Anat Cell Biol.
2022 Jun;55(2):155-160. 10.5115/acb.22.050.
Observation of mandibular second molar roots and root canal morphology using dental cone-beam computed tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Morphological Biology, Ohu University School of Dentistry, Koriyama, Japan
- KMID: 2531202
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.22.050
Abstract
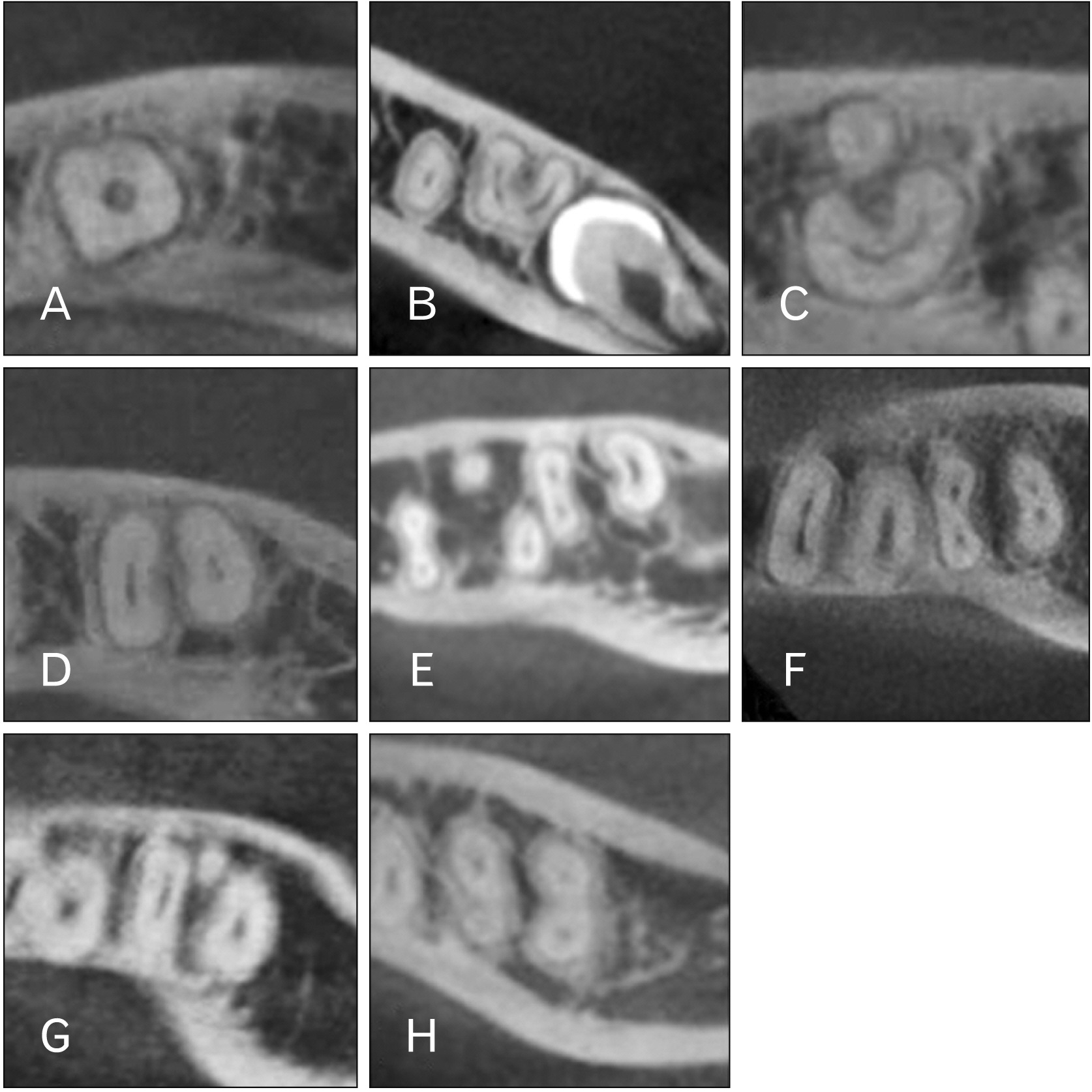
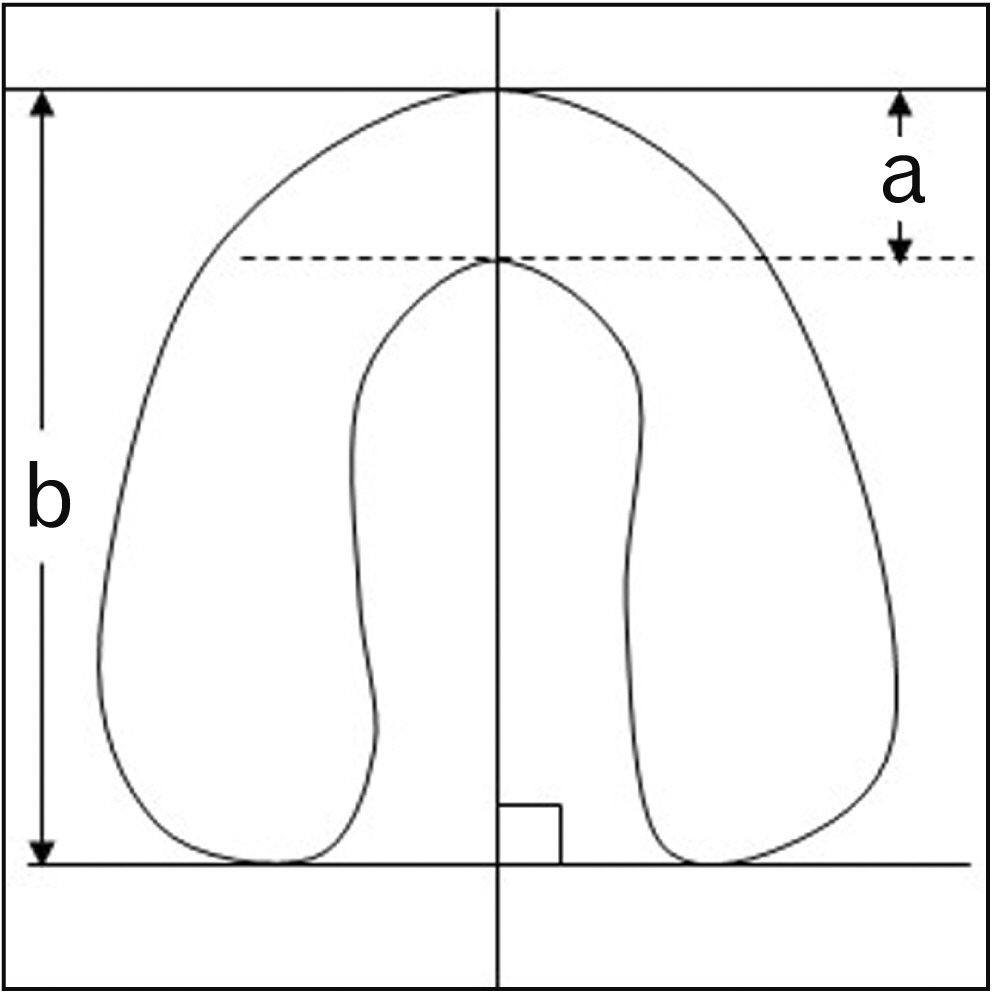
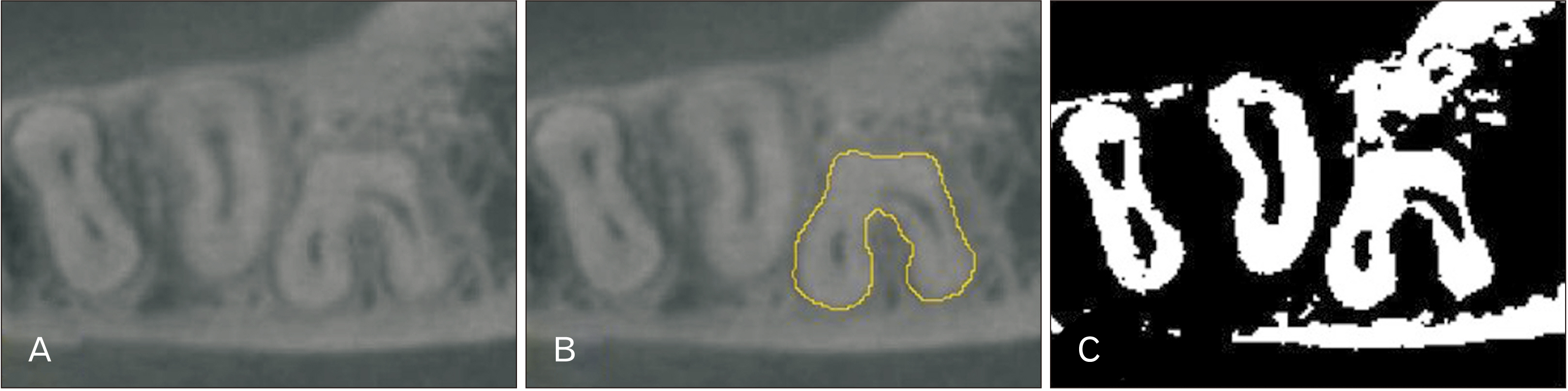
- The mandibular second molars show various morphological features in the roots and root canal, and a guttershaped root (GSR) caused by fusion of the mesial and distal roots is frequently encountered. In this study the number of the roots associated with mandibular second molars were observed using dental cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). For those with a GSR, determination of root morphology and root canal classification were performed. CBCT image data from 173 Japanese mandibular second molars were obtained. Using sliced images, the number of the roots and root morphology were determined. In cases with a GSR, the ratio for the fused roots was determined and root canal morphology features were classified. A GSR was found in 61 (35.3%), with greater prevalence in females. In addition, the overall ratio of the fused part to root thickness in those with a GSR was 48.7%, with no significant difference related to sex. Furthermore, a C-shaped root canal morphology was commonly observed in both males and females with a GSR. In the present cohort examined in Japanese, most of the mandibular second molar were found to have two roots, with a GSR noted in 35.5%. While a GSR was more often observed in females, a C-shaped root canal was the most common root canal morphology in both sexs. It is considered that assessment using CBCT findings is helpful for precise determination of root canal morphology and presence of a GSR in mandibular second molars.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Accuracy verification of dental cone-beam computed tomography of mandibular incisor root canals and assessment of its morphology and aging-related changes
Katsuyuki Aoki, Masamitsu Serikawa, Takuya Harada, Akinobu Usami
Anat Cell Biol. 2023;56(2):185-190. doi: 10.5115/acb.22.247.Dental characteristics on panoramic radiographs as parameters for non-invasive age estimation: a pilot study
Harin Cheong, Akiko Kumagai, Sehyun Oh, Sang-Seob Lee
Anat Cell Biol. 2023;56(4):474-481. doi: 10.5115/acb.23.140.
Reference
-
References
1. Zare Jahromi M, Jafari Golestan F, Mashhadi Esmaeil M, Moouavizahed Sh, Sarami M. 2013; Root and canal morphology of mandibular second molar in an Iranian population by clearing method. J Dent (Shiraz). 14:78–81. PMID: 24724124. PMCID: PMC3977544.2. Neelakantan P, Subbarao C, Subbarao CV, Ravindranath M. 2010; Root and canal morphology of mandibular second molars in an Indian population. J Endod. 36:1319–22. DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2010.04.001. PMID: 20647088.
Article3. Gulabivala K, Opasanon A, Ng YL, Alavi A. 2002; Root and canal morphology of Thai mandibular molars. Int Endod J. 35:56–62. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2591.2002.00452.x. PMID: 11853239.
Article4. Peiris R, Takahashi M, Sasaki K, Kanazawa E. 2007; Root and canal morphology of permanent mandibular molars in a Sri Lankan population. Odontology. 95:16–23. DOI: 10.1007/s10266-007-0074-8. PMID: 17660977.
Article5. Singh S, Pawar M, Podar R, Kulkarni G, Bhanushali N. 2020; Root canal morphology of South Asian Indian mandibular first, second, and third molar: a dye penetration and clearing study. J Conserv Dent. 23:284–8. DOI: 10.4103/JCD.JCD_379_20. PMID: 33551601. PMCID: PMC7861074.
Article6. Melton DC, Krell KV, Fuller MW. 1991; Anatomical and histological features of C-shaped canals in mandibular second molars. J Endod. 17:384–8. DOI: 10.1016/S0099-2399(06)81990-4. PMID: 1809802.
Article7. Manning SA. 1990; Root canal anatomy of mandibular second molars. Part I. Int Endod J. 23:34–9. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.1990.tb00800.x. PMID: 2391179.
Article8. Song JS, Choi HJ, Jung IY, Jung HS, Kim SO. 2010; The prevalence and morphologic classification of distolingual roots in the mandibular molars in a Korean population. J Endod. 36:653–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2009.10.007. PMID: 20307739.
Article9. Kim SY, Kim BS, Kim Y. 2016; Mandibular second molar root canal morphology and variants in a Korean subpopulation. Int Endod J. 49:136–44. DOI: 10.1111/iej.12437. PMID: 25652228.
Article10. Helvacioglu-Yigit D, Sinanoglu A. 2013; Use of cone-beam computed tomography to evaluate C-shaped root canal systems in mandibular second molars in a Turkish subpopulation: a retrospective study. Int Endod J. 46:1032–8. DOI: 10.1111/iej.12094. PMID: 23521079.11. Zheng Q, Zhang L, Zhou X, Wang Q, Wang Y, Tang L, Song F, Huang D. 2011; C-shaped root canal system in mandibular second molars in a Chinese population evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography. Int Endod J. 44:857–62. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01896.x. PMID: 21599707.
Article12. Katakami K, Mishima A, Shiozaki K, Shimoda S, Hamada Y, Kobayashi K. 2008; Characteristics of accessory mental foramina observed on limited cone-beam computed tomography images. J Endod. 34:1441–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2008.08.033. PMID: 19026870.
Article13. Kim SY, Yang SE. 2012; Cone-beam computed tomography study of incidence of distolingual root and distance from distolingual canal to buccal cortical bone of mandibular first molars in a Korean population. J Endod. 38:301–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2011.10.023. PMID: 22341064.
Article14. Vizzotto MB, Silveira PF, Arús NA, Montagner F, Gomes BP, da Silveira HE. 2013; CBCT for the assessment of second mesiobuccal (MB2) canals in maxillary molar teeth: effect of voxel size and presence of root filling. Int Endod J. 46:870–6. DOI: 10.1111/iej.12075. PMID: 23442087.
Article15. Blattner TC, George N, Lee CC, Kumar V, Yelton CD. 2010; Efficacy of cone-beam computed tomography as a modality to accurately identify the presence of second mesiobuccal canals in maxillary first and second molars: a pilot study. J Endod. 36:867–70. DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2009.12.023. PMID: 20416435.
Article16. Morikage N, Hamada T, Usami A, Takada S. 2017; Topographical relationship between positions of lingual foramina and attachment of mylohyoid muscle in mental region. Surg Radiol Anat. 39:735–9. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-016-1804-9. PMID: 28078367.
Article17. Yoza T, Serikawa M, Sugita T, Harada T, Usami A. 2021; Cone-beam computed tomography observation of maxillary first premolar canal shapes. Anat Cell Biol. 54:424–30. DOI: 10.5115/acb.21.110. PMID: 34465669. PMCID: PMC8693140.
Article18. Suzuki M, Tsujimoto Y, Kondo S. 2015; Morphological variations of the root canal system in C-shaped roots of the mandibular second molar in a Japanese population. Int J Oral-Med Sci. 13:81–8. DOI: 10.5466/ijoms.13.81.
Article19. Carlsen O, Alexandersen V. 1990; Radix entomolaris: identification and morphology. Scand J Dent Res. 98:363–73. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1990.tb00986.x. PMID: 2293344.
Article20. Chandra SS, Chandra S, Shankar P, Indira R. 2011; Prevalence of radix entomolaris in mandibular permanent first molars: a study in a South Indian population. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 112:e77–82. DOI: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2011.02.016. PMID: 21550269.
Article21. Kato A, Hishikawa T, Inagaki K, Yamamoto G, Mitani A, Honda M. 2020; Evaluation of root morphology of maxillary and mandibular second molars lost due to periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 55:753–61. DOI: 10.1111/jre.12764. PMID: 32449986.
Article22. Fan B, Cheung GS, Fan M, Gutmann JL, Bian Z. 2004; C-shaped canal system in mandibular second molars: Part I--Anatomical features. J Endod. 30:899–903. DOI: 10.1097/01.don.0000136207.12204.e4. PMID: 15564874.
Article23. Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW. 2012; NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods. 9:671–5. DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.2089. PMID: 22930834. PMCID: PMC5554542.
Article24. Kondo S, Yamada H, Kanazawa E. 2001; Metrical studies of the crown components of the Japanese mandibular molars. Anthropol Sci. 109:213–23. DOI: 10.1537/ase.109.213.
Article25. Special Committee to Revise the Joint AAE/AAOMR Position Statement on use of CBCT in Endodontics. 2015; AAE and AAOMR joint position statement: use of cone beam computed tomography in endodontics 2015 update. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 120:508–12. DOI: 10.1016/j.oooo.2015.07.033. PMID: 26346911.26. George R, Rutley EB, Walsh LJ. 2008; Evaluation of smear layer: a comparison of automated image analysis versus expert observers. J Endod. 34:999–1002. DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2008.05.003. PMID: 18634934.
Article27. Barsness SA, Bowles WR, Fok A, McClanahan SB, Harris SP. 2015; An anatomical investigation of the mandibular second molar using micro-computed tomography. Surg Radiol Anat. 37:267–72. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-014-1364-9. PMID: 25189812.
Article28. Haddad GY, Nehme WB, Ounsi HF. 1999; Diagnosis, classification, and frequency of C-shaped canals in mandibular second molars in the Lebanese population. J Endod. 25:268–71. DOI: 10.1016/S0099-2399(99)80157-5. PMID: 10425954.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence and features of distolingual roots in mandibular molars analyzed by cone-beam computed tomography
- Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with three roots and seven root canals with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography
- Asymmetry in mesial root number and morphology in mandibular second molars: a case report
- Detection of maxillary second molar with two palatal roots using cone beam computed tomography: a case report
- A cone-beam computed tomographic study of C-shaped root and root canal in maxillary molars