1314–8.22. Papaioannou D, Shen C, Nicolet D, et al. Prognostic and biological significance of the proangiogenic factor EGFL7 in acute myeloid leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017; 114:E4641–7.
Article23. Yang C, Wang YL, Sun D, Zhu XL, Li Z, Ni CF. Increased expression of epidermal growth factor-like domain-containing protein 7 is predictive of poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018; 14:867–72.
Article24. Oh J, Park SH, Lee TS, Oh HK, Choi JH, Choi YS. High expression of epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 is correlated with poor differentiation and poor prognosis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. J Gynecol Oncol. 2014; 25:334–41.
Article25. Li Z, Xue TQ, Yang C, Wang YL, Zhu XL, Ni CF. EGFL7 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis through increasing CKS2 expression by activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. J Cell Biochem. 2018; 119:10327–37.26. Liu Q, Zhang J, Gao H, et al. Role of EGFL7/EGFR-signaling pathway in migration and invasion of growth hormone-producing pituitary adenomas. Sci China Life Sci. 2018; 61:893–901.
Article27. Nichol D, Shawber C, Fitch MJ, et al. Impaired angiogenesis and altered Notch signaling in mice overexpressing endothelial Egfl7. Blood. 2010; 116:6133–43.
Article28. Bill M, Pathmanathan A, Karunasiri M, et al. EGFL7 antagonizes NOTCH signaling and represents a novel therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2020; 26:669–78.
Article29. Tang H, Xiao WR, Liao YY, et al. EGFL7 silencing inactivates the Notch signaling pathway; enhancing cell apoptosis and suppressing cell proliferation in human cutaneous melanoma. Neoplasma. 2019; 66:187–96.
Article30. Schmidt M, De Maziere A, Smyczek T, et al. The role of Egfl7 in vascular morphogenesis. Novartis Found Symp. 2007; 283:18–28.31. Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011; 144:646–74.
Article32. Yeung S, Smyczek T, Cheng J, et al. Abstract 3295: inhibiting vascular morphogenesis in tumors: EGFL7 as a novel therapeutic target. Cancer Res. 2011; 71:3295.
Article33. Garcia-Carbonero R, van Cutsem E, Rivera F, et al. Randomized phase II trial of parsatuzumab (anti-EGFL7) or placebo in combination with FOLFOX and bevacizumab for first-line metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncologist. 2017; 22:375.
Article34. von Pawel J, Spigel DR, Ervin T, et al. Randomized phase II trial of parsatuzumab (anti-EGFL7) or placebo in combination with carboplatin, paclitaxel, and bevacizumab for first-line nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer. Oncologist. 2018; 23:654.
Article35. Bicker F, Schmidt MH. EGFL7: a new player in homeostasis of the nervous system. Cell Cycle. 2010; 9:1263–9.
Article36. Shahcheraghi SH, Tchokonte-Nana V, Lotfi M, Lotfi M, Ghorbani A, Sadeghnia HR. Wnt/beta-catenin and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in glioblastoma: two main targets for drug design: a review. Curr Pharm Des. 2020; 26:1729–41.
Article37. Bos JL, de Rooij J, Reedquist KA. Rap1 signalling: adhering to new models. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001; 2:369–77.
Article38. Han J, Lim CJ, Watanabe N, et al. Reconstructing and deconstructing agonist-induced activation of integrin alphaIIbbeta3. Curr Biol. 2006; 16:1796–806.39. Sayyah J, Bartakova A, Nogal N, Quilliam LA, Stupack DG, Brown JH. The Ras-related protein, Rap1A, mediates thrombin-stimulated, integrin-dependent glioblastoma cell proliferation and tumor growth. J Biol Chem. 2014; 289:17689–98.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Radiologist’s Guide to IDH-Wildtype Glioblastoma for Efficient Communication With Clinicians: Part I–Essential Information on Preoperative and Immediate Postoperative Imaging
- Immunohistochemical Classification of Primary and Secondary Glioblastomas
- High expression of epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 is correlated with poor differentiation and poor prognosis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer
- Early High-Grade Transformation of IDH-Mutant Central Nervous System WHO Grade 2 Astrocytoma: A Case Report
- The prognostic significance of p16 expression pattern in diffuse gliomas