Korean J Pain.
2022 Apr;35(2):173-182. 10.3344/kjp.2022.35.2.173.
Anti-nociceptive effects of dual neuropeptide antagonist therapy in mouse model of neuropathic and inflammatory pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Wonkwang University College of Medicine, Iksan, Korea
- 2Salk Institute for Biological Studies, La Jolla, CA, USA
- KMID: 2527768
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2022.35.2.173
Abstract
- Background
Neurokinin-1 (NK1) and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) play a vital role in pain pathogenesis, and these proteins’ antagonists have attracted attention as promising pharmaceutical candidates. The authors investigated the antinociceptive effect of co-administration of the CGRP antagonist and an NK1 antagonist on pain models compared to conventional single regimens.
Methods
C57Bl/6J mice underwent sciatic nerve ligation for the neuropathic pain model and were injected with 4% formalin into the hind paw for the inflammatory pain model. Each model was divided into four groups: vehicle, NK1 antagonist, CGRP antagonist, and combination treatment groups. The NK1 antagonist aprepitant (BIBN4096, 1 mg/kg) or the CGRP antagonist olcegepant (MK-0869, 10 mg/ kg) was injected intraperitoneally. Mechanical allodynia, thermal hypersensitivity, and anxiety-related behaviors were assessed using the von Frey, hot plate, and elevated plus-maze tests. The flinching and licking responses were also evaluated after formalin injection.
Results
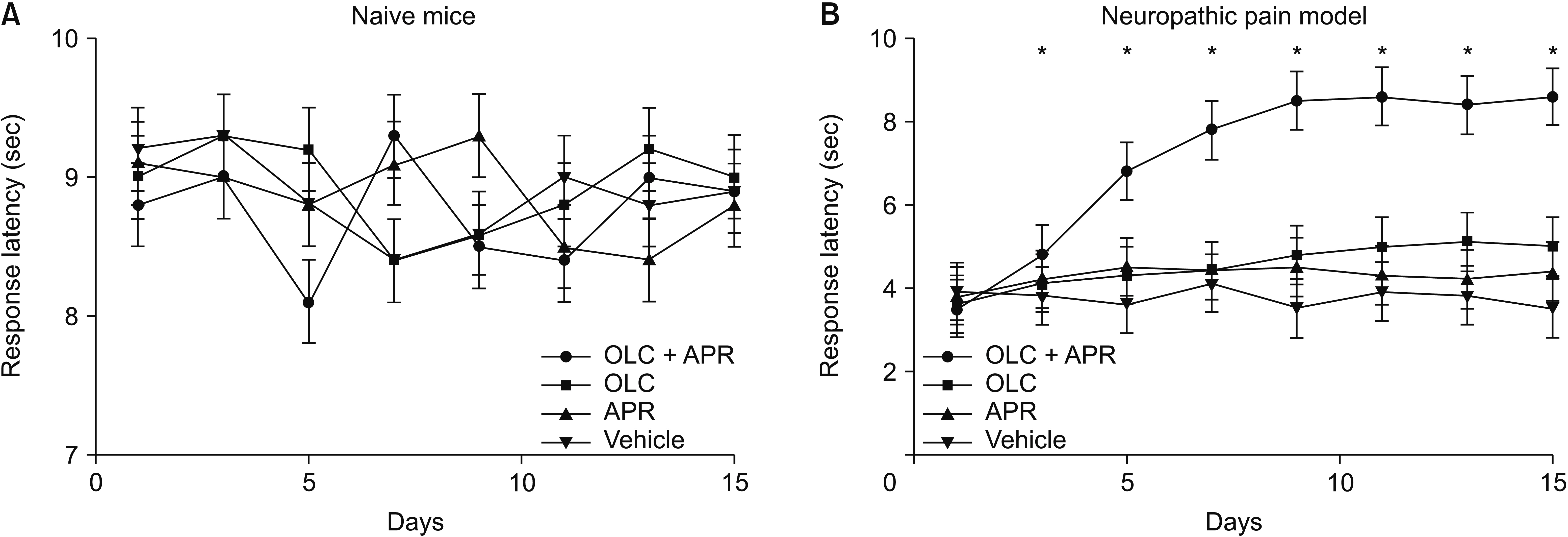
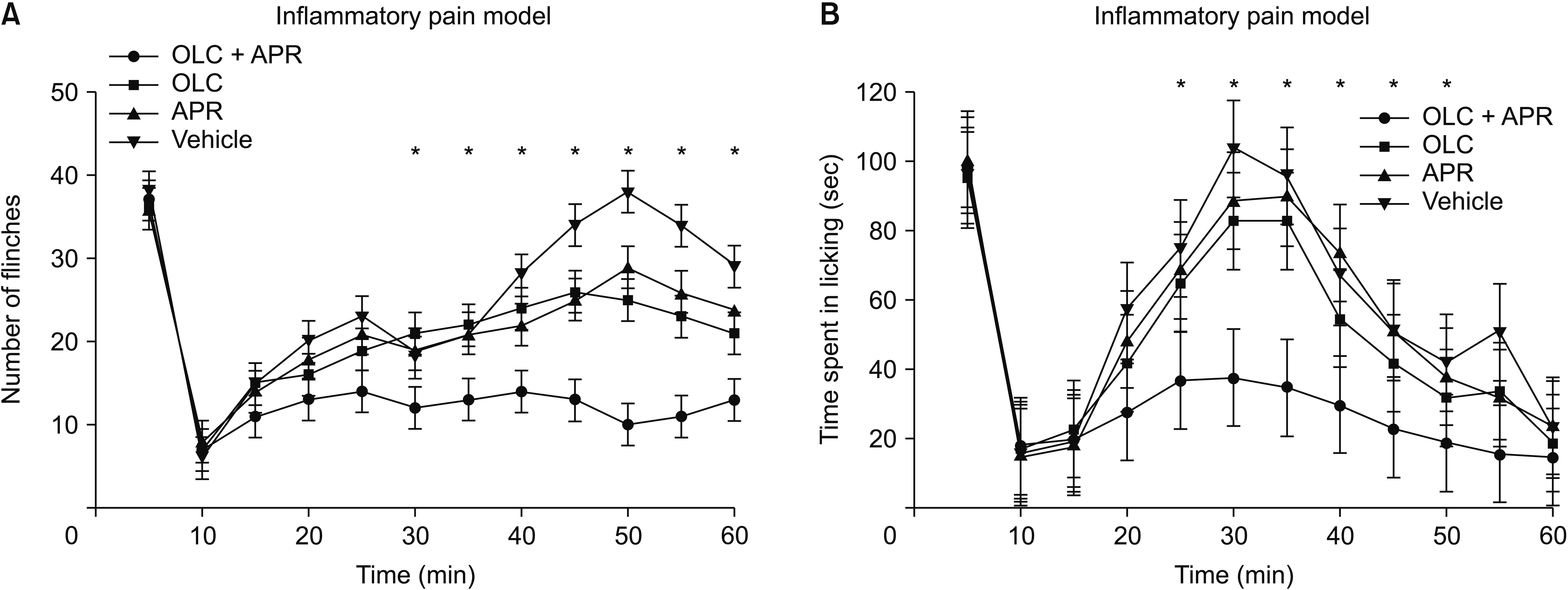
Co-administration of aprepitant and olcegepant more significantly alleviated pain behaviors than administration of single agents or vehicle, increasing the mechanical threshold and improving the response latency. Anxiety-related behaviors were also markedly improved after dual treatment compared with either naive mice or the neuropathic pain model in the dual treatment group. Flinching frequency and licking response after formalin injection decreased significantly in the dual treatment group. Isobolographic analysis showed a meaningful additive effect between the two compounds.
Conclusions
A combination pharmacological therapy comprised of multiple neuropeptide antagonists could be a more effective therapeutic strategy for alleviating neuropathic or inflammatory pain.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in central post-stroke pain: current status and future perspective
Riva Satya Radiansyah, Deby Wahyuning Hadi
Korean J Pain. 2023;36(4):408-424. doi: 10.3344/kjp.23220.
Reference
-
1. Schou WS, Ashina S, Amin FM, Goadsby PJ, Ashina M. 2017; Calcitonin gene-related peptide and pain: a systematic review. J Headache Pain. 18:34. DOI: 10.1186/s10194-017-0741-2. PMID: 28303458. PMCID: PMC5355411.
Article2. van Hecke O, Austin SK, Khan RA, Smith BH, Torrance N. 2014; Neuropathic pain in the general population: a systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain. 155:654–62. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.11.013. PMID: 24291734.
Article3. Cavalli E, Mammana S, Nicoletti F, Bramanti P, Mazzon E. 2019; The neuropathic pain: an overview of the current treatment and future therapeutic approaches. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 33:2058738419838383. DOI: 10.1177/2058738419838383. PMID: 30900486. PMCID: PMC6431761.
Article4. Bouhassira D, Chassany O, Gaillat J, Hanslik T, Launay O, Mann C, et al. 2012; Patient perspective on herpes zoster and its complications: an observational prospective study in patients aged over 50 years in general practice. Pain. 153:342–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2011.10.026. PMID: 22138256.
Article5. Iyengar S, Ossipov MH, Johnson KW. 2017; The role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in peripheral and central pain mechanisms including migraine. Pain. 158:543–59. DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000831. PMID: 28301400. PMCID: PMC5359791.
Article6. Hunyady Á, Hajna Z, Gubányi T, Scheich B, Kemény Á, Gaszner B, et al. 2019; Hemokinin-1 is an important mediator of pain in mouse models of neuropathic and inflammatory mechanisms. Brain Res Bull. 147:165–73. DOI: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.01.015. PMID: 30664920.
Article7. Navratilova E, Porreca F. 2019; Substance P and inflammatory pain: getting it wrong and right simultaneously. Neuron. 101:353–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.01.034. PMID: 30731054.
Article8. Chen W, Marvizon JC. 2020; Neurokinin 1 receptor activation in the rat spinal cord maintains latent sensitization, a model of inflammatory and neuropathic chronic pain. Neuropharmacology. 177:108253. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108253. PMID: 32736088.
Article9. Ramírez-García PD, Retamal JS, Shenoy P, Imlach W, Sykes M, Truong N, et al. 2019; A pH-responsive nanoparticle targets the neurokinin 1 receptor in endosomes to prevent chronic pain. Nat Nanotechnol. 14:1150–9. DOI: 10.1038/s41565-019-0568-x. PMID: 31686009. PMCID: PMC7765343.
Article10. Teodoro FC, Tronco Júnior MF, Zampronio AR, Martini AC, Rae GA, Chichorro JG. 2013; Peripheral substance P and neurokinin-1 receptors have a role in inflammatory and neuropathic orofacial pain models. Neuropeptides. 47:199–206. DOI: 10.1016/j.npep.2012.10.005. PMID: 23177733.
Article11. Gautam M, Prasoon P, Kumar R, Reeta KH, Kaler S, Ray SB. 2016; Role of neurokinin type 1 receptor in nociception at the periphery and the spinal level in the rat. Spinal Cord. 54:172–82. DOI: 10.1038/sc.2015.206. PMID: 26690860.
Article12. Hirsch S, Corradini L, Just S, Arndt K, Doods H. 2013; The CGRP receptor antagonist BIBN4096BS peripherally alleviates inflammatory pain in rats. Pain. 154:700–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.01.002. PMID: 23473785.
Article13. Christensen SL, Petersen S, Kristensen DM, Olesen J, Munro G. 2019; Targeting CGRP via receptor antagonism and antibody neutralisation in two distinct rodent models of migraine-like pain. Cephalalgia. 39:1827–37. DOI: 10.1177/0333102419861726. PMID: 31288556.
Article14. Lee SE, Kim JH. 2007; Involvement of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in development and maintenance of neuropathic pain from spinal nerve injury model of rat. Neurosci Res. 58:245–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.neures.2007.03.004. PMID: 17428562.
Article15. Baron R, Binder A, Wasner G. 2010; Neuropathic pain: diagnosis, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 9:807–19. DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70143-5.
Article16. Finnerup NB, Kuner R, Jensen TS. 2021; Neuropathic pain: from mechanisms to treatment. Physiol Rev. 101:259–301. DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00045.2019. PMID: 32584191.
Article17. Hama A, Sagen J. 2014; Selective antinociceptive effects of a combination of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor peptide antagonist [Ser(1)]histogranin and morphine in rat models of pain. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2:e00032. DOI: 10.1002/prp2.32. PMID: 25505581. PMCID: PMC4184704.
Article18. Michot B, Bourgoin S, Viguier F, Hamon M, Kayser V. 2012; Differential effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor blockade by olcegepant on mechanical allodynia induced by ligation of the infraorbital nerve vs the sciatic nerve in the rat. Pain. 153:1939–48. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2012.06.009. PMID: 22795918.
Article19. Betti C, Starnowska J, Mika J, Dyniewicz J, Frankiewicz L, Novoa A, et al. 2015; dual alleviation of acute and neuropathic pain by fused opioid agonist-neurokinin 1 antagonist peptidomimetics. ACS Med Chem Lett. 6:1209–14. DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5b00359. PMID: 26713106. PMCID: PMC4677362.
Article20. Kang SJ, Liu S, Ye M, Kim DI, Kim JH, Oh TG, et al. 2020. Unified neural pathways that gate affective pain and multisensory innate threat signals to the amygdala. BioRxiv. 2020.11.17.385104 [Preprint]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.17.385104. cited 2020 Nov 18. DOI: 10.1101/2020.11.17.385104.
Article21. Medeiros P, Dos Santos IR, Júnior IM, Palazzo E, da Silva JA, Machado HR, et al. 2021; An adapted chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve produces sensory, affective, and cognitive impairments: a peripheral mononeuropathy model for the study of comorbid neuropsychiatric disorders associated with neuropathic pain in rats. Pain Med. 22:338–51. DOI: 10.1093/pm/pnaa206. PMID: 32875331.
Article22. Mannangatti P, Sundaramurthy S, Ramamoorthy S, Jayanthi LD. 2017; Differential effects of aprepitant, a clinically used neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist on the expression of conditioned psychostimulant versus opioid reward. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 234:695–705. DOI: 10.1007/s00213-016-4504-6. PMID: 28013351. PMCID: PMC5266628.
Article23. Mulder IA, Li M, de Vries T, Qin T, Yanagisawa T, Sugimoto K, et al. 2020; Anti-migraine calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonists worsen cerebral ischemic outcome in mice. Ann Neurol. 88:771–84. DOI: 10.1002/ana.25831. PMID: 32583883. PMCID: PMC7540520.
Article24. Lee IO, Jeong YS. 2002; Effects of different concentrations of formalin on paw edema and pain behaviors in rats. J Korean Med Sci. 17:81–5. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2002.17.1.81. PMID: 11850594. PMCID: PMC3054816.
Article25. Greco R, Mangione AS, Siani F, Blandini F, Vairetti M, Nappi G, et al. 2014; Effects of CGRP receptor antagonism in nitroglycerin-induced hyperalgesia. Cephalalgia. 34:594–604. DOI: 10.1177/0333102413517776. PMID: 24366981.
Article26. Zhuo M. 2016; Neural mechanisms underlying anxiety-chronic pain interactions. Trends Neurosci. 39:136–45. DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2016.01.006. PMID: 26878750.
Article27. Walf AA, Frye CA. 2007; The use of the elevated plus maze as an assay of anxiety-related behavior in rodents. Nat Protoc. 2:322–8. DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2007.44. PMID: 17406592. PMCID: PMC3623971.
Article28. Tallarida RJ. 2016; Drug combinations: tests and analysis with isoboles. Curr Protoc Pharmacol. 72:9.19.1–19. DOI: 10.1002/0471141755.ph0919s72. PMID: 26995550. PMCID: PMC4839184.
Article29. Keller M, Montgomery S, Ball W, Morrison M, Snavely D, Liu G, et al. 2006; Lack of efficacy of the substance p (neurokinin1 receptor) antagonist aprepitant in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 59:216–23. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.07.013. PMID: 16248986.
Article30. Tebas P, Tuluc F, Barrett JS, Wagner W, Kim D, Zhao H, et al. 2011; A randomized, placebo controlled, double masked phase IB study evaluating the safety and antiviral activity of aprepitant, a neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist in HIV-1 infected adults. PLoS One. 6:e24180. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024180. PMID: 21931661. PMCID: PMC3169584.
Article31. Voss T, Lipton RB, Dodick DW, Dupre N, Ge JY, Bachman R, et al. 2016; A phase IIb randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ubrogepant for the acute treatment of migraine. Cephalalgia. 36:887–98. DOI: 10.1177/0333102416653233. PMID: 27269043.
Article32. Herbert MK, Holzer P. 2002; [Why are substance P(NK1)-receptor antagonists ineffective in pain treatment?]. Anaesthesist. 51:308–19. German. DOI: 10.1007/s00101-002-0296-7. PMID: 12063723.33. Hill R. 2000; NK1 (substance P) receptor antagonists--why are they not analgesic in humans? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 21:244–6. DOI: 10.1016/S0165-6147(00)01502-9.34. Kroenke K, Outcalt S, Krebs E, Bair MJ, Wu J, Chumbler N, et al. 2013; Association between anxiety, health-related quality of life and functional impairment in primary care patients with chronic pain. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 35:359–65. DOI: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2013.03.020. PMID: 23639186.
Article35. De Gregorio D, McLaughlin RJ, Posa L, Ochoa-Sanchez R, Enns J, Lopez-Canul M, et al. 2019; Cannabidiol modulates serotonergic transmission and reverses both allodynia and anxiety-like behavior in a model of neuropathic pain. Pain. 160:136–50. DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001386. PMID: 30157131. PMCID: PMC6319597.
Article36. McWilliams LA, Goodwin RD, Cox BJ. 2004; Depression and anxiety associated with three pain conditions: results from a nationally representative sample. Pain. 111:77–83. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2004.06.002. PMID: 15327811.
Article37. Roeska K, Doods H, Arndt K, Treede RD, Ceci A. 2008; Anxiety-like behaviour in rats with mononeuropathy is reduced by the analgesic drugs morphine and gabapentin. Pain. 139:349–57. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2008.05.003. PMID: 18565660.
Article38. Wu Y, Yao X, Jiang Y, He X, Shao X, Du J, et al. 2017; Pain aversion and anxiety-like behavior occur at different times during the course of chronic inflammatory pain in rats. J Pain Res. 10:2585–93. DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S139679. PMID: 29158690. PMCID: PMC5683785.
Article39. Muñoz M, Coveñas R. 2014; Involvement of substance P and the NK-1 receptor in human pathology. Amino Acids. 46:1727–50. DOI: 10.1007/s00726-014-1736-9. PMID: 24705689.
Article40. Zocchi A, Varnier G, Arban R, Griffante C, Zanetti L, Bettelini L, et al. 2003; Effects of antidepressant drugs and GR 205171, an neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptor antagonist, on the response in the forced swim test and on monoamine extracellular levels in the frontal cortex of the mouse. Neurosci Lett. 345:73–6. DOI: 10.1016/S0304-3940(03)00305-7.
Article41. Borbély É, Hajna Z, Nabi L, Scheich B, Tékus V, László K, et al. 2017; Hemokinin-1 mediates anxiolytic and anti-depressant-like actions in mice. Brain Behav Immun. 59:219–32. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.09.004. PMID: 27621226.
Article42. Schorscher-Petcu A, Austin JS, Mogil JS, Quirion R. 2009; Role of central calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in locomotor and anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in two mouse strains exhibiting a CGRP-dependent difference in thermal pain sensitivity. J Mol Neurosci. 39:125–36. DOI: 10.1007/s12031-009-9201-z. PMID: 19381879.
Article43. Araya EI, Turnes JM, Barroso AR, Chichorro JG. 2020; Contribution of intraganglionic CGRP to migraine-like responses in male and female rats. Cephalalgia. 40:689–700. DOI: 10.1177/0333102419896539. PMID: 31856582.
Article44. Puig S, Sorkin LS. 1996; Formalin-evoked activity in identified primary afferent fibers: systemic lidocaine suppresses phase-2 activity. Pain. 64:345–55. DOI: 10.1016/0304-3959(95)00121-2.
Article45. Cho SY, Park AR, Yoon MH, Lee HG, Kim WM, Choi JI. 2013; Antinociceptive effect of intrathecal nefopam and interaction with morphine in formalin-induced pain of rats. Korean J Pain. 26:14–20. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2013.26.1.14. PMID: 23342202. PMCID: PMC3546204.
Article46. Rivat C, Laboureyras E, Laulin JP, Le Roy C, Richebé P, Simonnet G. 2007; Non-nociceptive environmental stress induces hyperalgesia, not analgesia, in pain and opioid-experienced rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 32:2217–28. DOI: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301340. PMID: 17299508.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neuropathic Pain: How to Assess and Treat a Maladaptive Pain Response
- Neuropathic Pain Management with NMDA Receeptor Antagonist (Ketamine ) in Pain Clinic
- Analgesic therapy according to disease specific pathophysiology
- All about pain pharmacology: what pain physicians should know
- Evaluation and diagnosis of neuropathic pain