J Rheum Dis.
2022 Apr;29(2):89-97. 10.4078/jrd.2022.29.2.89.
Evaluation of Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 as an Objective Indicator for the Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Treated With Methotrexate Versus Tocilizumab: 24-week Results From a Prospective Randomized Controlled Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- 2Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Medical Research Center, Institute of Human-Environment Interface Biology, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2527548
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2022.29.2.89
Abstract
Objective
This study aims to evaluate the change in serum metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) following the management of active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and define the relationships between MMP-3 and disease activity indices.
Methods
Data from a previously reported a 24-week, randomized controlled trial to investigate efficacy of tocilizumab in active RA refractory to methotrexate were analyzed. The serum level of MMP-3 were measured at week 0, 12, 20, and 24. The changes in MMP-3, and the relationship between MMP-3 and clinical parameters was assessed based on treatment group, methotrexate with or without tocilizumab.
Results
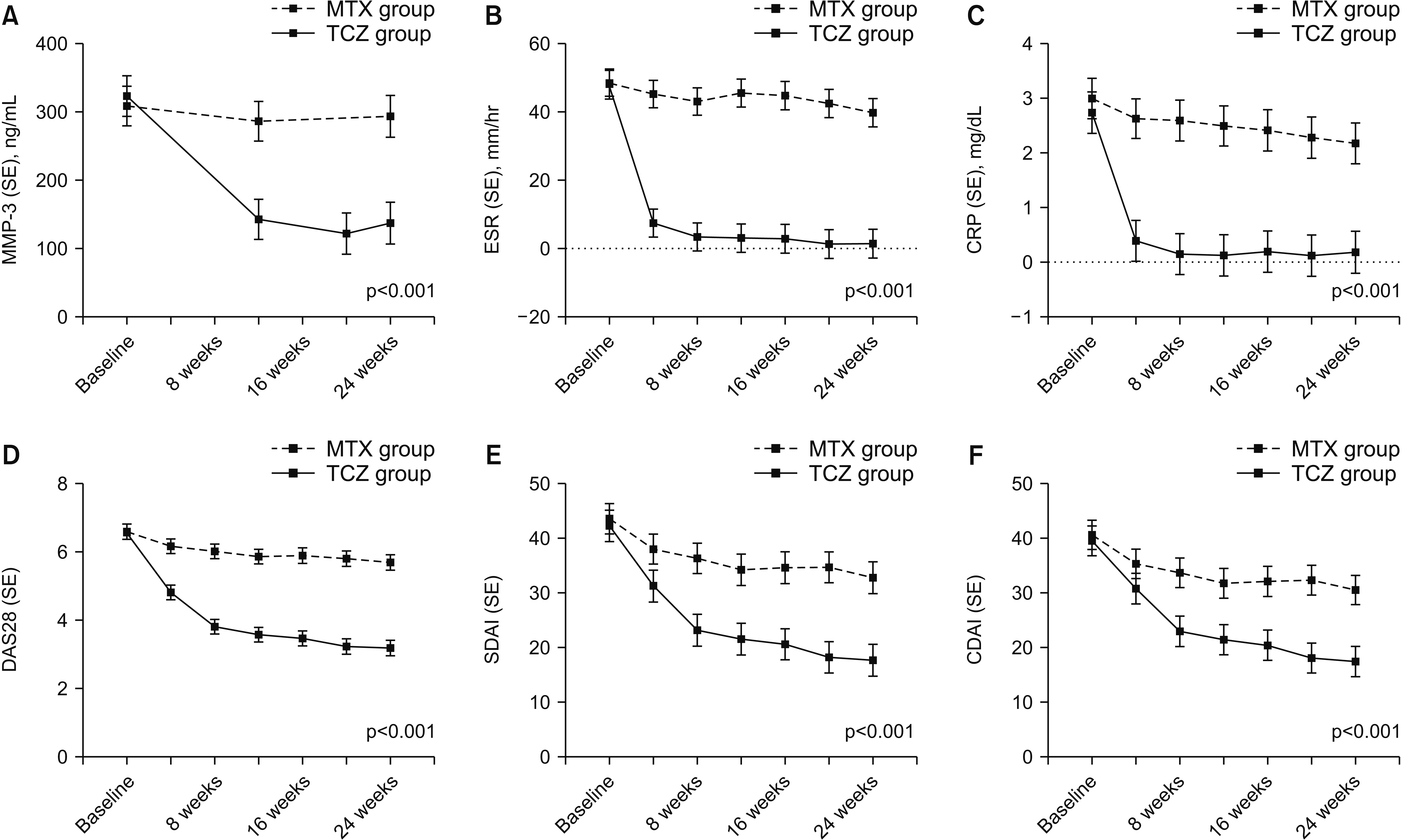
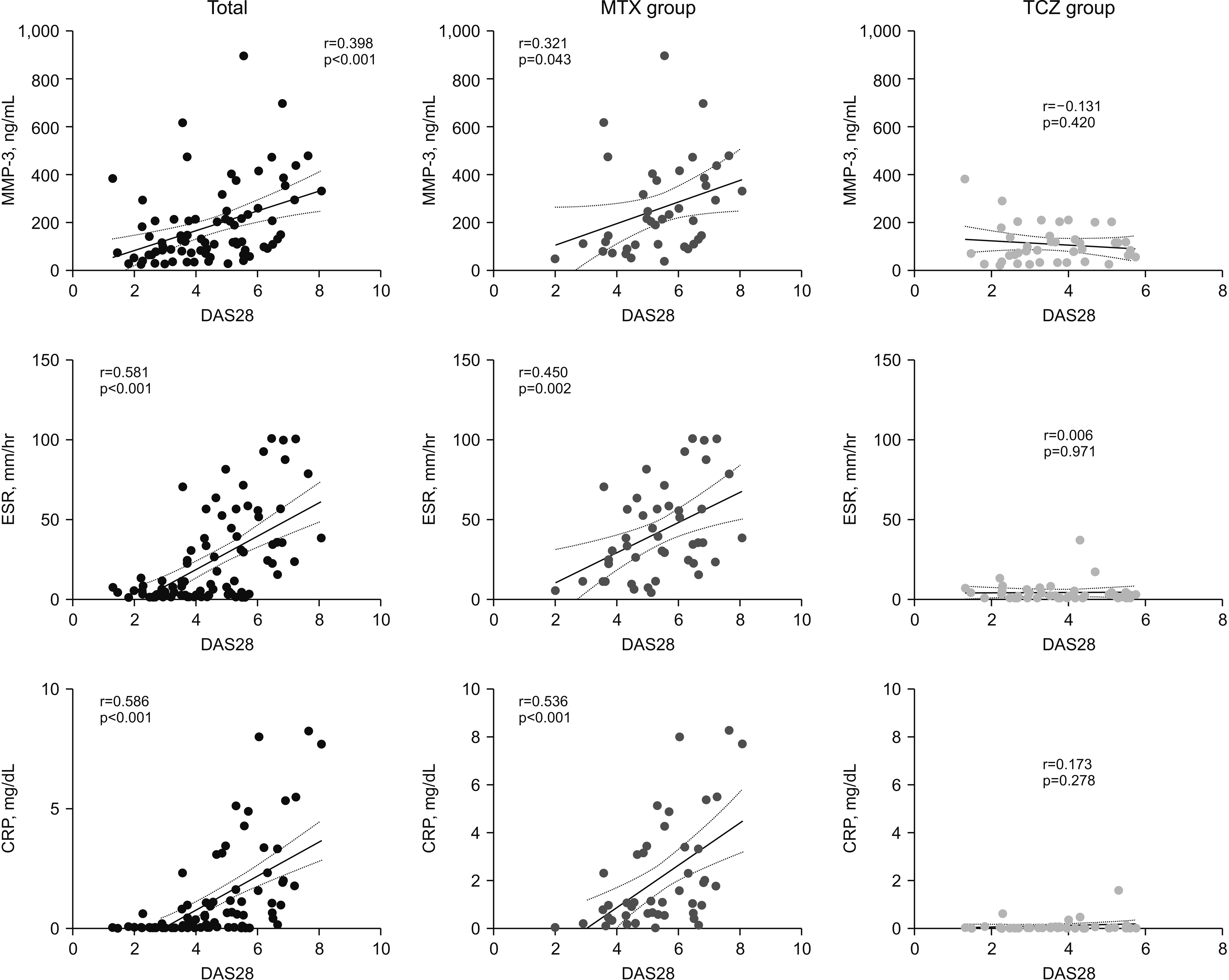
A total of 95 patients were included in this study. The serum MMP-3 significantly decreased and showed similar pattern with other disease activity indices during treatment period in both treatment groups (p<0.001). The MMP-3 was positively correlated with ESR, CRP, DAS28, SDAI, and CDAI for 302 visits throughout 24 weeks (p<0.001). In another correlation analysis to evaluate the treatment effect at 24 week time point, methotrexate group showed significant correlation between serum markers: MMP-3 (r=0.321, p=0.043); ESR (r=0.450, p=0.002); and CRP (r=0.536, p<0.001), with DAS28, but tocilizumab group didn’t show meaningful correlation between serum markers and DAS28 (p>0.05).
Conclusion
Serum MMP-3 showed positive correlation with disease activity indices in active RA patients. Furthermore, serum MMP-3 significantly decreased from baseline to week 20. As there is no single serum marker that can represent the disease activity particularly in tocilizumab treatment, MMP-3 might be a useful adjunct indicator to evaluate the treatment response in active RA patients.
Figure
Reference
-
1. McInnes IB, Schett G. 2011; The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 365:2205–19. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1004965. PMID: 22150039.
Article2. Choy EH, Panayi GS. 2001; Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 344:907–16. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM200103223441207. PMID: 11259725.
Article3. Aletaha D, Smolen JS. 2018; Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis: a review. JAMA. 320:1360–72. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2018.13103. PMID: 30285183.4. Kim SH, Jeong HJ, Kim JM, Jun JB, Son CN. 2020; Clinical significance of elevated serum immunoglobulin G4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheum Dis. 27:96–9. DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2020.27.2.96.
Article5. Felson DT, Smolen JS, Wells G, Zhang B, van Tuyl LH, Funovits J, et al. 2011; American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism provisional definition of remission in rheumatoid arthritis for clinical trials. Arthritis Rheum. 63:573–86. DOI: 10.1002/art.30129. PMID: 21294106. PMCID: PMC3115717.6. Wells G, Becker JC, Teng J, Dougados M, Schiff M, Smolen J, et al. 2009; Validation of the 28-joint Disease Activity Score (DAS28) and European League Against Rheumatism response criteria based on C-reactive protein against disease progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and comparison with the DAS28 based on erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Ann Rheum Dis. 68:954–60. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2007.084459. PMID: 18490431. PMCID: PMC2674547.
Article7. Smolen JS, Beaulieu A, Rubbert-Roth A, Ramos-Remus C, Rovensky J, Alecock E, et al. 2008; Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial. Lancet. 371:987–97. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60453-5.
Article8. Genovese MC, McKay JD, Nasonov EL, Mysler EF, da Silva NA, Alecock E, et al. 2008; Interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab reduces disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: the tocilizumab in combination with traditional disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy study. Arthritis Rheum. 58:2968–80. DOI: 10.1002/art.23940. PMID: 18821691.
Article9. Burrage PS, Mix KS, Brinckerhoff CE. 2006; Matrix metalloproteinases: role in arthritis. Front Biosci. 11:529–43. DOI: 10.2741/1817. PMID: 16146751.
Article10. Kobayashi A, Naito S, Enomoto H, Shiomoi T, Kimura T, Obata K, et al. 2007; Serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin 1) for monitoring synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 131:563–70. DOI: 10.5858/2007-131-563-SLOMMS. PMID: 17425385.
Article11. Ribbens C, Andre B, Jaspar JM, Kaye O, Kaiser MJ, De Groote D, et al. 2000; Matrix metalloproteinase-3 serum levels are correlated with disease activity and predict clinical response in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 27:888–93.12. Baek HJ, Lim MJ, Park W, Park SH, Shim SC, Yoo DH, et al. 2019; Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in Korean patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Korean J Intern Med. 34:917–31. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2017.159. PMID: 29334721. PMCID: PMC6610180.
Article13. Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. 1988; The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 31:315–24. DOI: 10.1002/art.1780310302. PMID: 3358796.
Article14. Funahashi K, Koyano S, Miura T, Hagiwara T, Okuda K, Matsubara T. 2009; Efficacy of tocilizumab and evaluation of clinical remission as determined by CDAI and MMP-3 level. Mod Rheumatol. 19:507–12. DOI: 10.3109/s10165-009-0203-z. PMID: 19609487.
Article15. Ally MM, Hodkinson B, Meyer PW, Musenge E, Tikly M, Anderson R. 2013; Serum matrix metalloproteinase-3 in comparison with acute phase proteins as a marker of disease activity and radiographic damage in early rheumatoid arthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2013:183653. DOI: 10.1155/2013/183653. PMID: 23690656. PMCID: PMC3649689.
Article16. Zhou L, Wang G, Liu X, Song J, Chen L, Xu H. 2017; Matrix metalloproteinase-3 and the 7-joint ultrasound score in the assessment of disease activity and therapeutic efficacy in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 19:250. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-017-1449-z. PMID: 29141665. PMCID: PMC5688630.
Article17. Nakajima A, Terayama K, Sonobe M, Aoki Y, Takahashi H, Akatsu Y, et al. 2019; Serum levels of reactive oxygen metabolites at 12 weeks during tocilizumab therapy are predictive of 52 weeks-disease activity score-remission in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Rheumatol. 3:48. DOI: 10.1186/s41927-019-0096-1. PMID: 31891116. PMCID: PMC6912997.18. Nishimoto N, Terao K, Mima T, Nakahara H, Takagi N, Kakehi T. 2008; Mechanisms and pathologic significances in increase in serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and soluble IL-6 receptor after administration of an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, tocilizumab, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and Castleman disease. Blood. 112:3959–64. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-05-155846. PMID: 18784373.
Article19. Ma JD, Wei XN, Zheng DH, Mo YQ, Chen LF, Zhang X, et al. 2015; Continuously elevated serum matrix metalloproteinase-3 for 3 ~ 6 months predict one-year radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther. 17:289. DOI: 10.1186/s13075-015-0803-2. PMID: 26467222. PMCID: PMC4606896.20. Tchetverikov I, Lard LR, DeGroot J, Verzijl N, TeKoppele JM, Breedveld FC, et al. 2003; Matrix metalloproteinases-3, -8, -9 as markers of disease activity and joint damage progression in early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 62:1094–9. DOI: 10.1136/ard.62.11.1094. PMID: 14583574. PMCID: PMC1754368.
Article21. Shinozaki M, Inoue E, Nakajima A, Hara M, Tomatsu T, Kamatani N, et al. 2007; Elevation of serum matrix metalloproteinase-3 as a predictive marker for the long-term disability of rheumatoid arthritis patients in a prospective observational cohort IORRA. Mod Rheumatol. 17:403–8. DOI: 10.3109/s10165-007-0608-5. PMID: 17929133.
Article22. Hattori Y, Kojima T, Kaneko A, Kida D, Hirano Y, Fujibayashi T, et al. 2018; High rate of improvement in serum matrix metalloproteinase-3 levels at 4 weeks predicts remission at 52 weeks in RA patients treated with adalimumab. Mod Rheumatol. 28:119–25. DOI: 10.1080/14397595.2017.1317320. PMID: 28463029.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Tocilizumab-induced Transaminitis in a Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient with Macrophage Activation Syndrome
- Description of the Efficacy and Safety of Three New Biologics in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Tocilizumab Increases Body Weight and Serum Adipokine Levels in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Independently of Their Treatment Response: a Retrospective Cohort Study
- Hyperpigmentation Probably Induced by Methotrexate in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Changes in the cholesterol profile of patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologics or Janus kinase inhibitors