Nutr Res Pract.
2022 Jun;16(3):392-404. 10.4162/nrp.2022.16.3.392.
Association between drinking behaviors and components of metabolic syndrome in subjects in their 20s and 30s: data obtained from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016–2018)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Pusan National University, Busan 46241, Korea
- KMID: 2530399
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2022.16.3.392
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
Numerous studies have examined the relationship between drinking behaviors and metabolic syndrome (MetS) for adults, but these include very few studies for young adults. This study therefore undertook to investigate the association between drinking behaviors and components of MetS among adult drinkers aged 20–30 years.
SUBJECTS/METHODS
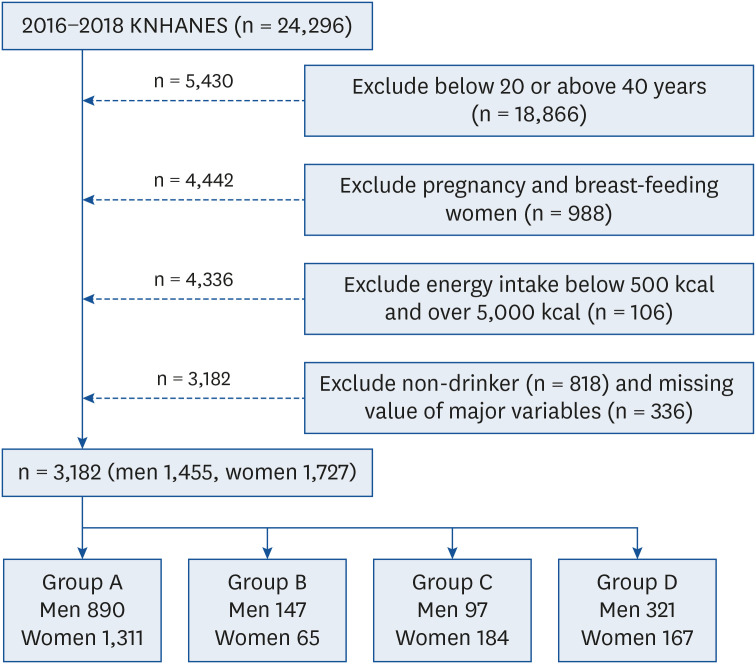
Using the 2016–2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data, drinking behaviors of adults in the age group 20–30 years were divided into 4 groups: 1) group A, good drinking habits; 2) group B, frequent binge drinking but not frequent drinking; 3) group C, frequent drinking but not frequent binge drinking; 4) group D, frequent drinking and binge drinking. The association between MetS components and drinking behaviors was analyzed by applying multiple logistic regression analysis.
RESULTS
We determined the prevalence risk compared to group A. In men, the prevalence risk of high triglyceride (TG) increased 2.051-fold in group C and 1.965-fold in group D.Moreover, in group D, the prevalence risk of low high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) increased 0.668-fold, high blood pressure (BP) increased 2.147-fold, and MetS increased 1.567-fold. In women, there was an increased prevalence risk of low HDL-C (0.353-fold) and MetS (3.438-fold) in group C, whereas group D showed increased prevalence risk of abdominal obesity (2.959-fold), high TG (1.824-fold, and low HDL-C (0.424-fold).
CONCLUSIONS
Our study indicates that frequent drinking increases the risk of high TG, whereas frequent and binge drinking increases the risk of high TG, low HDL-C, high BP, and prevalence of MetS in men. In women, frequent drinking without binge drinking increases the risk of low HDL-C and MetS, whereas frequent and binge drinking increases the risk of abdominal obesity, high TG, and low HDL-C. We propose that improvements in the drinking behaviors can reduce the prevalence of MetS.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee ES, Seo YM. Factors related to high risk drinking in adult drinkers by age group. J East West Nurs Res. 2021; 27:51–60.2. World Health Organization (WHO). Global status report on alcohol and health 2018 [Internet]. Geneva: WHO;2018. cited 2020 December 14. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565639.3. Park H. Prevalence and related risk factors of problem drinking in Korean adult population. J Korea Acad Ind Coop Soc. 2018; 19:389–397.4. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Korean health statistics 2019: Korea Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VIII-1) [Internet]. Cheongju: Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency;2019. cited 2020 December 14. Available from: https://knhanes.kdca.go.kr/knhanes/sub03/sub03_06_02.do.5. Park GH, Rho JO. Comparison of health care practice, dietary behavior, and nutrient intakes, considering the alcohol drinking status of industrial workers in the Chungnam area. J Nutr Health. 2021; 54:277–291.6. Lim JY. One-person household women's problem drinking in early adulthood : association with alcohol expectancy, loneliness, stress, and depression [master's thesis]. Seoul: Yonse University;2020.7. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Result of the 2020 survey on consumption of liquor [Internet]. Cheongju: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety;2020. cited 2021 August 14. Available from: https://www.mfds.go.kr/brd/m_99/view.do?seq=44892.8. Bang SY. The relations between metabolic syndrome, physical activity, and dietary patterns in Korean adults. J Korea Acad Ind Coop Soc. 2019; 20:662–672.9. Kim M, Lee S, Shin KS, Son DY, Kim SH, Joe H, Yoo BW, Hong SH, Cho CY, Shin HS, et al. The change of metabolic syndrome prevalence and its risk factors in Korean adults for decade: Korea Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for 2008–2017. Korean J Fam Pract. 2020; 10:44–52.10. Huh JH, Kang DR, Jang JY, Shin JH, Kim JY, Choi S, Cho EJ, Park JS, Sohn IS, Jo SH, et al. Metabolic syndrome epidemic among Korean adults: Korean survey of cardiometabolic syndrome (2018). Atherosclerosis. 2018; 277:47–52. PMID: 30172084.11. Bae Y, Choi SY, Seo YM. Factors affecting the metabolic syndrome of in adults aged the 20–30 years using the National Health and Nutrition Survey Data for 2016. J Korean Data Anal Soc. 2019; 21:1539–1551.12. Jang YE, Park JH, Roh SS, Koo JS, Seo BI. Effects of Polygoni Multiflori Radix on prevention of hyperlipidemia and liver damage induced by alcohol. Korean J Herbol. 2015; 30:77–82.13. Oh JE. Relationship between heavy drinking, binge drinking, and metabolic syndrome in obese and non-obese Korean male adults. Nutr Res Pract. 2018; 12:166–172. PMID: 29629034.14. Oh SW. Effects of alcohol on obesity and metabolic syndrome. Korean J Obes. 2009; 18:1–7.15. Suh WY, Kim SS, Kim JS, Yoon SJ, Paik SC, Yang JS. Relationship between alcohol consumption and obesity according to facial flushing in Korean males. Korean J Obes. 2015; 24:206–211.16. Lee ES. Effects of abdominal obesity and risk drinking on the hypertension risk in Korean adults. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2018; 29:349–358.17. Park SE. Predictive factors on metabolic syndrome of Korean adult in age groups-focused on dietary and health behavior [master's thesis]. Seoul: Hanyang University;2016.18. Kim Y. The Korea Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES): current status and challenges. Epidemiol Health. 2014; 36:e2014002. PMID: 24839580.19. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Download of raw data of Korea Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey [Internet]. Cheongju: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2018. cited 2021 January 25. Available from: https://knhanes.cdckdca.go.kr/knhanes/mainsub03/sub03_02_05.do.20. Bae YJ. Nutrient and food intakes of Korean female adults depending on perceived stress - based on the 2014–2015 Korea Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey -. Korean J Food Nutr. 2017; 30:759–770.21. Park E, Choi SJ, Lee HY. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome and related risk factors based on the KNHANES V 2010. J Agric Med Community Health. 2013; 38:1–13.22. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Guidebook for data users (2016–2018) of Korea Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey [Internet]. Cheongju: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2018. cited 2021 January 25. Available from: https://knhanes.kdca.go.kr/knhanes/sub03/sub03_06_02.do.23. Seo MH, Lee WY, Kim SS, Kang JH, Kang JH, Kim KK, Kim BY, Kim YH, Kim WJ, Kim EM, et al. 2018 Korean Society for the Study of Obesity guideline for the management of obesity in Korea. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2019; 28:40–45. PMID: 31089578.24. Kim N, Jeon MS. Chocolate consumption and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in the Korean adult population: an analysis based on the 2014–2016 Korea Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Nutr Res Pract. 2021; 15:80–94. PMID: 33542794.25. Lee H, Lee S, Lee E. Characteristics and factors related to problem drinking of the elderly in Korea. J Korea Soc Health Inform Stat. 2012; 37:64–75.26. Choi SY, Kang YS, Kim GE, Park MY, Kim SH. An investigation of the nutrient intakes according to the alcohol consumption level in male workers. Korean J Food Nutr. 2009; 22:669–677.27. Kim S, Goh E, Lee DR, Park MS. The association between eating frequency and metabolic syndrome. Korean J Health Promot. 2011; 11:9–17.28. Kim SK, Hong SH, Chung JH, Cho KB. Association between alcohol consumption and metabolic syndrome in a community-based cohort of Korean adults. Med Sci Monit. 2017; 23:2104–2110. PMID: 28465500.29. Kim SJ, Cho YC. The association of AUDIT levels with obesity indices, liver function tests, and serum lipid levels in male health checkup examinees. J Korea Acad Ind Coop Soc. 2015; 16:3230–3242.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors Affecting the Improvement of Adult Atopic Dermatitis in Their 20s and 30s: The Seventh Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2016–2018
- Relationship between Health Behaviors and Metabolic Syndrome in Cancer Survivors in Korea: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2013–2018
- The correlation between triglyceride to HDL cholesterol ratio and metabolic syndrome, nutrition intake in Korean adults: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016
- Clustering Effects of Metabolic Factors and the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome
- Health behaviors and eating habits in people’s 20s and 30s according to food content usage level on social media: a cross-sectional study